
Waste hierarchy
Encyclopedia
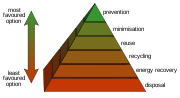
The waste hierarchy refers to the 3 (or 4) Rs of reduce, reuse
Reuse
To reuse is to use an item more than once. This includes conventional reuse where the item is used again for the same function, and new-life reuse where it is used for a different function. In contrast, recycling is the breaking down of the used item into raw materials which are used to make new...
, recycle
Recycling
Recycling is processing used materials into new products to prevent waste of potentially useful materials, reduce the consumption of fresh raw materials, reduce energy usage, reduce air pollution and water pollution by reducing the need for "conventional" waste disposal, and lower greenhouse...
, (and recover)or ([reuse]) ([recycle]) ([recover]) and [(remix]) which classify waste management
Waste management
Waste management is the collection, transport, processing or disposal,managing and monitoring of waste materials. The term usually relates to materials produced by human activity, and the process is generally undertaken to reduce their effect on health, the environment or aesthetics...
strategies according to their desirability. The Rs are meant to be a hierarchy, in order of importance. However in Europe the waste hierarchy
European Waste Hierarchy
The European waste hierarchy refers to the 5 steps included in the article 4 of the Waste Framework Directive:Prevention - preventing and reducing waste generation....
has 5 steps: reduce, reuse, recycle, recovery, and disposal.
The waste hierarchy has taken many forms over the past decade, but the basic concept has remained the cornerstone of most waste minimisation
Waste minimisation
Waste minimization is the process and the policy of reducing the amount of waste produced by a person or a society.Waste minimization involves efforts to minimize resource and energy use during manufacture. For the same commercial output, usually the fewer materials are used, the less waste is...
strategies. The aim of the waste hierarchy is to extract the maximum practical benefits from products and to generate the minimum amount of waste.
Some waste management experts have recently incorporated a additional R: "Re-think", with the implied meaning that the present system may have fundamental flaws, and that a thoroughly effective system of waste management may need an entirely new way of looking at waste. Source reduction involves efforts to reduce hazardous waste and other materials by modifying industrial production. Source reduction methods involve changes in manufacturing technology, raw material inputs, and product formulation. At times, the term "pollution prevention" may refer to source reduction.
Another method of source reduction is to increase incentives for recycling. Many communities in the United States are implementing variable rate pricing for waste disposal (also known as Pay As You Throw - PAYT) which has been effective in reducing the size of the municipal waste stream.
Source reduction is typically measured by efficiencies and cutbacks in waste. Toxics use reduction
Toxics use reduction
Toxics use reduction is an approach to pollution prevention that targets and measures reductions in the upfront use of toxic materials. Toxics use reduction emphasizes the more preventive aspects of source reduction but, due to its emphasis on toxic chemical inputs, has been opposed more vigorously...
is a more controversial approach to source reduction that targets and measures reductions in the upstream use of toxic materials. Toxics use reduction emphasizes the more preventive aspects of source reduction but, due to its emphasis on toxic chemical inputs, has been opposed more vigorously by chemical manufacturers. Toxics use reduction programs have been set up by legislation in some states, e.g., Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Oregon.
How the hierarchy works
The Rs are categories at the top of our disposal options. They include a variety of initiatives for disposing of discards. Generally, options lowest on the list are least desirable.Reduce - to buy less and use less. Incorporates common sense ideas like turning off the lights, rain barrels, and taking shorter showers, but also plays a part in composting/grasscycling
Grasscycling
Grasscycling refers to leaving grass clippings on the lawn when mowing.The term is a portmanteau word combining "grass" and "recycling", and had come into use by at least 1990 as part of the push to reduce the huge quantities of clippings going into landfills, up to half of some cities' summertime...
(transportation energy is reduced), low-flow toilets, and programmable thermostats. Includes the terms Re-think, Precycle, Carpool
Carpool
Carpooling , is the sharing of car journeys so that more than one person travels in a car....
, Efficient
Efficient
Efficient may refer to:* Efficiency, the extent to which time or effort is well used for the intended task or purpose* Efficient , a Thoroughbred racehorse...
, and Environmental Footprint
Ecological footprint
The ecological footprint is a measure of human demand on the Earth's ecosystems. It is a standardized measure of demand for natural capital that may be contrasted with the planet's ecological capacity to regenerate. It represents the amount of biologically productive land and sea area necessary to...
.
Reuse - elements of the discarded item are used again. Initiatives include hand-me-downs, garage sale
Garage sale
A garage sale, also known as a yard sale, rummage sale, tag sale, lawn sale, attic sale, moving sale, or junk sale, is an informal, irregularly scheduled event for the sale of used goods by private individuals, in which "block sales" are allowed, so that sellers are not required to obtain business...
s, quilting
Quilting
Quilting is a sewing method done to join two or more layers of material together to make a thicker padded material. A quilter is the name given to someone who works at quilting. Quilting can be done by hand, by sewing machine, or by a specialist longarm quilting system.The process of quilting uses...
, travel mugs
Flask
Flask may refer to:* Laboratory flask, laboratory glassware for holding larger volumes than simple test tubes* Vacuum flask a container designed to keep warm drinks warm and refrigerated drinks cold...
, and composting (nutrients). Includes the terms laundry
Laundry
Laundry is a noun that refers to the act of washing clothing and linens, the place where that washing is done, and/or that which needs to be, is being, or has been laundered...
, repair, regift
Regift
Regifting or regiving is the act of taking a gift that has been received and giving it to somebody else, sometimes in the guise of a new gift. One example of a formalization of this activity are the white elephant gift exchanges, in which items can be regifted from year to year.In the USA,...
, and upcycle.
Recycle - discards are separated into materials that may be incorporated into new products. This is different from Reuse in that energy is used to change the physical properties of the material. Initiatives include Composting, Beverage Container Deposits and buying products with a high content of post-consumer material.
Within recycling there is distinction between two types:
- Upcycle- converting low-value materials in high-value products (more desirable)
- Downcycle - converting valuable products into low-value raw materials (less desirable)
Generate - capturing useful material for waste to energy programs. Includes Methane Collection, Gasification and Digestion, and the term Recover.
Incinerate - high temperature destruction of material. Differs from Gasification in that oxygen is used; differs from burning in that high temperatures consume material efficiently and emissions are controlled.
Devastate - to discard into the natural environment, or to "trash" the planet. Includes Litter, Burn Barrels, Unnecessary Vehicle Idling, and Dumping discards onto land or into water.
Incentives for 3R
The 3R’s of reduce, reuse and recycle have been considered to be a base of environmental awareness and a way of promoting ecological balance through conscious behaviour and choices. It is generally accepted that these patterns of behaviour and consumer choices will lead to savings in materials and energy which will benefit the environment.In this context it may be enquired whether certain economic instruments may be considered to further strengthen these behaviours and choices. An example may be to reduce the sales tax or value added tax on goods that are made by recycling used materials, such as paper, plastics, glass, metals. Another example may be to reduce sales tax or value added tax on second-hand goods, which may include books, clothes, house-hold gadgets, bicycles, cars and automobiles, office equipment, medical and scientific equipment, telecommunication equipment, agricultural equipment, industrial and manufacturing equipment, boats, ships, trains and trams, aeroplanes, oil rigs, and so forth.
An additional approach may be to reduce the interest rates on the financial loans, which companies avail of, for their commercial activities in the recycling, re-use and resale of used material and equipments.
It is plausible that this may have a significant impact on consumer behaviour, and may strengthen those sections of the economy and trade that are associated with such goods and services. Additionally, this would be consistent with supporting consumer behaviour and choices that are beneficial for the environment and for the economy.
External links
- Letsrecycle News Article on European Debate on Waste Hierarchy
- Getting to Zero Waste
- Recovered Resource Blog
- Action RE-buts in Québec

