
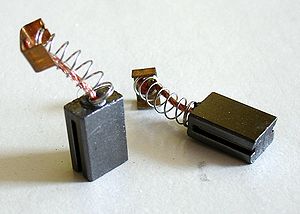
Brush (electric)
Encyclopedia
Wire
A wire is a single, usually cylindrical, flexible strand or rod of metal. Wires are used to bear mechanical loads and to carry electricity and telecommunications signals. Wire is commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. Standard sizes are determined by various...
s and moving parts, most commonly in a rotating shaft
Axle
An axle is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to its surroundings, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle...
. Typical applications include electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
s, alternator
Alternator
An alternator is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current.Most alternators use a rotating magnetic field but linear alternators are occasionally used...
s and electric generators.
Etymology
For the electrics motor or generator to function, the coilCoil
A coil is a series of loops. A coiled coil is a structure in which the coil itself is in turn also looping.-Electromagnetic coils:An electromagnetic coil is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet...
s of the rotor
Rotor (electric)
The rotor is the non-stationary part of a rotary electric motor, electric generator or alternator, which rotates because the wires and magnetic field of the motor are arranged so that a torque is developed about the rotor's axis. In some designs, the rotor can act to serve as the motor's armature,...
must be connected to complete an electrical circuit. To accomplish this, a copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
or brass
Brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc; the proportions of zinc and copper can be varied to create a range of brasses with varying properties.In comparison, bronze is principally an alloy of copper and tin...
commutator
Commutator (electric)
A commutator is a rotary electrical switch in certain types of electric motors or electrical generators that periodically reverses the current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. In a motor, it applies power to the best location on the rotor, and in a generator, picks off power...
or 'slip ring
Slip ring
A slip ring is a method of making an electrical connection through a rotating assembly. Slip rings, also called rotary electrical interfaces, rotating electrical connectors, collectors, swivels, or electrical rotary joints, are commonly found in electric motors, electrical generators for AC...
s' are affixed to the shaft
Axle
An axle is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to its surroundings, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle...
, and spring
Spring (device)
A spring is an elastic object used to store mechanical energy. Springs are usually made out of spring steel. Small springs can be wound from pre-hardened stock, while larger ones are made from annealed steel and hardened after fabrication...
s press braid
Braid
A braid is a complex structure or pattern formed by intertwining three or more strands of flexible material such as textile fibres, wire, or human hair...
ed copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
wire
Wire
A wire is a single, usually cylindrical, flexible strand or rod of metal. Wires are used to bear mechanical loads and to carry electricity and telecommunications signals. Wire is commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. Standard sizes are determined by various...
'brushes' onto the rings which conduct the current. Such brushes provided poor commutation as they moved from one commutator segment to the next. The cure was the introduction of 'high resistance brushes' made from graphite
Graphite
The mineral graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon. It was named by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1789 from the Ancient Greek γράφω , "to draw/write", for its use in pencils, where it is commonly called lead . Unlike diamond , graphite is an electrical conductor, a semimetal...
(sometimes with added copper). Although the resistance was of the order of tens of milliohms, they were high resistance enough to provide a gradual shift of current from one commutator segment to the next. The term brush has remained in use to this day. As the brushes are slowly abraded
Abrasion (mechanical)
Abrasion is the process of scuffing, scratching, wearing down, marring, or rubbing away. It can be intentionally imposed in a controlled process using an abrasive...
, they may have to be replaced, if this is possible.
Metal fiber brushes are currently being developed again. These brushes may have advantages over current carbon brushes, but have not yet seen wide implementation.
Types of carbon brushes
There are distinguished basically three types of carbon brushes:- brushes for automotive applications: Direct CurrentDirect currentDirect current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
, voltage 12-48 V - brushes for household applications: Alternating CurrentAlternating currentIn alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
, voltage 110 / 220 V - brushes for industrial motors: both Alternating Current and Direct Current, various voltages
Mixing components
Exact composition of the brush depends on the application. Graphite/carbon powder is commonly used. Copper is used for better conductance (rare for AC applications and not on automotive fuel pumps which run on carbon commutators). Binders, mostly phenol- or other resins or pitch, are mixed in so the powder holds its shape when compacted. Other additives include metal powders, and solid lubricants like MoS2, WS2. Much know-how and research is needed in order to define a brush grade mixture for each application or motor.Compacting the mixture
The brush compound is compacted in a tool consisting of upper and lower punch and die, on mechanical or hydraulic presses. In this step, depending on later processing, the copper-wire (called shunt wire) can be inserted automatically through a hole in the upper punch and fixed into the pressed brush block by the powder pressed around. After this process, the brush is still very fragile and in professional jargon called a 'green brush'.Firing of green brushes
Heat treatment of the 'green brushes' under artificial atmosphere (usually HydrogenHydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
). Temperatures up to 1200°C. This process is called sintering
Sintering
Sintering is a method used to create objects from powders. It is based on atomic diffusion. Diffusion occurs in any material above absolute zero, but it occurs much faster at higher temperatures. In most sintering processes, the powdered material is held in a mold and then heated to a temperature...
or baking. During sintering, the binders either burn off or carbonize and form a crystalline structure between the carbon, copper and other additives. Baking is followed by graphatisation (heat treatment). The heat treatment is transformed by a temperature curve exactly defined for each material mixture. Besides the mixture composition, the used temperature curve is the second big 'secret' of each brush manufacturer. After the heat treatment, the brush structure is modified in a way which makes copying of the brush nearly impossible for competing companies.
Secondary operations
Sintering causes the brushes to shrink and to bend. They must be ground to net shape. Some companies use additional treatments in order to enlarge durability of brush (and therefore application), for example impregnation on the running surface by special oils, resins and grease.Manufacturing of carbon brushes requires a very high knowledge of materials and experience in mixture compositions. Very small changes in brush contents by just a few percent of components by weight can significantly change the properties of brushes on their applications. There are just a handful of brush developing companies in the world, which are mostly specialized on certain types of brushes.
Carbon brushes are one of the least costly parts in an electro motor. On the other hand, they usually are the key part which delivers the durability ("life-time") and performance to the motor they are used in. Their production requires very high attention to quality control and production process control throughout all steps of the production process.

