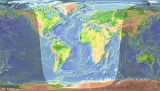
Daylight
Encyclopedia
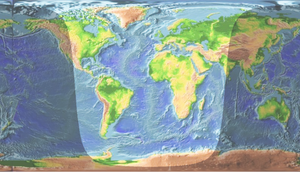
Sunlight
Sunlight, in the broad sense, is the total frequency spectrum of electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through the Earth's atmosphere, and solar radiation is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon.When the direct solar radiation is not blocked...
outdoors during the daytime
Daytime (astronomy)
On Earth, daytime is roughly the period on any given point of the planet's surface during which it experiences natural illumination from indirect or direct sunlight....
. This includes direct sunlight
Sunlight
Sunlight, in the broad sense, is the total frequency spectrum of electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through the Earth's atmosphere, and solar radiation is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon.When the direct solar radiation is not blocked...
, diffuse sky radiation
Diffuse sky radiation
Diffuse sky radiation is solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface after having been scattered from the direct solar beam by molecules or suspensoids in the atmosphere. It is also called skylight, diffuse skylight, or sky radiation and is the reason for changes in the colour of the sky...
, and (often) both of these reflected from the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
and terrestrial objects. Sunlight scattered or reflected from objects in outer space (that is, beyond the Earth's atmosphere) is generally not considered daylight. Thus, moonlight
Moonlight
Moonlight is the light that reaches Earth from the Moon. This light does not originate from the Moon, but from sunlight. The Moon does not, however, reflect sunlight like a mirror, but it reflects light from those portions of its surface which the Sun's light strikes. See diffuse reflection.In...
is never considered daylight, despite being "indirect sunlight". Daytime is the period of time each day when daylight occurs.
Definition
Daylight is present at a particular location, to some degree, whenever the sunSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
is above the horizon at that location. (This is true for slightly more than 50% of the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
at any given time. For an explanation of why it is not exactly half, see here). However, the outdoor illuminance
Illuminance
In photometry, illuminance is the total luminous flux incident on a surface, per unit area. It is a measure of the intensity of the incident light, wavelength-weighted by the luminosity function to correlate with human brightness perception. Similarly, luminous emittance is the luminous flux per...
can vary from 120,000 lux
Lux
The lux is the SI unit of illuminance and luminous emittance, measuring luminous flux per unit area. It is used in photometry as a measure of the intensity, as perceived by the human eye, of light that hits or passes through a surface...
for direct sunlight at noon
Noon
Noon is usually defined as 12 o'clock in the daytime. The word noon is also used informally to mean midday regarding the location of the sun not the middle of a persons day. Although this is a time around the middle of the day when people in many countries take a lunch break...
, which may cause eye pain
Pain
Pain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
, to less than 5 lux
Lux
The lux is the SI unit of illuminance and luminous emittance, measuring luminous flux per unit area. It is used in photometry as a measure of the intensity, as perceived by the human eye, of light that hits or passes through a surface...
for thick storm clouds with the sun at the horizon (even <1 lux for the most extreme case), which may make shadows from distant street light
Street light
A street light, lamppost, street lamp, light standard, or lamp standard is a raised source of light on the edge of a road or walkway, which is turned on or lit at a certain time every night. Modern lamps may also have light-sensitive photocells to turn them on at dusk, off at dawn, or activate...
s visible. It may be darker under unusual circumstances such as a solar eclipse
Solar eclipse
As seen from the Earth, a solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, and the Moon fully or partially blocks the Sun as viewed from a location on Earth. This can happen only during a new moon, when the Sun and the Moon are in conjunction as seen from Earth. At least...
or very high levels of atmospheric smoke (See New England's Dark Day
New England's Dark Day
New England's Dark Day refers to an event that occurred on May 19, 1780, when an unusual darkening of the day sky was observed over the New England states and parts of Canada. The primary cause of the event is believed to have been a combination of smoke from forest fires, a thick fog, and cloud...
), dust, or volcanic ash.
Daylight intensity in different conditions
| Illuminance | Example |
|---|---|
| 120,000 lux | Brightest sunlight |
| 110,000 lux | Bright sunlight |
| 20,000 lux | Shade illuminated by entire clear blue sky, midday |
| 10,000 - 25,000 lux | Typical overcast day, midday |
| <200 lux | Extreme of darkest storm clouds, midday |
| 400 lux | Sunrise Sunrise Sunrise is the instant at which the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon in the east. Sunrise should not be confused with dawn, which is the point at which the sky begins to lighten, some time before the sun itself appears, ending twilight... or sunset Sunset Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west... on a clear day (ambient illumination). |
| 40 lux | Fully overcast, sunset/sunrise |
| <1 lux | Extreme of darkest storm clouds, sunset/rise |
For comparison, nighttime illuminance levels are:
| Illuminance | Example |
|---|---|
| <1 lux | Moonlight Moonlight Moonlight is the light that reaches Earth from the Moon. This light does not originate from the Moon, but from sunlight. The Moon does not, however, reflect sunlight like a mirror, but it reflects light from those portions of its surface which the Sun's light strikes. See diffuse reflection.In... |
| 0.25 lux | Full Moon on a clear night |
| 0.01 lux | Quarter Moon |
| 0.002 lux | Starlight clear moonless night sky including airglow |
| 0.0002 lux | Starlight clear moonless night sky excluding airglow |
| 0.00014 lux | Venus at brightest |
| 0.0001 lux | Starlight overcast moonless night sky |
For a table of approximate daylight intensity in the Solar System, see sunlight.
Effects
Mental health
Mental health describes either a level of cognitive or emotional well-being or an absence of a mental disorder. From perspectives of the discipline of positive psychology or holism mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and procure a balance between life activities and...
problems are registered during the winter months than during the summer months due to the shortened periods of daylight . Cases of depression
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
specifically linked to limited daylight are referred to as seasonal affective disorder
Seasonal affective disorder
Seasonal affective disorder , also known as winter depression, winter blues, summer depression, summer blues, or seasonal depression, is a mood disorder in which people who have normal mental health throughout most of the year experience depressive symptoms in the winter or summer, spring or autumn...
.
Daylighting
Daylighting
Daylighting is the practice of placing windows or other openings and reflective surfaces so that during the day natural light provides effective internal lighting. Particular attention is given to daylighting while designing a building when the aim is to maximize visual comfort or to reduce energy...
is lighting an indoor space with openings such as window
Window
A window is a transparent or translucent opening in a wall or door that allows the passage of light and, if not closed or sealed, air and sound. Windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent material like float glass. Windows are held in place by frames, which...
s and skylights that allow daylight into the building. This type of lighting is chosen to save energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
, to avoid hypothesized adverse health effects of over-illumination
Over-illumination
Over-illumination is the presence of lighting intensity beyond that required for a specified activity. Over-illumination was commonly ignored between 1950 and 1995, especially in office and retail environments; only since then has the interior design community begun to reconsider this practice.The...
by artificial light, and also for aesthetics
Aesthetics
Aesthetics is a branch of philosophy dealing with the nature of beauty, art, and taste, and with the creation and appreciation of beauty. It is more scientifically defined as the study of sensory or sensori-emotional values, sometimes called judgments of sentiment and taste...
. The amount of daylight received into an indoor space or room is defined as a daylight factor
Daylight factor
A daylight factor is the ratio of internal light level to external light level and is defined as follows:where,Ei = illumiance due to daylight at a point on the indoors working plane,...
, being the ratio between the measured internal and external light levels. Artificial lighting energy use can be reduced by simply installing fewer electric lights because daylight is present, or by dimming/switching electric lights automatically in response to the presence of daylight, a process known as daylight harvesting
Daylight harvesting
Daylight Harvesting is the term used in sustainable architecture and the building controls and active daylighting industries for a control system that reduces the use of artificial lighting with electric lamps in building interiors when natural daylight is available, in order to reduce energy...
.
In recent years, work has taken place to recreate the effects of daylight artificially. This is however expensive in terms of both equipment and energy consumption and is applied almost exclusively in specialist areas such as filmmaking
Filmmaking
Filmmaking is the process of making a film, from an initial story, idea, or commission, through scriptwriting, casting, shooting, directing, editing, and screening the finished product before an audience that may result in a theatrical release or television program...
, where light of such intensity is required anyway. In some filmmaking
Filmmaking
Filmmaking is the process of making a film, from an initial story, idea, or commission, through scriptwriting, casting, shooting, directing, editing, and screening the finished product before an audience that may result in a theatrical release or television program...
locations, such as Sweden, there is too much light due to long summer days. As a result, in films like Marianne
Marianne (2011 film)
Marianne is a 2011 Swedish horror film, directed by Filip Tegstedt, that premiered at the 2011 Fantasia International Film Festival on 2 August 2011....
, night scenes have to be shot during the daylight hours and digitally altered later.
See also
- TwilightTwilightTwilight is the time between dawn and sunrise or between sunset and dusk, during which sunlight scattering in the upper atmosphere illuminates the lower atmosphere, and the surface of the earth is neither completely lit nor completely dark. The sun itself is not directly visible because it is below...
- MoonlightMoonlightMoonlight is the light that reaches Earth from the Moon. This light does not originate from the Moon, but from sunlight. The Moon does not, however, reflect sunlight like a mirror, but it reflects light from those portions of its surface which the Sun's light strikes. See diffuse reflection.In...
- Daylight saving timeDaylight saving timeDaylight saving time —also summer time in several countries including in British English and European official terminology —is the practice of temporarily advancing clocks during the summertime so that afternoons have more daylight and mornings have less...
- DaylightingDaylightingDaylighting is the practice of placing windows or other openings and reflective surfaces so that during the day natural light provides effective internal lighting. Particular attention is given to daylighting while designing a building when the aim is to maximize visual comfort or to reduce energy...
- Daytime (astronomy)Daytime (astronomy)On Earth, daytime is roughly the period on any given point of the planet's surface during which it experiences natural illumination from indirect or direct sunlight....
- Right to light
- Day lengthDay lengthDay length, or length of day, or length of daytime, refers to the time each day from the moment the upper limb of the sun's disk appears above the horizon during sunrise to the moment when the upper limb disappears below the horizon during sunset...
External links
- Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors - Rights to Light Determination Homepage
- Daylight Chart shows sunrise and sunset times in a chart, for any location in the world.
- http://www.gandraxa.com/length_of_day.xml Deriving the formulas to calculate the length of day.

