
Agriculture in Bangladesh
Encyclopedia
Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
has a primarily agrarian economy. Agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
is the single largest producing sector of the economy since it comprises about 18.6% (data released on November, 2010) of the country's GDP and employs around 45% of the total labor force. The performance of this sector has an overwhelming impact on major macroeconomic objectives like employment
Employment
Employment is a contract between two parties, one being the employer and the other being the employee. An employee may be defined as:- Employee :...
generation, poverty
Poverty
Poverty is the lack of a certain amount of material possessions or money. Absolute poverty or destitution is inability to afford basic human needs, which commonly includes clean and fresh water, nutrition, health care, education, clothing and shelter. About 1.7 billion people are estimated to live...
alleviation, human resources development and food security
Food security
Food security refers to the availability of food and one's access to it. A household is considered food-secure when its occupants do not live in hunger or fear of starvation. According to the World Resources Institute, global per capita food production has been increasing substantially for the past...
.
A plurality of Bangladeshis earn their living from agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
. Although rice
Rice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
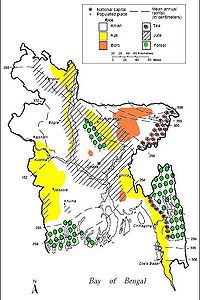
and jute
Jute
Jute is a long, soft, shiny vegetable fibre that can be spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from plants in the genus Corchorus, which has been classified in the family Tiliaceae, or more recently in Malvaceae....
are the primary crops, wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
is assuming greater importance. Tea
Tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by adding cured leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant to hot water. The term also refers to the plant itself. After water, tea is the most widely consumed beverage in the world...
is grown in the northeast. Because of Bangladesh's fertile soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
and normally ample water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
supply, rice can be grown and harvested three times a year in many areas. Due to a number of factors, Bangladesh's labor-intensive agriculture has achieved steady increases in food grain production despite the often unfavorable weather conditions. These include better flood control and irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
, a generally more efficient use of fertilizers, and the establishment of better distribution and rural credit networks. With 35.8 million metric tons produced in 2000, rice is Bangladesh's principal crop. National sales of the classes of insecticide
Insecticide
An insecticide is a pesticide used against insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against the eggs and larvae of insects respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and the household. The use of insecticides is believed to be one of the major factors behind...
used on rice, including granular carbofuran, synthetic pyrethroids, and malathion exceeded 13,000 tons of formulated product in 2003. The insecticides not only represent an environmental threat, but are a significant expenditure to poor rice farmers. The Bangladesh Rice Research Institute
Bangladesh Rice Research Institute
BRRI or Bangladesh Rice Research Institute is the foremost agricultural research institute in Bangladesh, located in Gazipur.-External links:*...
is working with various NGOs and international organizations to reduce insecticide use in rice.
In comparison to rice, wheat output in 1999 was 1.9 million metric tons. Population pressure continues to place a severe burden on productive capacity, creating a food deficit, especially of wheat. Foreign assistance and commercial import
Import
The term import is derived from the conceptual meaning as to bring in the goods and services into the port of a country. The buyer of such goods and services is referred to an "importer" who is based in the country of import whereas the overseas based seller is referred to as an "exporter". Thus...
s fill the gap. Underemployment
Underemployment
Underemployment refers to an employment situation that is insufficient in some important way for the worker, relative to a standard. Examples include holding a part-time job despite desiring full-time work, and overqualification, where the employee has education, experience, or skills beyond the...
remains a serious problem, and a growing concern for Bangladesh's agricultural sector will be its ability to absorb additional manpower. Finding alternative sources of employment will continue to be a daunting problem for future governments, particularly with the increasing numbers of landless peasant
Peasant
A peasant is an agricultural worker who generally tend to be poor and homeless-Etymology:The word is derived from 15th century French païsant meaning one from the pays, or countryside, ultimately from the Latin pagus, or outlying administrative district.- Position in society :Peasants typically...
s who already account for about half the rural labor force.
Food crops
Although rice and jute are the primary crops, maizeMaize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
and vegetables are assuming greater importance. Due to the expansion of irrigation networks, some wheat producers have switched to cultivation of maize which is used mostly as poultry
Poultry
Poultry are domesticated birds kept by humans for the purpose of producing eggs, meat, and/or feathers. These most typically are members of the superorder Galloanserae , especially the order Galliformes and the family Anatidae , commonly known as "waterfowl"...
feed. Tea is grown in the northeast. Because of Bangladesh's fertile soil and normally ample water supply, rice can be grown and harvested three times a year in many areas. Due to a number of factors, Bangladesh's labor-intensive agriculture has achieved steady increases in food grain production despite the often unfavorable weather conditions. These include better flood control and irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
, a generally more efficient use of fertilizers, and the establishment of better distribution and rural credit networks. With 28.8 million metric tons produced in 2005-2006 (July–June), rice is Bangladesh's principal crop. By comparison, wheat output in 2005-2006 was 9 million metric tons. Population pressure continues to place a severe burden on productive capacity, creating a food deficit, especially of wheat. Foreign assistance and commercial imports fill the gap. Underemployment
Underemployment
Underemployment refers to an employment situation that is insufficient in some important way for the worker, relative to a standard. Examples include holding a part-time job despite desiring full-time work, and overqualification, where the employee has education, experience, or skills beyond the...
remains a serious problem, and a growing concern for Bangladesh's agricultural sector will be its ability to absorb additional manpower. Finding alternative sources of employment will continue to be a daunting problem for future governments, particularly with the increasing numbers of landless peasant
Peasant
A peasant is an agricultural worker who generally tend to be poor and homeless-Etymology:The word is derived from 15th century French païsant meaning one from the pays, or countryside, ultimately from the Latin pagus, or outlying administrative district.- Position in society :Peasants typically...
s who already account for about half the rural labor force.
Bangladesh is the fourth largest rice
Rice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
producing country in the world. National sales of the classes of insecticide used on rice, including granular carbofuran
Carbofuran
Carbofuran is one of the most toxic carbamate pesticides. It is marketed under the trade names Furadan, by FMC Corporation and Curater, among several others. It is used to control insects in a wide variety of field crops, including potatoes, corn and soybeans...
, synthetic pyrethroid
Pyrethroid
A pyrethroid is an organic compound similar to the natural pyrethrins produced by the flowers of pyrethrums . Pyrethroids now constitute a major commercial household insecticides...
s, and malathion
Malathion
Malathion is an organophosphate parasympathomimetic which binds irreversibly to cholinesterase. Malathion is an insecticide of relatively low human toxicity, however one recent study has shown that children with higher levels of organophosphate pesticide metabolites in their urine are more likely...
exceeded 13,000 tons of formulated product in 2003 http://www.petrra-irri.org/html/doc_download.asp?id=72 http://72.14.235.104/search?q=cache:smXdmw1ov2AJ:www.petrra-irri.org/html/doc_download.asp%3Fid%3D72+insecticide+consumption+rice+Bangladesh&hl=en&gl=th&ct=clnk&cd=1. The insecticides not only represent an environmental threat, but are a significant expenditure to poor rice farmers. The Bangladesh Rice Research Institute
Bangladesh Rice Research Institute
BRRI or Bangladesh Rice Research Institute is the foremost agricultural research institute in Bangladesh, located in Gazipur.-External links:*...
is working with various NGOs and international organizations to reduce insecticide use in rice http://www.irri.org/publications/today/pdfs/3-4/RiceToday3-4.pdf#search=%22LITE%20rice%20Bangladesh%20Reason%20to%20Cheer%22.
Wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
is not a traditional crop in Bangladesh, and in the late 1980s little was consumed in rural
Rural
Rural areas or the country or countryside are areas that are not urbanized, though when large areas are described, country towns and smaller cities will be included. They have a low population density, and typically much of the land is devoted to agriculture...
areas. During the 1960s and early 1970s, however, it was the only commodity for which local consumption increased because external food aid was most often provided in the form of wheat. In the first half of the 1980s, domestic wheat production rose to more than 1 million tons per year but was still only 7 to 9 percent of total food grain production. Record production of nearly 1.5 million tons was achieved in FY 1985, but the following year saw a decrease to just over 1 million tons. About half the wheat is grown on irrigated land. The proportion of land devoted to wheat remained essentially unchanged between 1980 and 1986, at a little less than 6 percent of total planted area.
Wheat also accounts for the great bulk of imported food grains, exceeding 1 million tons annually and going higher than 1.8 million tons in FY 1984, FY 1985, and FY 1987. The great bulk of the imported wheat is financed under aid programs of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, the European Economic Community
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community The European Economic Community (EEC) The European Economic Community (EEC) (also known as the Common Market in the English-speaking world, renamed the European Community (EC) in 1993The information in this article primarily covers the EEC's time as an independent...
, and the World Food Programme
World Food Programme
The World Food Programme is the food aid branch of the United Nations, and the world's largest humanitarian organization addressing hunger worldwide. WFP provides food, on average, to 90 million people per year, 58 million of whom are children...
.
Food grains are cultivated primarily for subsistence. Only a small percentage of total production makes its way into commercial channels. Other Bangladeshi food crops, however, are grown chiefly for the domestic market. They include potatoes and sweet potatoes, with a combined record production of 1.9 million tons in FY 1984; oilseeds, with an annual average production of 250,000 tons; and fruit
Fruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
s such as bananas, jackfruit
Jackfruit
The jackfruit is a species of tree in the Artocarpus genus of the mulberry family . It is native to parts of Southern and Southeast Asia. It is the national fruit of Bangladesh, . The jackfruit tree is believed to be indigenous to the southwestern rain forests of India...
, mangoes, and pineapple
Pineapple
Pineapple is the common name for a tropical plant and its edible fruit, which is actually a multiple fruit consisting of coalesced berries. It was given the name pineapple due to its resemblance to a pine cone. The pineapple is by far the most economically important plant in the Bromeliaceae...
s. Estimates of sugarcane
Sugarcane
Sugarcane refers to any of six to 37 species of tall perennial grasses of the genus Saccharum . Native to the warm temperate to tropical regions of South Asia, they have stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sugar, and measure two to six metres tall...
production put annual production at more than 7 million tons per year, most of it processed into a coarse, unrefined sugar known as gur
Gur
-People:*Mordechai Gur , Israeli politician and the 10th Chief of Staff of the Israeli Defense Forces-Places:*A village in Tibet, see Gur, Tibet*Gur place name in ancient Israel near Megiddo*Guernsey, one of the Channel Islands-Other:...
, and sold domestically.

