.gif)
Aristarchus (crater)
Encyclopedia
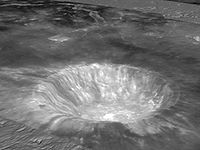
Aristarchus is a prominent lunar impact crater
that lies in the northwest part of the Moon's
near side. It is considered the brightest of the large formations on the lunar surface, with an albedo
nearly double that of most lunar features. The feature is bright enough to be visible to the naked eye, and is dazzling in a large telescope
. It is also readily identified when most of the lunar surface is illuminated by earthshine
.
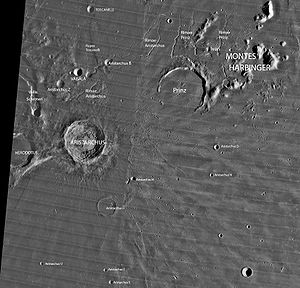
The crater is located at the southeastern edge of the Aristarchus plateau, an elevated area that contains a number of volcanic features, such as sinuous rilles. This area is also noted for the large number of reported transient lunar phenomena, as well as recent emissions of radon
gas as measured by the Lunar Prospector
spacecraft.
Aristarchus was originally named after the Greek astronomer Aristarchus of Samos
by the Italian
map maker Giovanni Riccioli
. His work Almagestum novum ("New Almagest"), published in 1651, gave the spot-shaped telescopic features (later called craters) eponym
s of noted astronomers and philosophers. Although it was already widely adopted, the name didn't become an official international standard until a vote by the IAU General Assembly
in 1935.
 Aristarchus is located on an elevated rocky rise, known as the Aristarchus plateau, in the midst of the Oceanus Procellarum
Aristarchus is located on an elevated rocky rise, known as the Aristarchus plateau, in the midst of the Oceanus Procellarum
, a large expanse of lunar mare
. This is a tilted crustal block, about 200 km across, that rises to a maximum elevation of 2 km above the mare in the southeastern section. Aristarchus is just to the east of the crater Herodotus
and the Vallis Schröteri
, and south of a system of narrow sinuous rille
s named Rimae Aristarchus
.
The main reason for the crater's brightness is that it is a young formation, approximately 450 million years old, and the solar wind
has not yet had time to darken the excavated material by the process of space weathering
. The impact occurred following the creation of the ray crater Copernicus
, but before the appearance of Tycho
.
The brightest feature of this crater is the steep central peak. Sections of the interior floor appear relatively level, but Lunar Orbiter photograph
s reveal the surface is covered in many small hills, streaky gouges, and some minor fractures. The crater has a terraced outer wall, roughly or polygon
al in shape, and covered in a bright blanket of ejecta. These spread out into bright rays
to the south and south-east, suggesting that Aristarchus was most likely formed by an oblique impact from the northeast, and their composition includes material from both the Aristarchus plateau and the lunar mare
.
photography
to take images of the crater area. He discovered the plateau had an anomalous appearance in the ultraviolet, and an area to the north appeared to give indications of a sulfur
deposit. This colorful area is sometimes referred to as "Wood's Spot", an alternate name for the Aristarchus Plateau.
 Spectra taken of this crater during the Clementine mission
Spectra taken of this crater during the Clementine mission
were used to perform mineral
mapping. The data indicated that the central peak is a type of rock called anorthosite
, which is a slow-cooling form of igneous rock composed of plagioclase
feldspar
. By contrast the outer wall is troctolite
, a rock composed of equal parts plagioclase
and olivine
.
The Aristarchus region was part of a Hubble Space Telescope
study in 2005 that was investigating the presence of oxygen
-rich glassy soils in the form of the mineral ilmenite
. Baseline measurements were made of the Apollo 15
and Apollo 17
landing sites, where the chemistry is known, and these were compared to Aristarchus. The Hubble Advanced Camera for Surveys was used to photograph the crater in visual and ultraviolet
light. The crater was determined to have especially rich concentrations of ilmenite, a titanium oxide
mineral that could potentially be used in the future by a lunar settlement
for extracting oxygen.
passed 110 kilometers above the Aristarchus plateau, a significant rise in alpha particle
s was detected. These particles are believed to be caused by the decay of radon-222
, a radioactive gas
with a half-life
of only 3.8 days. The Lunar Prospector
mission later confirmed Radon-222 emissions from this crater. These observations could be explained by either the slow and visually imperceptible diffusion of gas to the surface, or by discrete explosive events.
 Surrounding Aristarchus are several smaller craters, many of which are probably secondary crater
Surrounding Aristarchus are several smaller craters, many of which are probably secondary crater
s. Secondary craters form when large blocks ejected from the primary crater reimpact the surface at high velocities. By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing a letter on the side of the crater mid-point that is closest to the primary crater.
The following craters have been renamed by the IAU
.
Impact crater
In the broadest sense, the term impact crater can be applied to any depression, natural or manmade, resulting from the high velocity impact of a projectile with a larger body...
that lies in the northwest part of the Moon's
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
near side. It is considered the brightest of the large formations on the lunar surface, with an albedo
Albedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
nearly double that of most lunar features. The feature is bright enough to be visible to the naked eye, and is dazzling in a large telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
. It is also readily identified when most of the lunar surface is illuminated by earthshine
Planetshine
The phenomenon known as planetshine occurs when reflected sunlight from a planet illuminates the night side of one of its moons. Typically, this results in the moon's night side being bathed in a soft, faint light. The best known example of planetshine is earthshine, which can be seen from Earth...
.
The crater is located at the southeastern edge of the Aristarchus plateau, an elevated area that contains a number of volcanic features, such as sinuous rilles. This area is also noted for the large number of reported transient lunar phenomena, as well as recent emissions of radon
Radon
Radon is a chemical element with symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as the decay product of uranium or thorium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of 3.8 days...
gas as measured by the Lunar Prospector
Lunar Prospector
The Lunar Prospector mission was the third selected by NASA for full development and construction as part of the Discovery Program. At a cost of $62.8 million, the 19-month mission was designed for a low polar orbit investigation of the Moon, including mapping of surface composition and possible...
spacecraft.
Aristarchus was originally named after the Greek astronomer Aristarchus of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos
Aristarchus, or more correctly Aristarchos , was a Greek astronomer and mathematician, born on the island of Samos, in Greece. He presented the first known heliocentric model of the solar system, placing the Sun, not the Earth, at the center of the known universe...
by the Italian
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
map maker Giovanni Riccioli
Giovanni Battista Riccioli
Giovanni Battista Riccioli was an Italian astronomer and a Catholic priest in the Jesuit order...
. His work Almagestum novum ("New Almagest"), published in 1651, gave the spot-shaped telescopic features (later called craters) eponym
Eponym
An eponym is the name of a person or thing, whether real or fictitious, after which a particular place, tribe, era, discovery, or other item is named or thought to be named...
s of noted astronomers and philosophers. Although it was already widely adopted, the name didn't become an official international standard until a vote by the IAU General Assembly
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union IAU is a collection of professional astronomers, at the Ph.D. level and beyond, active in professional research and education in astronomy...
in 1935.
Selenography

Oceanus Procellarum
Oceanus Procellarum is a vast lunar mare on the western edge of the near side of the Earth's Moon. Its name derives from the old superstition that its appearance during the second quarter heralded bad weather...
, a large expanse of lunar mare
Lunar mare
The lunar maria are large, dark, basaltic plains on Earth's Moon, formed by ancient volcanic eruptions. They were dubbed maria, Latin for "seas", by early astronomers who mistook them for actual seas. They are less reflective than the "highlands" as a result of their iron-rich compositions, and...
. This is a tilted crustal block, about 200 km across, that rises to a maximum elevation of 2 km above the mare in the southeastern section. Aristarchus is just to the east of the crater Herodotus
Herodotus (crater)
Herodotus is a lunar crater located on a low shelf in the midst of the Oceanus Procellarum. To the east is the slightly larger crater Aristarchus. West across the mare is Schiaparelli. Almost due south on the mare surface is a solitary lunar dome designated Herodotus Omega .The crater Herodotus has...
and the Vallis Schröteri
Vallis Schröteri
Schroter's Valley, frequently known by the Latinized name Vallis Schröteri, is a sinuous valley or rille on the surface of the near side of the Moon. It is located on a rise of continental ground, sometimes called the Aristarchus plateau, that is surrounded by the Oceanus Procellarum to the south...
, and south of a system of narrow sinuous rille
Rille
Rille is typically used to describe any of the long, narrow depressions in the lunar surface that resemble channels. Typically a rille can be up to several kilometers wide and hundreds of kilometers in length...
s named Rimae Aristarchus
Rimae Aristarchus
The Rimea Aristarchus is a system of narrow sinuous rilles to the north of the Aristarchus crater. They extend for a distance of 121 km....
.
The main reason for the crater's brightness is that it is a young formation, approximately 450 million years old, and the solar wind
Solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles ejected from the upper atmosphere of the Sun. It mostly consists of electrons and protons with energies usually between 1.5 and 10 keV. The stream of particles varies in temperature and speed over time...
has not yet had time to darken the excavated material by the process of space weathering
Space weathering
Space weathering is a blanket term used for a number of processes that act on any body exposed to the harsh space environment. Airless bodies incur many weathering processes:* collisions of galactic cosmic rays and solar cosmic rays,* irradiation, implantation, and sputtering from solar wind...
. The impact occurred following the creation of the ray crater Copernicus
Copernicus (lunar crater)
Copernicus is a prominent lunar impact crater named after the astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus, located in eastern Oceanus Procellarum. It is estimated to be about 800 million years old, and typifies craters that formed during the Copernican period in that it has a prominent ray system.-...
, but before the appearance of Tycho
Tycho (crater)
Tycho is a prominent lunar impact crater located in the southern lunar highlands, named after the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe . To the south is the crater Street; to the east is Pictet, and to the north-northeast is Sasserides. The surface around Tycho is replete with craters of various sizes,...
.
The brightest feature of this crater is the steep central peak. Sections of the interior floor appear relatively level, but Lunar Orbiter photograph
Photograph
A photograph is an image created by light falling on a light-sensitive surface, usually photographic film or an electronic imager such as a CCD or a CMOS chip. Most photographs are created using a camera, which uses a lens to focus the scene's visible wavelengths of light into a reproduction of...
s reveal the surface is covered in many small hills, streaky gouges, and some minor fractures. The crater has a terraced outer wall, roughly or polygon
Polygon
In geometry a polygon is a flat shape consisting of straight lines that are joined to form a closed chain orcircuit.A polygon is traditionally a plane figure that is bounded by a closed path, composed of a finite sequence of straight line segments...
al in shape, and covered in a bright blanket of ejecta. These spread out into bright rays
Ray system
A ray system comprises radial streaks of fine ejecta thrown out during the formation of an impact crater, looking a bit like many thin spokes coming from the hub of a wheel. The rays can extend for lengths up to several times the diameter of their originating crater, and are often accompanied by...
to the south and south-east, suggesting that Aristarchus was most likely formed by an oblique impact from the northeast, and their composition includes material from both the Aristarchus plateau and the lunar mare
Lunar mare
The lunar maria are large, dark, basaltic plains on Earth's Moon, formed by ancient volcanic eruptions. They were dubbed maria, Latin for "seas", by early astronomers who mistook them for actual seas. They are less reflective than the "highlands" as a result of their iron-rich compositions, and...
.
Remote sensing
In 1911, Professor Robert W. Wood used ultravioletUltraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
photography
Photography
Photography is the art, science and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film...
to take images of the crater area. He discovered the plateau had an anomalous appearance in the ultraviolet, and an area to the north appeared to give indications of a sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
deposit. This colorful area is sometimes referred to as "Wood's Spot", an alternate name for the Aristarchus Plateau.

Clementine mission
Clementine was a joint space project between the Ballistic Missile Defense Organization and NASA...
were used to perform mineral
Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
mapping. The data indicated that the central peak is a type of rock called anorthosite
Anorthosite
Anorthosite is a phaneritic, intrusive igneous rock characterized by a predominance of plagioclase feldspar , and a minimal mafic component...
, which is a slow-cooling form of igneous rock composed of plagioclase
Plagioclase
Plagioclase is an important series of tectosilicate minerals within the feldspar family. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a solid solution series, more properly known as the plagioclase feldspar series...
feldspar
Feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming tectosilicate minerals which make up as much as 60% of the Earth's crust....
. By contrast the outer wall is troctolite
Troctolite
Troctolite is a mafic intrusive rock type. It consists essentially of major but variable amounts of olivine and calcic plagioclase along with variable minor pyroxene. It is an olivine-rich, pyroxene-depleted relative of gabbro. However, unlike gabbro, no troctolite corresponds in composition to a...
, a rock composed of equal parts plagioclase
Plagioclase
Plagioclase is an important series of tectosilicate minerals within the feldspar family. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a solid solution series, more properly known as the plagioclase feldspar series...
and olivine
Olivine
The mineral olivine is a magnesium iron silicate with the formula 2SiO4. It is a common mineral in the Earth's subsurface but weathers quickly on the surface....
.
The Aristarchus region was part of a Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
study in 2005 that was investigating the presence of oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
-rich glassy soils in the form of the mineral ilmenite
Ilmenite
Ilmenite is a weakly magnetic titanium-iron oxide mineral which is iron-black or steel-gray. It is a crystalline iron titanium oxide . It crystallizes in the trigonal system, and it has the same crystal structure as corundum and hematite....
. Baseline measurements were made of the Apollo 15
Apollo 15
Apollo 15 was the ninth manned mission in the American Apollo space program, the fourth to land on the Moon and the eighth successful manned mission. It was the first of what were termed "J missions", long duration stays on the Moon with a greater focus on science than had been possible on previous...
and Apollo 17
Apollo 17
Apollo 17 was the eleventh and final manned mission in the American Apollo space program. Launched at 12:33 a.m. EST on December 7, 1972, with a three-member crew consisting of Commander Eugene Cernan, Command Module Pilot Ronald Evans, and Lunar Module Pilot Harrison Schmitt, Apollo 17 remains the...
landing sites, where the chemistry is known, and these were compared to Aristarchus. The Hubble Advanced Camera for Surveys was used to photograph the crater in visual and ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
light. The crater was determined to have especially rich concentrations of ilmenite, a titanium oxide
Titanium oxide
Titanium oxide may refer to:* Titanium dioxide , TiO2* Titanium oxide , TiO, a non-stoichiometric oxide* Titanium oxide , Ti2O3* Ti3O* Ti2O* δ-TiOx...
mineral that could potentially be used in the future by a lunar settlement
Colonization of the Moon
The colonization of the Moon is the proposed establishment of permanent human communities on the Moon. Advocates of space exploration have seen settlement of the Moon as a logical step in the expansion of humanity beyond the Earth. Recent indication that water might be present in noteworthy...
for extracting oxygen.
Transient lunar phenomena
The region of the Aristarchus plateau has been the site of many reported transient lunar phenomena, with a total of 122 such reports by 2007; the highest recorded for any lunar feature. Such events include temporary obscurations and colorations of the surface, and catalogues of these show that more than one-third of the most reliable spottings come from this locale. In 1971 when Apollo 15Apollo 15
Apollo 15 was the ninth manned mission in the American Apollo space program, the fourth to land on the Moon and the eighth successful manned mission. It was the first of what were termed "J missions", long duration stays on the Moon with a greater focus on science than had been possible on previous...
passed 110 kilometers above the Aristarchus plateau, a significant rise in alpha particle
Alpha particle
Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus, which is classically produced in the process of alpha decay, but may be produced also in other ways and given the same name...
s was detected. These particles are believed to be caused by the decay of radon-222
Radon
Radon is a chemical element with symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as the decay product of uranium or thorium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of 3.8 days...
, a radioactive gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
with a half-life
Half-life
Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
of only 3.8 days. The Lunar Prospector
Lunar Prospector
The Lunar Prospector mission was the third selected by NASA for full development and construction as part of the Discovery Program. At a cost of $62.8 million, the 19-month mission was designed for a low polar orbit investigation of the Moon, including mapping of surface composition and possible...
mission later confirmed Radon-222 emissions from this crater. These observations could be explained by either the slow and visually imperceptible diffusion of gas to the surface, or by discrete explosive events.
Satellite craters

Secondary crater
Secondary craters are impact craters formed by the ejecta that was thrown out of a larger crater. They sometimes form radial crater chains.-External links:*...
s. Secondary craters form when large blocks ejected from the primary crater reimpact the surface at high velocities. By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing a letter on the side of the crater mid-point that is closest to the primary crater.
| Aristarchus | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | 26.3° N | 46.8° W | 7 km |
| D | 23.7° N | 42.9° W | 5 km |
| F | 21.7° N | 46.5° W | 18 km |
| H | 22.6° N | 45.7° W | 4 km |
| N | 22.8° N | 42.9° W | 3 km |
| S | 19.3° N | 46.2° W | 4 km |
| T | 19.6° N | 46.4° W | 4 km |
| U | 19.7° N | 48.6° W | 4 km |
| Z | 25.5° N | 48.4° W | 8 km |
The following craters have been renamed by the IAU
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union IAU is a collection of professional astronomers, at the Ph.D. level and beyond, active in professional research and education in astronomy...
.
- Aristarchus A — See VäisäläVäisälä (crater)Väisälä is a tiny lunar crater located on a rise in the Oceanus Procellarum. Sharing the same continental island are the brilliant crater Aristarchus to the south-southeast and Herodotus to the south-southwest. Väisälä lies just to the west of the Rupes Toscanelli fault line, and the Rimae...
. - Aristarchus C — See ToscanelliToscanelli (crater)Toscanelli is a tiny, bowl-shaped lunar crater that is located to the north of the prominent crater Aristarchus, in the northwestern part of the Moon. The crater lies at the southern end of a rille that proceeds towards the north. This rille is part of a nearby system that has the designation Rimae...
.

