
International Universal Recycling Codes
Encyclopedia
Recycling codes are used to identify the material from which an item is made, to facilitate easier recycling
or other reprocessing. Such symbols have been defined for batteries
, biomatter/organic material
, glass, metals, paper, and plastics.
Recycling
Recycling is processing used materials into new products to prevent waste of potentially useful materials, reduce the consumption of fresh raw materials, reduce energy usage, reduce air pollution and water pollution by reducing the need for "conventional" waste disposal, and lower greenhouse...
or other reprocessing. Such symbols have been defined for batteries
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
, biomatter/organic material
Biodegradable waste
Biodegradable waste is a type of waste, typically originating from plant or animal sources, which may be degraded by other living organisms. Waste that cannot be broken down by other living organisms are called non-biodegradable....
, glass, metals, paper, and plastics.
| Symbol | Code | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Plastic A plastic material is any of a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic organic solids used in the manufacture of industrial products. Plastics are typically polymers of high molecular mass, and may contain other substances to improve performance and/or reduce production costs... s (see resin identification code Resin identification code The SPI resin identification coding system is a set of symbols placed on plastics to identify the polymer type. It was developed by the Society of the Plastics Industry in 1988, and is used internationally.... ) |
|||
 |
#1 PET(E) | Polyethylene terephthalate Polyethylene terephthalate Polyethylene terephthalate , commonly abbreviated PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P, is a thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in synthetic fibers; beverage, food and other liquid containers; thermoforming applications; and engineering resins often in combination... |
Polyester fibers, soft drink bottles |
 |
#2 PEHD or HDPE | High-density polyethylene | Plastic bottles, plastic bags, trash cans, imitation wood |
 |
#3 PVC | Polyvinyl chloride Polyvinyl chloride Polyvinyl chloride, commonly abbreviated PVC, is a thermoplastic polymer. It is a vinyl polymer constructed of repeating vinyl groups having one hydrogen replaced by chloride. Polyvinyl chloride is the third most widely produced plastic, after polyethylene and polypropylene. PVC is widely used in... |
Window frames, bottles for chemicals, flooring |
 |
#4 PELD or LDPE | Low-density polyethylene | Plastic bags, buckets, soap dispenser bottles, plastic tubes |
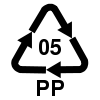 |
#5 PP | Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene , also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging, textiles , stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes... |
Bumpers, car interior trim, industrial fibers |
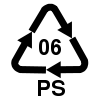 |
#6 PS | Polystyrene Polystyrene Polystyrene ) also known as Thermocole, abbreviated following ISO Standard PS, is an aromatic polymer made from the monomer styrene, a liquid hydrocarbon that is manufactured from petroleum by the chemical industry... |
Toys, flower pots, video cassettes, ashtrays, trunks |
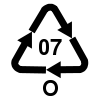 |
#7 O(ther) | All other plastics | |
| #9 or #ABS | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene is a common thermoplastic. Its melting point is approximately 105 °C .... |
Monitor/TV cases, coffee makers, cell phones, most computer plastic | |
| Batteries Battery (electricity) An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power... (see also battery recycling Battery recycling Battery recycling is a recycling activity that aims to reduce the number of batteries being disposed as municipal solid waste. Batteries contain a number of heavy metals and toxic chemicals, their dumping has raised concern over risks of soil contamination and water pollution.-Battery recycling by... ) |
|||
| #8 Lead | Lead–acid battery | ||
| #9 or #19 Alkaline | Alkaline battery Alkaline battery Alkaline batteries are a type of primary batteries dependent upon the reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide . A rechargeable alkaline battery allows reuse of specially designed cells.... |
||
| #10 NiCD | Nickel–cadmium battery | ||
| #11 NiMH | Nickel–metal hydride battery | ||
| #12 Li | Lithium battery Lithium battery Lithium batteries are disposable batteries that have lithium metal or lithium compounds as an anode. Depending on the design and chemical compounds used, lithium cells can produce voltages from 1.5 V to about 3.7 V, over twice the voltage of an ordinary zinc–carbon battery or alkaline battery... |
||
| #13 SO(Z) | Silver-oxide battery Silver-oxide battery A silver oxide battery , not to be confused with a similar but different silver–zinc battery, which is a secondary cell, is a primary cell with relatively very high energy/weight ratio. They are costly due to the high price of silver... |
||
| #14 CZ | Zinc–carbon battery | ||
| Paper Paper Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets.... |
|||
 |
#20 C PAP (PCB) | Cardboard | |
 |
#21 PAP | Other paper Paper Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets.... |
Mixed paper magazine Magazine Magazines, periodicals, glossies or serials are publications, generally published on a regular schedule, containing a variety of articles. They are generally financed by advertising, by a purchase price, by pre-paid magazine subscriptions, or all three... s, mail Mail Mail, or post, is a system for transporting letters and other tangible objects: written documents, typically enclosed in envelopes, and also small packages are delivered to destinations around the world. Anything sent through the postal system is called mail or post.In principle, a postal service... |
 |
#22 PAP | Paper Paper Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets.... |
|
| #23 PBD (PPB) | Paperboard Paperboard Paperboard is a thick paper based material. While there is no rigid differentiation between paper and paperboard, paperboard is generally thicker than paper. According to ISO standards, paperboard is a paper with a basis weight above 224 g/m2, but there are exceptions. Paperboard can be single... |
Greeting cards, frozen food Frozen food Freezing food preserves it from the time it is prepared to the time it is eaten. Since early times, farmers, fishermen, and trappers have preserved their game and produce in unheated buildings during the winter season. Freezing food slows down decomposition by turning water to ice, making it... boxes, book covers |
|
| Metal Metal A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light... s |
|||
 |
#40 FE | Steel Steel Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten... |
|
 |
#41 ALU | Aluminium Aluminium Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances.... |
|
| Biomatter/Organic material Biodegradable waste Biodegradable waste is a type of waste, typically originating from plant or animal sources, which may be degraded by other living organisms. Waste that cannot be broken down by other living organisms are called non-biodegradable.... |
|||
 |
#50 FOR | Wood Wood Wood is a hard, fibrous tissue found in many trees. It has been used for hundreds of thousands of years for both fuel and as a construction material. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin which resists compression... |
|
 |
#51 FOR | Cork Cork (material) Cork is an impermeable, buoyant material, a prime-subset of bark tissue that is harvested for commercial use primarily from Quercus suber , which is endemic to southwest Europe and northwest Africa... |
Bottle stoppers, place mats, construction material |
 |
#60 COT | Cotton Cotton Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal.... |
|
 |
#61 TEX | Jute Jute Jute is a long, soft, shiny vegetable fibre that can be spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from plants in the genus Corchorus, which has been classified in the family Tiliaceae, or more recently in Malvaceae.... |
|
| #62-69 TEX | Other Textile Textile A textile or cloth is a flexible woven material consisting of a network of natural or artificial fibres often referred to as thread or yarn. Yarn is produced by spinning raw fibres of wool, flax, cotton, or other material to produce long strands... s |
||
| Glass Glass Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives... |
|||
 |
#70 GLS | Mixed Glass Container Container glass Container glass is a type of glass for the production of glass containers, such as bottles, jars, drinkware, and bowls. Container glass stands in contrast to flat glass and fiberglass... /Multi-Part Container |
|
 |
#71 GLS | Clear Glass | |
 |
#72 GLS | Green Glass | |
| #73 GLS | Dark Sort Glass | ||
| #74 GLS | Light Sort Glass | ||
| #75 GLS | Light Leaded Glass | Televisions, high-end electronics display glass | |
| #76 GLS | Leaded Glass | Older television Television Television is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound... s, ash trays Ashtray An ashtray is a receptacle for ash and butts from cigarettes and cigars. Ashtrays are typically made of fireproof material such as glass, heat-resistant plastic, pottery, metal, or rock.... , older beverage holders |
|
| #77 GLS | Copper Mixed/Copper Backed Glass | Electronics Electronics Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies... , LCD Display heads, Clock Clock A clock is an instrument used to indicate, keep, and co-ordinate time. The word clock is derived ultimately from the Celtic words clagan and clocca meaning "bell". A silent instrument missing such a mechanism has traditionally been known as a timepiece... s/Watch Watch A watch is a small timepiece, typically worn either on the wrist or attached on a chain and carried in a pocket, with wristwatches being the most common type of watch used today. They evolved in the 17th century from spring powered clocks, which appeared in the 15th century. The first watches were... es |
|
| #78 GLS | Silver Mixed/Silver Backed Glass | Mirror Mirror A mirror is an object that reflects light or sound in a way that preserves much of its original quality prior to its contact with the mirror. Some mirrors also filter out some wavelengths, while preserving other wavelengths in the reflection... s, formal table settings |
|
| #79 GLS | Gold Mixed/Gold Backed Glass | Computer glass, formal table settings | |
| #81 PapPet | paper + plastic | consumer packaging, pet food bags, cold store grocery bags, Icecream containers, cardboard cans, disposable plates | |
| #84 PapAl | paper + aluminium | liquid storage containers, juice boxes, cardboard cans, Cigarette pack liners, gum wrappers, cartage shells for blanks, fireworks colouring material. | |
| #87 Card-stock Laminate | Biodegradable plastic | laminating material, special occasion cards, bookmarks, business cards, flyers/advertising | |
See also
- Resin identification codeResin identification codeThe SPI resin identification coding system is a set of symbols placed on plastics to identify the polymer type. It was developed by the Society of the Plastics Industry in 1988, and is used internationally....
- Japanese recycling symbolsJapanese recycling symbolsJapan has a system of recycling marks, , which indicate and classify recyclable materials.They are similar to the resin identification codes, in that they have surrounding arrows, with text inside to indicate the type of material....
- Waste hierarchyWaste hierarchyThe waste hierarchy refers to the 3 Rs of reduce, reuse, recycle, or and [ which classify waste management strategies according to their desirability. The Rs are meant to be a hierarchy, in order of importance...
- Waste managementWaste managementWaste management is the collection, transport, processing or disposal,managing and monitoring of waste materials. The term usually relates to materials produced by human activity, and the process is generally undertaken to reduce their effect on health, the environment or aesthetics...
External links
- Christie Engineering Standard – Packaging Labeling and Design for Environment Guidelines Includes lists of material codes in several countries.
- Packaging Ordinance Germany Includes lists of material codes in Germany.

