1894 Atlantic hurricane season
Encyclopedia
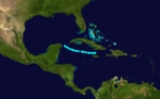
The 1894 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the summer and the first half of fall in 1894. The 1894 season was a fairly inactive one, with seven storms forming, five of which became hurricanes.
and Jamaica
on June 6. It moved westward, remaining weak until dissipating on June 9 over the Yucatán Channel. No damage or deaths were reported.
and drifted northward. After reaching a peak of 60 mi/h winds it hit southern Alabama
on August 8. It turned to the west-northwest, and dissipated on August 9, bringing very heavy rainfall and tornadoes.
and South America
, east of the Lesser Antilles
. It stayed out at sea and did not hit any land. It dissipated in the North Atlantic. Its maximum sustained winds were at 115 mi/h.
, and turned north and hit Florida
with 120 mph (193 km/h) winds. It then went back out to sea and hit South Carolina
, tracked through North Carolina
, and then made its way out to sea, where it eventually dissipated. Its maximum sustained winds were at 120 mph (193 km/h). This storm was responsible for an estimated 200 deaths.
On September 20, as the storm passed through the Lesser Antilles, it produced heavy rains and high winds over several islands. On Martinique
, high winds and continuous, torrential rains impacted the island. Despite the intensity of the storm, there were no reports of damage in the Lesser Antilles. In Hispanola, more than 500 homes and two churches were destroyed; numerous other structures sustained damage, mainly having their roofs blown off.
. It tracked northwest and went by Cuba
. It slammed into the Florida Panhandle
with 105 mph (169 km/h) winds. It tracked through Georgia
, South Carolina, North Carolina, Connecticut
, Massachusetts
, New Hampshire
, Maine
, and up through Canada
. Its maximum sustained winds were at 120 mph (193 km/h). The hurricane caused about a million dollars in damage.
as a Category 2 hurricane, and peaked out as a Category 4 with 135 mi/h winds and an estimated 27.50 inches (931 mbar
) pressure over the open Atlantic waters several hundred miles north of Puerto Rico
. Continuing to head out to sea, the hurricane weakened, and was last seen on October 20 as a weakening minimal hurricane estimated at Category 1 intensity.
Tropical Storm One
A tropical storm formed between CubaCuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
and Jamaica
Jamaica
Jamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, in length, up to in width and 10,990 square kilometres in area. It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola, the island harbouring the nation-states Haiti and the Dominican Republic...
on June 6. It moved westward, remaining weak until dissipating on June 9 over the Yucatán Channel. No damage or deaths were reported.
Tropical Storm Two
The second storm formed on August 5 in the Gulf of MexicoGulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
and drifted northward. After reaching a peak of 60 mi/h winds it hit southern Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
on August 8. It turned to the west-northwest, and dissipated on August 9, bringing very heavy rainfall and tornadoes.
Hurricane Three
A tropical storm developed on August 30 and lasted until September 9. It formed between AfricaAfrica
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
and South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
, east of the Lesser Antilles
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
. It stayed out at sea and did not hit any land. It dissipated in the North Atlantic. Its maximum sustained winds were at 115 mi/h.
Hurricane Four
On September 18 a tropical storm was first observed and lasted until September 30. It formed to the east-southeast of the Lesser Antilles. It hit the Lesser Antilles and then the Greater AntillesGreater Antilles
The Greater Antilles are one of three island groups in the Caribbean. Comprising Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola , and Puerto Rico, the Greater Antilles constitute almost 90% of the land mass of the entire West Indies.-Greater Antilles in context :The islands of the Caribbean Sea, collectively known as...
, and turned north and hit Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
with 120 mph (193 km/h) winds. It then went back out to sea and hit South Carolina
South Carolina
South Carolina is a state in the Deep South of the United States that borders Georgia to the south, North Carolina to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Originally part of the Province of Carolina, the Province of South Carolina was one of the 13 colonies that declared independence...
, tracked through North Carolina
North Carolina
North Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte...
, and then made its way out to sea, where it eventually dissipated. Its maximum sustained winds were at 120 mph (193 km/h). This storm was responsible for an estimated 200 deaths.
On September 20, as the storm passed through the Lesser Antilles, it produced heavy rains and high winds over several islands. On Martinique
Martinique
Martinique is an island in the eastern Caribbean Sea, with a land area of . Like Guadeloupe, it is an overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department. To the northwest lies Dominica, to the south St Lucia, and to the southeast Barbados...
, high winds and continuous, torrential rains impacted the island. Despite the intensity of the storm, there were no reports of damage in the Lesser Antilles. In Hispanola, more than 500 homes and two churches were destroyed; numerous other structures sustained damage, mainly having their roofs blown off.
Hurricane Five
The fifth storm formed on October 1 and lasted until October 12. It formed to the northwest of the Panama CanalPanama Canal
The Panama Canal is a ship canal in Panama that joins the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean and is a key conduit for international maritime trade. Built from 1904 to 1914, the canal has seen annual traffic rise from about 1,000 ships early on to 14,702 vessels measuring a total of 309.6...
. It tracked northwest and went by Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
. It slammed into the Florida Panhandle
Florida Panhandle
The Florida Panhandle, an informal, unofficial term for the northwestern part of Florida, is a strip of land roughly 200 miles long and 50 to 100 miles wide , lying between Alabama on the north and the west, Georgia also on the north, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. Its eastern boundary is...
with 105 mph (169 km/h) winds. It tracked through Georgia
Georgia (U.S. state)
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788...
, South Carolina, North Carolina, Connecticut
Connecticut
Connecticut is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, and the state of New York to the west and the south .Connecticut is named for the Connecticut River, the major U.S. river that approximately...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010...
, New Hampshire
New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state was named after the southern English county of Hampshire. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Canadian...
, Maine
Maine
Maine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost...
, and up through Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
. Its maximum sustained winds were at 120 mph (193 km/h). The hurricane caused about a million dollars in damage.
Hurricane Six
A tropical storm formed on October 11 southeast of the Lesser Antilles as a tropical storm. It traveled north through the Lesser AntillesLesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
as a Category 2 hurricane, and peaked out as a Category 4 with 135 mi/h winds and an estimated 27.50 inches (931 mbar
Bar (unit)
The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
) pressure over the open Atlantic waters several hundred miles north of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
. Continuing to head out to sea, the hurricane weakened, and was last seen on October 20 as a weakening minimal hurricane estimated at Category 1 intensity.
Hurricane Seven
The final storm formed on October 21 and lasted until October 31. It formed far north of the Lesser Antilles. It traveled westward towards the Bahamas, but swerved northeast and out to sea, threatening no land. Its maximum sustained winds were at 100 mph (161 km/h).See also
- List of tropical cyclones
- List of Atlantic hurricane seasons

