Television interference
Encyclopedia
Television interference (TVI) is a particular case of electromagnetic interference
which affects television
reception
. Many natural and man-made phenomena can disrupt the reception of television signals. These include naturally occurring and artificial spark discharges, and effects due to the operation of radio transmitters.
In this article, only conventional UHF (or VHF) AM TV will be considered. Satellite TV tends to be FM TV and operates around 6 or 10 GHz
(microwave
s). While this page is mainly concentrated on UHF AM TV, many of the principles can be applied in cases where other devices are being troubled by poor reception. Also the advice on radio transmitter
interference can be helpful in cases of non-radio equipment such as Hi-Fi units and stereo
s.
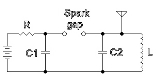
Many systems where radio frequency interface is caused by sparking can be modeled as the following circuit. The source of energy charges C1 via a resistance, and when the spark gap breaks down, the electricity passes through L and excites the resonant LC circuit. The energy in the LC circuit is then radiated through the aerial.
As an example, when a person walks over a nylon
carpet, the rubbing of shoes on carpet performs the role of a battery and resistor, while the person acts as a capacitor
(C1 and C2), and the air between a hand and a door knob is a spark gap
. Stray inductance acts as L.
Other possible sources of such interference include:
Thyristor
and Triac
regulators without proper chokes
are a common source of EMI
as well. It is likely that a thyristor
(SCR) power controller using the variable phase angle method will generate harmonics of the mains supply, while the spark at a contact will be a very wide band source whose frequency is not related to the power supply frequency. In Thyristor
control systems the potential for EMI
problems can be minimised by using zero crossing
switching where the thyristor
is switched on at the moment of time when the AC
voltage changes from one direction to the other.
E = Eo sin (ωt) - {Eo sin (2ωt)}/2 + {Eo sin (3ωt)}/3 ......
As the term goes on for ever to higher and higher frequencies the square wave contains harmonics of the fundamental which go on upwards in frequency for ever, these harmonics are responsible for much of the interference created by computer
s. Always remember that a modern PC is a device which is operating in the VHF/UHF using square wave
s. As the cases on many computers are not perfect shields, some of this radio frequency energy can leak out and cause interference to radio (and sometimes TV) reception.
area of south east London
the signal from the TV mast is so strong that it may cause the TV's front end to be overloaded. Check for this by inserting an attenuator inside with the TV aerial connection. If you start by trying with 10 dB, and then move to 20 dB then this might provide a cure.
In that part of London the TV transmitter (Crystal Palace Transmitter
) and the Croydon Transmitter
tower which has VHF pager transmitters are both such strong sources of radiowaves that FM only UHF (432 MHz) and VHF (144 MHz) radiosets can become overwhelmed when they are attached to a beam aerial which is pointed at the Crystal Palace and Croydon towers respectively. The receiver of the FT-290R2 which is a 144 MHz multimode (FM/CW/SSB
) radio is more able to cope with such strong out of band signals.
So this problem of overloading is not confined to TV sets only. One of the reasons these FM radio sets have this shortcoming is the fact that they often use two diode
s which are wired across the front end of the RF front end
. These two diodes act in the same way as the rusty bolt, the receiver then experiences a great array of mixing (intermodulation) products some of which fall upon the frequency which the radio is tuned to.
It is vital that before you attempt to start to locate an unwanted source of radio signals that you first check that the unwanted signal is not being generated in the front end of your radio set. By adding either an attenuator or a band pass filter to the radio its front end can be protected from these out of band signals.
Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
which affects television
Television
Television is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
reception
Television antenna
A television antenna, or TV aerial, is an antenna specifically designed for the reception of over the air broadcast television signals, which are transmitted at frequencies from about 41 to 250 MHz in the VHF band, and 470 to 960 MHz in the UHF band in different countries...
. Many natural and man-made phenomena can disrupt the reception of television signals. These include naturally occurring and artificial spark discharges, and effects due to the operation of radio transmitters.
In this article, only conventional UHF (or VHF) AM TV will be considered. Satellite TV tends to be FM TV and operates around 6 or 10 GHz
GHZ
GHZ or GHz may refer to:# Gigahertz .# Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state — a quantum entanglement of three particles.# Galactic Habitable Zone — the region of a galaxy that is favorable to the formation of life....
(microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
s). While this page is mainly concentrated on UHF AM TV, many of the principles can be applied in cases where other devices are being troubled by poor reception. Also the advice on radio transmitter
Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications a transmitter or radio transmitter is an electronic device which, with the aid of an antenna, produces radio waves. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating...
interference can be helpful in cases of non-radio equipment such as Hi-Fi units and stereo
STEREO
STEREO is a solar observation mission. Two nearly identical spacecraft were launched into orbits that cause them to respectively pull farther ahead of and fall gradually behind the Earth...
s.
Static electricity and sparks
The sparks generated by static electricity can generate interference.Many systems where radio frequency interface is caused by sparking can be modeled as the following circuit. The source of energy charges C1 via a resistance, and when the spark gap breaks down, the electricity passes through L and excites the resonant LC circuit. The energy in the LC circuit is then radiated through the aerial.
As an example, when a person walks over a nylon
Nylon
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers known generically as polyamides, first produced on February 28, 1935, by Wallace Carothers at DuPont's research facility at the DuPont Experimental Station...
carpet, the rubbing of shoes on carpet performs the role of a battery and resistor, while the person acts as a capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
(C1 and C2), and the air between a hand and a door knob is a spark gap
Spark gap
A spark gap consists of an arrangement of two conducting electrodes separated by a gap usually filled with a gas such as air, designed to allow an electric spark to pass between the conductors. When the voltage difference between the conductors exceeds the gap's breakdown voltage, a spark forms,...
. Stray inductance acts as L.
Sparks and allied phenomena
Horizontal lines randomly arranged on a television screen may be caused by sparking in a malfunctioning electrical device. Electric railways can also be a strong source of this type of interference.Other possible sources of such interference include:
- Thermostats, fridges, freezers, fish tank heaters, central heating systems
- These can create sparks as they turn on or off; as they age they can become worse. In some rare cases they can create non-stop interference through sparking.
- Electric motors
- Motors which have a commutator can suffer from sparking at the brushesBrush (electric)A brush is a device which conducts current between stationary wires and moving parts, most commonly in a rotating shaft. Typical applications include electric motors, alternators and electric generators.-Etymology:...
.
- Motors which have a commutator can suffer from sparking at the brushes
- Ignition systems on cars and motorbikes.
Devices which switch at powerline frequency
- Power line hardware, this can generate sparks at either a 100 or 120 Hz rate
- Light dimmers and other solid state power control devices.
Thyristor
Thyristor
A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as bistable switches, conducting when their gate receives a current trigger, and continue to conduct while they are forward biased .Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and...
and Triac
Triac
Triac may refer to:* TRIAC , an electronics component* Triac , a green vehicle* Tiratricol, a common thyroid hormone analogue used for treating thyroid hormone resistance syndrome...
regulators without proper chokes
Choke (electronics)
A choke is a coil of insulated wire, often wound on a magnetic core, used as a passive inductor which blocks higher-frequency alternating current in an electrical circuit while passing signals of much lower frequency and direct current by having an impedance largely determined by reactance, which...
are a common source of EMI
Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
as well. It is likely that a thyristor
Thyristor
A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as bistable switches, conducting when their gate receives a current trigger, and continue to conduct while they are forward biased .Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and...
(SCR) power controller using the variable phase angle method will generate harmonics of the mains supply, while the spark at a contact will be a very wide band source whose frequency is not related to the power supply frequency. In Thyristor
Thyristor
A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as bistable switches, conducting when their gate receives a current trigger, and continue to conduct while they are forward biased .Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and...
control systems the potential for EMI
Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
problems can be minimised by using zero crossing
Zero crossing
Zero-crossing is a commonly used term in electronics, mathematics, and image processing. In mathematical terms, a "zero-crossing" is a point where the sign of a function changes Zero-crossing is a commonly used term in electronics, mathematics, and image processing. In mathematical terms, a...
switching where the thyristor
Thyristor
A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as bistable switches, conducting when their gate receives a current trigger, and continue to conduct while they are forward biased .Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and...
is switched on at the moment of time when the AC
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
voltage changes from one direction to the other.
Devices which switch faster than 200 Hz
- Computers and other digital electronic equipment. These devices create and use signals which are switched on/off at great speed. It is the case that any repetitive signal can be reduced down to a Fourier seriesFourier seriesIn mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a set of simple oscillating functions, namely sines and cosines...
of sine waves. It so happens that a perfect square wave is
E = Eo sin (ωt) - {Eo sin (2ωt)}/2 + {Eo sin (3ωt)}/3 ......
As the term goes on for ever to higher and higher frequencies the square wave contains harmonics of the fundamental which go on upwards in frequency for ever, these harmonics are responsible for much of the interference created by computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
s. Always remember that a modern PC is a device which is operating in the VHF/UHF using square wave
Square wave
A square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels...
s. As the cases on many computers are not perfect shields, some of this radio frequency energy can leak out and cause interference to radio (and sometimes TV) reception.
- Switch mode power packs can be a source of interference. These are used in consumer electronic/electrical products and in some lighting systems.
Strong TV signals
It is possible to also get a bad picture if the signal strength of the TV transmitter is too high, for instance in the BromleyBromley
Bromley is a large suburban town in south east London, England and the administrative headquarters of the London Borough of Bromley. It was historically a market town, and prior to 1963 was in the county of Kent and formed the administrative centre of the Municipal Borough of Bromley...
area of south east London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
the signal from the TV mast is so strong that it may cause the TV's front end to be overloaded. Check for this by inserting an attenuator inside with the TV aerial connection. If you start by trying with 10 dB, and then move to 20 dB then this might provide a cure.
In that part of London the TV transmitter (Crystal Palace Transmitter
Crystal Palace Transmitter
The Crystal Palace transmitting station is a broadcasting and telecommunications site in the Crystal Palace area of the London Borough of Bromley, England .Its tower is the third-tallest structure in London...
) and the Croydon Transmitter
Croydon Transmitter
The Croydon transmitting station is a broadcasting and telecommunications facility located on Beulah Hill in Upper Norwood, London, England , in the London Borough of Croydon, owned by Arqiva. It was founded in 1955 and initially used a small lattice tower...
tower which has VHF pager transmitters are both such strong sources of radiowaves that FM only UHF (432 MHz) and VHF (144 MHz) radiosets can become overwhelmed when they are attached to a beam aerial which is pointed at the Crystal Palace and Croydon towers respectively. The receiver of the FT-290R2 which is a 144 MHz multimode (FM/CW/SSB
SSB
- Organizations :* '* Societas Sanctae Birgittae, the Society of Saint Bridget* Society of the Sisters of Bethany, an Anglican religious order* Statistics Norway, , Norwegian government statistics bureau...
) radio is more able to cope with such strong out of band signals.
So this problem of overloading is not confined to TV sets only. One of the reasons these FM radio sets have this shortcoming is the fact that they often use two diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
s which are wired across the front end of the RF front end
RF front end
In a radio receiver circuit, the RF front end is a generic term for all the circuitry between the antenna and the first intermediate frequency stage. It consists of all the components in the receiver that process the signal at the original incoming radio frequency , before it is converted to a...
. These two diodes act in the same way as the rusty bolt, the receiver then experiences a great array of mixing (intermodulation) products some of which fall upon the frequency which the radio is tuned to.
It is vital that before you attempt to start to locate an unwanted source of radio signals that you first check that the unwanted signal is not being generated in the front end of your radio set. By adding either an attenuator or a band pass filter to the radio its front end can be protected from these out of band signals.
See also
- Television interference (ghosting)
- Television interference (Co-channel reception)
- EMC problem (excessive field strength)EMC problem (excessive field strength)An EMC problem occurs when an electronic or electromagnetic system is adversely affected by the high field strengths produced by a radio transmitter. EMC problems are not due to defects in the transmitter, and so do not necessarily require improvements in the radio transmitter design, such as...

