Intermodulation
Encyclopedia
Amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent...
of signals
Signal (electrical engineering)
In the fields of communications, signal processing, and in electrical engineering more generally, a signal is any time-varying or spatial-varying quantity....
containing two or more different frequencies in a system with nonlinearities. The intermodulation between each frequency component will form additional signals at frequencies that are not just at harmonic
Harmonic
A harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
frequencies (integer
Integer
The integers are formed by the natural numbers together with the negatives of the non-zero natural numbers .They are known as Positive and Negative Integers respectively...
multiple
Multiple
The word multiple can refer to:*Multiple , multiples of numbers*List of multiple discoveries, instances of scientists, working independently of each other, reaching similar findings...
s) of either, but also at the sum and difference frequencies of the original frequencies and at multiples of those sum and difference frequencies.
Intermodulation is caused by non-linear behaviour of the signal processing
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
being used. The theoretical outcome of these non-linearities can be calculated by generating a Volterra series
Volterra Series
The Volterra series is a model for non-linear behavior similar to the Taylor series. It differs from the Taylor series in its ability to capture 'memory' effects. The Taylor series can be used to approximate the response of a nonlinear system to a given input if the output of this system depends...
of the characteristic, while the usual approximation
Approximation
An approximation is a representation of something that is not exact, but still close enough to be useful. Although approximation is most often applied to numbers, it is also frequently applied to such things as mathematical functions, shapes, and physical laws.Approximations may be used because...
of those non-linearities is obtained by generating a Taylor series
Taylor series
In mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point....
.
Intermodulation is rarely desirable in radio or audio processing, as it creates unwanted spurious emission
Spurious emission
A spurious emission is any radio frequency not deliberately created or transmitted, especially in a device which normally does create other frequencies...
s, often in the form of sidebands. For radio transmissions this increases the occupied bandwidth, leading to adjacent channel interference
Interference (communication)
In communications and electronics, especially in telecommunications, interference is anything which alters, modifies, or disrupts a signal as it travels along a channel between a source and a receiver. The term typically refers to the addition of unwanted signals to a useful signal...
, which can reduce audio clarity or increase spectrum usage. It should not be confused with harmonic distortion (which does have widespread use in audio
Sound recording and reproduction
Sound recording and reproduction is an electrical or mechanical inscription and re-creation of sound waves, such as spoken voice, singing, instrumental music, or sound effects. The two main classes of sound recording technology are analog recording and digital recording...
effects processing), nor with intentional modulation (such as a frequency mixer
Frequency mixer
In electronics a mixer or frequency mixer is a nonlinear electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum f1 + f2 and difference f1 -...
in superheterodyne receiver
Superheterodyne receiver
In electronics, a superheterodyne receiver uses frequency mixing or heterodyning to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency, which can be more conveniently processed than the original radio carrier frequency...
s) where signals to be modulated are presented to an intentional nonlinear element (multiplied
Analog multiplier
In electronics, an analog multiplier is a device which takes two analog signals and produces an output which is their product. Such circuits can be used to implement related functions such as squares , and square roots....
) (see non-linear mixers such as mixer diodes and even single-transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
oscillator-mixer circuits). In audio, the intermodulation products are nonharmonically related to the input frequencies and therefore "off-key" with respect to the common Western musical scale.
Causes of intermodulation
A linear system cannot produce intermodulation. If the input of a linear time-invariantLTI system theory
Linear time-invariant system theory, commonly known as LTI system theory, comes from applied mathematics and has direct applications in NMR spectroscopy, seismology, circuits, signal processing, control theory, and other technical areas. It investigates the response of a linear and time-invariant...
system is a signal of a single frequency, then the output is a signal of the same frequency; only the amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
and phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
can differ from the input signal. However, non-linear systems generate harmonic
Harmonic
A harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
s, meaning that if the input of a non-linear system is a signal of a single frequency,
 then the output is a signal which includes a number of integer multiples of the input frequency; (i.e some of
then the output is a signal which includes a number of integer multiples of the input frequency; (i.e some of  ).
).Intermodulation occurs when the input to a non-linear system is composed of two or more frequencies. Consider an input signal that contains three frequency components at
 ,
,  , and
, and  ; which may be expressed as
; which may be expressed as
where the
 and
and  are the amplitudes and phases of the three components, respectively.
are the amplitudes and phases of the three components, respectively.We obtain our output signal,
 , by passing our input through a non-linear function:
, by passing our input through a non-linear function:
 will contain the three frequencies of the input signal,
will contain the three frequencies of the input signal,  ,
,  , and
, and  (which are known as the fundamental frequencies), as well as a number of linear combination
(which are known as the fundamental frequencies), as well as a number of linear combinationLinear combination
In mathematics, a linear combination is an expression constructed from a set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results...
s of the fundamental frequencies, each of the form

where
 ,
,  , and
, and  are arbitrary integers which can assume positive or negative values. These are the intermodulation products (or IMPs).
are arbitrary integers which can assume positive or negative values. These are the intermodulation products (or IMPs).In general, each of these frequency components will have a different amplitude and phase, which depends on the specific non-linear function being used, and also on the amplitudes and phases of the original input components.
More generally, given an input signal containing an arbitrary number
 of frequency components
of frequency components  , the output signal will contain a number of frequency components, each of which may be described by
, the output signal will contain a number of frequency components, each of which may be described by
where the coefficients
 are arbitrary integer values.
are arbitrary integer values.Intermodulation order
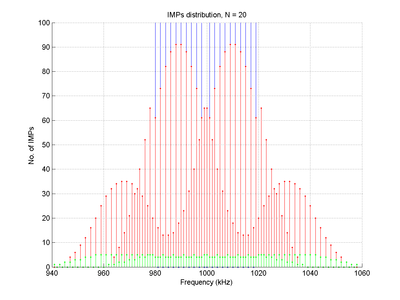
 of a given intermodulation product is the sum of the absolute values of the coefficients,
of a given intermodulation product is the sum of the absolute values of the coefficients,
For example, in our original example above, third-order intermodulation products (IMPs) occur where
 :
:

In many radio and audio applications, odd-order IMPs are of most interest, as they fall within the vicinity of the original frequency components, and may therefore interfere with the desired behaviour.
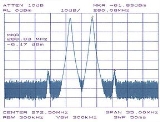
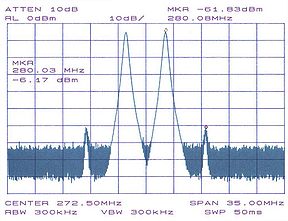
Passive intermodulation
As explained in a previous section, intermodulation can only occur in non-linear systems. Non-linear systems are generally composed of active components, meaning that the components must be biased with an external power source which is not the input signal (i.e. the active components must be "turned on"). However, even passive components can perform in a non-linear manner and cause intermodulation. DiodeDiode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
s are widely known for their passive nonlinear effects, but parasitic nonlinearity can arise in other components as well. For example, audio transformers exhibit non-linear behavior near their saturation point, electrolytic capacitors can start to behave as rectifiers under large-signal conditions, and RF connector
RF connector
A coaxial RF connector is an electrical connector designed to work at radio frequencies in the multi-megahertz range.RF connectors are typically used with coaxial cables and are designed to maintain the shielding that the coaxial design offers. Better models also minimize the change in transmission...
s and antennas
Antenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
can exhibit non-linear characteristics. Even the air itself can behave in a non-linear fashion, which can be exploited to produce audible sound from intermodulation of ultrasonic frequencies
Sound from ultrasound
Sound from ultrasound is the name given here to situations when modulated ultrasound can make its carried signal audible without needing a receiver set...
.
Passive intermodulation (PIM) occurs in passive devices (which may include cables, antennas etc.) that are subjected to two or more high power tones. The PIM product is the result of the two (or more) high power tones mixing at device nonlinearities such as junctions of dis-similar metals, metal-oxide junctions and even loose connectors. The higher the signal amplitudes, the more pronounced the effect of the nonlinearities, and the more prominent the intermodulation that occurs - even though upon initial inspection, the system would appear to be linear and unable to generate intermodulation.
PIM can also occur in connectors, or when conductors made of two galvanically
Galvanization
Galvanization is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, in order to prevent rusting. The term is derived from the name of Italian scientist Luigi Galvani....
unmatched metals come in contact with each other. However, the most common source of passive intermodulation in connectors comes from the conduction of signal current through ferromagnetic metals such as nickel, which has a nonlinear magnetization-inductance hysteresis. This effect has been exploited to make reliable sources of PIM, which can be used to cancel unwanted PIM from a system.
Intermodulation in electronic circuits
Intermodulation is caused by nonlinearity or parameter limitations in an amplifier system. This nonlinearity can be characterized in many ways, including the slew rateSlew rate
In electronics, the slew rate represents the maximum rate of change of a signal at any point in a circuit.Limitations in slew rate capability can give rise to non linear effects in electronic amplifiers...
, crossover distortion
Crossover distortion
Crossover distortion is a type of distortion which is caused by switching between devices driving a load, most often when the devices are matched...
, reduced transistor current gain, or saturation of collector-emitter junctions near clipping. Slew-induced distortion
Slew-induced distortion
Slew-induced Distortion is caused when an amplifier or transducer is required to change output , i.e. slew, faster than it is able to do so without error. At such times any other signals may suffer considerable gain distortion, leading to Intermodulation distortion...
(SID) can produce intermodulation distortion (IMD) when the first signal is slewing (changing voltage) at the limit of the amplifier's power bandwidth
Power bandwidth
The power bandwidth of an amplifier is sometimes taken as the frequency range for which the rated power output of an amplifier can be maintained to at least half of the full rated power...
product. This induces an effective reduction in gain, partially amplitude-modulating
Amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent...
the second signal. If SID only occurs for a portion of the signal, it is called "transient" intermodulation distortion. This usually occurs due to soft clipping of the signal peaks.
Intermodulation in audio applications
Audio engineers usually strive to avoid intermodulation, as for anything other than extremely simple input waveforms, it introduces frequency components that are not harmonically related, which tends to sound unmusical and unpleasant. However, certain audio effects rely on amplitude modulationAmplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent...
; these include tremolo
Tremolo
Tremolo, or tremolando, is a musical term that describes various trembling effects, falling roughly into two types. The first is a rapid reiteration...
and ring modulation
Ring modulation
Ring modulation is a signal-processing effect in electronics, an implementation of amplitude modulation or frequency mixing, performed by multiplying two signals, where one is typically a sine-wave or another simple waveform. It is referred to as "ring" modulation because the analog circuit of...
. One way to generate such effects is through deliberate intermodulation in a non-linear device, but may also be achieved without intermodulation by an analog multiplier
Analog multiplier
In electronics, an analog multiplier is a device which takes two analog signals and produces an output which is their product. Such circuits can be used to implement related functions such as squares , and square roots....
. Transient intermodulation distortion, or TIM, occurs in amplifiers that employ negative feedback when signal delays make the amplifier incapable of correcting distortion when exposed to fast, transient signals.
Harmonic distortion occurs when non-linearity (in an amplifier
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
or loudspeaker
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
, for instance) only creates new frequencies that are harmonically related to the original signal. Intermodulation distortion occurs when a different type of non-linearity can create new frequencies that are not harmonically related to the original signal. All audio devices give rise to distortion
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
to some extent; harmonic distortion and intermodulaton distortion tests
Audio system measurements
Audio system measurements are made for several purposes. Designers take measurements so that they can specify the performance of a piece of equipment. Maintenance engineers make them to ensure equipment is still working to specification, or to ensure that the cumulative defects of an audio path are...
highlight different aspects of imperfections, and one type of distortion may be inaudibly low while the other is significantly high for some equipment under certain conditions.
In analog recording, wow
Wow
-Business:*WOW!, an internet, cable, and phone company*WOW! , a defunct ISP from CompuServe*WOW, a radio station in Omaha, Nebraska, started in 1922 by Woodmen of the World; today known as KXSP*WOW , English toy company...
and flutter
Flutter
In electronics and communication, flutter is the rapid variation of signal parameters, such as amplitude, phase, and frequency. Examples of electronic flutter are:...
are forms of intermodulation distortion caused by speed variations in the medium (usually tape
Tape
Tape refers to a strip of long, thin and narrow material, usually rolled up. Most commonly, it refers to:- Recording media :* Cassette tape* Digital Audio Tape * Digital Compact Cassette * Digital Tape Format* Magnetic tape sound recording...
). When the flutter rate is above a certain point, typically about 20Hz
Audio frequency
An audio frequency or audible frequency is characterized as a periodic vibration whose frequency is audible to the average human...
, the modulation products impressed into the musical signal no longer present as an audibly obvious flutter, yet continue to interfere with the signal as extraneous frequency modulation
Frequency modulation
In telecommunications and signal processing, frequency modulation conveys information over a carrier wave by varying its instantaneous frequency. This contrasts with amplitude modulation, in which the amplitude of the carrier is varied while its frequency remains constant...
, and the resulting sideband products manifest as distortion. This distortion results in a thicker, grainier texture due to the excess non-musical sum and difference components riding above and below the harmonic content of the material. Dewow and deflutter techniques such as those by Plangent Processes effectively minimize this distortion.
Measurement
Intermodulation distortion in audio is usually specified as the Root Mean SquareRoot mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
(RMS) value of the various sum-and-difference signals as a percentage of the original signal's RMS voltage, although it may be specified in terms of individual component strengths, in decibels
DB
DB may refer to:In science and technology:*Decibel , a logarithmic unit of measurement in acoustics and electronics*Dubnium , a chemical element*DB connector, a size of D-subminiature electrical connector...
, as is common with RF
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
work. Audio IMD standard tests
Audio system measurements
Audio system measurements are made for several purposes. Designers take measurements so that they can specify the performance of a piece of equipment. Maintenance engineers make them to ensure equipment is still working to specification, or to ensure that the cumulative defects of an audio path are...
include SMPTE standard RP120-1994 where two signals (at 60 Hz and 7 kHz, with 4:1 amplitude ratios) are used for the test; many other standards (such as DIN, CCIF) use other frequencies and amplitude ratios. Opinion varies over the ideal ratio of test frequencies (e.g. 3:4, or almost -but not exactly - 3:1 for example).
After feeding the equipment under test with low distortion input sinewaves, the output distortion can be measured by using a electronic filter
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
to remove the original frequencies, or spectral analysis may be made using Fourier Transformations in software or a dedicated spectrum analyser, or when determining intermodulation effects in communications equipment, may be made using the receiver under test itself.
Using modern a network analyzer
Network analyzer
Network analyzer may mean:* Packet analyzer, used on a computer data network* Network analyzer , a type of electronic test equipment...
with two internal RF sources and sensitive RF detectors simplifies the measurement setup and also provides a sensitivity level comparable to spectrum analyzers. Furthermore, a calibrated VNA setup also removes mismatch errors from measurements which otherwise would be present in spectrum analyzer measurements.
Meanwhile error-corrected IM measurement systems are available. These system support frequency converting vector-measurements of S-parameters.
The user can locate IM-sources and perform a vector or time-domain fitting or modelling of the IM-signals and components.
See also
- Rusty bolt effectRusty bolt effectThe rusty bolt effect is a description of radio interference due to interactions with dirty connections or corroded parts. It is more properly known as passive intermodulation, and can result from a variety of different causes such as ferromagnetic conduction metals, nonlinear microwave absorbers...
- Beat (acoustics)Beat (acoustics)In acoustics, a beat is an interference between two sounds of slightly different frequencies, perceived as periodic variations in volume whose rate is the difference between the two frequencies....
- Audio system measurementsAudio system measurementsAudio system measurements are made for several purposes. Designers take measurements so that they can specify the performance of a piece of equipment. Maintenance engineers make them to ensure equipment is still working to specification, or to ensure that the cumulative defects of an audio path are...
- Second-order intercept pointSecond-order intercept pointThe Second Order Intercept Point, also known as the SOI, IP2, or IIP2 , is a measure of linearity that quantifies the second-order distortion generated by nonlinear systems and devices. Examples of frequently used devices that are concerned with this measure are amplifiers and mixers...
- Third-order intercept pointThird-order intercept pointIn telecommunications, a third-order intercept point is a measure for weakly nonlinear systems and devices, for example receivers, linear amplifiers and mixers. It is based on the idea that the device nonlinearity can be modeled using a low-order polynomial, derived by means of Taylor series...
, a metric of an amplifier or system related to intermodulation

