
Protein-glutamate O-methyltransferase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a protein-glutamate O-methyltransferase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are S-adenosyl methionine
and protein L-glutamic acid
, whereas its two products
are S-adenosylhomocysteine and protein L-glutamate
methyl ester
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
s, specifically those transferring one-carbon group methyltransferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is S-adenosyl-L-methionine:protein-L-glutamate O-methyltransferase. Other names in common use include methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein O-methyltransferase, S-adenosylmethionine-glutamyl methyltransferase, methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein methyltransferase II, S-adenosylmethionine:protein-carboxyl O-methyltransferase, protein methylase II, MCP methyltransferase I, MCP methyltransferase II, protein O-methyltransferase, protein(aspartate)methyltransferase, protein(carboxyl)methyltransferase, protein carboxyl-methylase, protein carboxyl-O-methyltransferase, protein carboxylmethyltransferase II, protein carboxymethylase, protein carboxymethyltransferase, and protein methyltransferase II. This enzyme participates in bacterial chemotaxis - general and bacterial chemotaxis - organism-specific.
CheR protein
s are part of the chemotaxis
signaling
mechanism which methylates
the chemotaxis receptor
at specific glutamate
residues
. Methyl transfer from the ubiquitous S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet/SAM) to either nitrogen
, oxygen
or carbon
atom
s is frequently employed in diverse organism
s ranging from bacteria
to plant
s and mammal
s. The reaction is catalysed by methyltransferase
s (Mtases) and modifies DNA
, RNA
, protein
s and small molecules, such as catechol for regulatory purposes. The various aspects of the role of DNA methylation
in prokaryotic restriction-modification systems and in a number of cellular processes in eukaryotes including gene regulation and differentiation is well documented.
Flagellated bacteria swim towards favourable chemicals
and away from deleterious ones. Sensing of chemoeffector gradients involves chemotaxis
receptors, transmembrane (TM) proteins that detect stimuli through their periplasmic domains
and transduce
the signals
via their cytoplasm
ic domains . Signalling outputs from these receptors are influenced both by the binding of the chemoeffector ligand
to their periplasmic domains and by methylation of specific glutamate residues on their cytoplasmic domains. Methylation is catalysed by CheR, an S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase, which reversibly methylates specific glutamate residues within a coiled coil
region, to form gamma-glutamyl methyl ester residues. The structure of the Salmonella typhimurium chemotaxis receptor methyltransferase CheR, bound to S-adenosylhomocysteine, has been determined to a resolution of 2.0 Angstrom. The structure reveals CheR to be a two-domain protein, with a smaller N-terminal helical domain linked via a single polypeptide connection to a larger C-terminal alpha/beta domain. The C-terminal domain has the characteristics of a nucleotide-binding fold, with an insertion of a small anti-parallel beta-sheet subdomain. The S-adenosylhomocysteine-binding site is formed mainly by the large domain, with contributions from residues within the N-terminal domain and the linker region.
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB
accession codes and .
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- S-adenosyl-L-methionine + protein L-glutamate
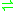 S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + protein L-glutamate methyl ester
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + protein L-glutamate methyl ester
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are S-adenosyl methionine
S-Adenosyl methionine
S-Adenosyl methionine is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers. SAM was first discovered in Italy by G. L. Cantoni in 1952. It is made from adenosine triphosphate and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase . Transmethylation, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation are the...
and protein L-glutamic acid
Glutamic acid
Glutamic acid is one of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids, and its codons are GAA and GAG. It is a non-essential amino acid. The carboxylate anions and salts of glutamic acid are known as glutamates...
, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are S-adenosylhomocysteine and protein L-glutamate
Glutamic acid
Glutamic acid is one of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids, and its codons are GAA and GAG. It is a non-essential amino acid. The carboxylate anions and salts of glutamic acid are known as glutamates...
methyl ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
Transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another . For example, an enzyme that catalyzed this reaction would be a transferase:In this example, A would be the donor, and B would be the acceptor...
s, specifically those transferring one-carbon group methyltransferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is S-adenosyl-L-methionine:protein-L-glutamate O-methyltransferase. Other names in common use include methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein O-methyltransferase, S-adenosylmethionine-glutamyl methyltransferase, methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein methyltransferase II, S-adenosylmethionine:protein-carboxyl O-methyltransferase, protein methylase II, MCP methyltransferase I, MCP methyltransferase II, protein O-methyltransferase, protein(aspartate)methyltransferase, protein(carboxyl)methyltransferase, protein carboxyl-methylase, protein carboxyl-O-methyltransferase, protein carboxylmethyltransferase II, protein carboxymethylase, protein carboxymethyltransferase, and protein methyltransferase II. This enzyme participates in bacterial chemotaxis - general and bacterial chemotaxis - organism-specific.
CheR protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s are part of the chemotaxis
Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis is the phenomenon in which somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food by swimming towards the highest concentration of food molecules,...
signaling
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
mechanism which methylates
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a hydrogen atom...
the chemotaxis receptor
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a receptor is a molecule found on the surface of a cell, which receives specific chemical signals from neighbouring cells or the wider environment within an organism...
at specific glutamate
Glutamic acid
Glutamic acid is one of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids, and its codons are GAA and GAG. It is a non-essential amino acid. The carboxylate anions and salts of glutamic acid are known as glutamates...
residues
Residue (chemistry)
In chemistry, residue is the material remaining after a distillation or an evaporation, or to a portion of a larger molecule, such as a methyl group. It may also refer to the undesired byproducts of a reaction....
. Methyl transfer from the ubiquitous S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet/SAM) to either nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
or carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s is frequently employed in diverse organism
Organism
In biology, an organism is any contiguous living system . In at least some form, all organisms are capable of response to stimuli, reproduction, growth and development, and maintenance of homoeostasis as a stable whole.An organism may either be unicellular or, as in the case of humans, comprise...
s ranging from bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
to plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s and mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s. The reaction is catalysed by methyltransferase
Methyltransferase
A methyltransferase is a type of transferase enzyme that transfers a methyl group from a donor to an acceptor.Methylation often occurs on nucleic bases in DNA or amino acids in protein structures...
s (Mtases) and modifies DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
, RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
, protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s and small molecules, such as catechol for regulatory purposes. The various aspects of the role of DNA methylation
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a hydrogen atom...
in prokaryotic restriction-modification systems and in a number of cellular processes in eukaryotes including gene regulation and differentiation is well documented.
Flagellated bacteria swim towards favourable chemicals
Chemical substance
In chemistry, a chemical substance is a form of matter that has constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. It cannot be separated into components by physical separation methods, i.e. without breaking chemical bonds. They can be solids, liquids or gases.Chemical substances are...
and away from deleterious ones. Sensing of chemoeffector gradients involves chemotaxis
Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis is the phenomenon in which somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food by swimming towards the highest concentration of food molecules,...
receptors, transmembrane (TM) proteins that detect stimuli through their periplasmic domains
Protein domain
A protein domain is a part of protein sequence and structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural...
and transduce
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
the signals
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
via their cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
ic domains . Signalling outputs from these receptors are influenced both by the binding of the chemoeffector ligand
Ligand (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. In a narrower sense, it is a signal triggering molecule, binding to a site on a target protein.The binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen...
to their periplasmic domains and by methylation of specific glutamate residues on their cytoplasmic domains. Methylation is catalysed by CheR, an S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase, which reversibly methylates specific glutamate residues within a coiled coil
Coiled coil
A coiled coil is a structural motif in proteins, in which 2-7 alpha-helices are coiled together like the strands of a rope . Many coiled coil type proteins are involved in important biological functions such as the regulation of gene expression e.g. transcription factors...
region, to form gamma-glutamyl methyl ester residues. The structure of the Salmonella typhimurium chemotaxis receptor methyltransferase CheR, bound to S-adenosylhomocysteine, has been determined to a resolution of 2.0 Angstrom. The structure reveals CheR to be a two-domain protein, with a smaller N-terminal helical domain linked via a single polypeptide connection to a larger C-terminal alpha/beta domain. The C-terminal domain has the characteristics of a nucleotide-binding fold, with an insertion of a small anti-parallel beta-sheet subdomain. The S-adenosylhomocysteine-binding site is formed mainly by the large domain, with contributions from residues within the N-terminal domain and the linker region.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, two structuresTertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
accession codes and .

