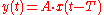
Distortion
Encyclopedia
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice. In some fields, however, distortion may be desirable; such is the case with electric guitar distortion.
The addition of noise
or other extraneous signals (hum
, interference
) is not considered to be distortion, though the effects of quantization distortion are sometimes considered noise. A quality measure that explicitly reflects both the noise and the distortion is the Signal-to-noise-and-distortion (SINAD) ratio.
and signal processing
, a noise-free "system
" can be characterised by a transfer function
, such that the output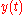 can be written as a function of the input
can be written as a function of the input  as
as
When the transfer function comprises only a perfect gain
constant A and perfect delay
T
the output is undistorted. Distortion occurs when the transfer function F is more complicated than this. If F is a linear function, for instance a filter whose gain and/or delay varies with frequency, then the signal will experience linear distortion. Linear distortion will not change the shape of a single sinuosoid, but will usually change the shape of a multi-tone signal.
This diagram shows the behaviour of a signal (made up of a square wave
followed by a sine wave
) as it is passed through various distorting functions.
The transfer function of an ideal amplifier, with perfect gain and delay, is only an approximation. The true behavior of the system is usually different. Nonlinearities in the transfer function of an active device (such as vacuum tube
s, transistor
s, and operational amplifier
s) are a common source of non-linear distortion; in passive components
(such as a coaxial cable
or optical fiber
), linear distortion can be caused by inhomogeneities, reflections, and so on in the propagation
path.
, subsystem, or device when the output
amplitude is not a linear function
of the input amplitude under specified conditions.
s that are whole number
multiples of a sound wave's frequencies. Nonlinearities that give rise to amplitude distortion in audio systems are most often measured in terms of the harmonic
s (overtones) added to a pure sinewave fed to the system. Harmonic distortion may be expressed in terms of the relative strength of individual components, in decibels
, or the Root Mean Square
of all harmonic components: Total harmonic distortion
(THD), as a percentage. The level at which harmonic distortion becomes audible is not straightforward. Different types of distortion (like crossover distortion) are more audible than others (like soft clipping) even if the THD measurements are identical. Harmonic distortion in RF
applications is rarely expressed as THD.
is an example of frequency distortion. In the audio case, this is mainly caused by room acoustics, poor loudspeakers and microphones, long loudspeaker cables in combination with frequency dependent loudspeaker impedance
, etc.
.
In a waveguide
, propagation velocity
varies with frequency.
In a filter, group delay tends to peak near the cut-off frequency, resulting in pulse distortion. When analog long distance trunks were commonplace, for example in 12 channel carrier, group delay distortion had to be corrected in repeaters.
An example of such correction is where LP/vinyl
recordings or FM audio
transmissions are deliberately pre-emphasised by a linear filter
, the reproducing system applies an inverse filter to make the overall system undistorted.
Correction is not possible if the inverse does not exist, for instance if the transfer function
has flat spots (the inverse would map multiple input points to a single output point). This results in a loss of information, which is uncorrectable. Such a situation can occur when an amplifier is overdriven, resulting in clipping
or slew rate
distortion, when for a moment the output is determined by the characteristics of the amplifier alone, and not by the input signal.
, distortion is the shifting of the significant instants of the signal pulses from their proper positions relative to the beginning of the start pulse
. The magnitude of the distortion is expressed in percent of an ideal unit pulse
length. This is sometimes called 'bias' distortion.
Telegraphic distortion is a similar older problem, distorting the ratio between "mark" and "space" intervals. http://www.freepatentsonline.com/3725787.html
In this context, distortion refers to any kind of deformation of a waveform, compared to an input, usually Clipping, harmonic distortion and intermodulation distortion (mixing
phenomena) caused by non-linear behavior of electronic components and power supply limitations. Terms for specific types of nonlinear audio distortion include: crossover distortion
, slew-Induced Distortion
(SID) and transient intermodulation (TIM).
Distortion in music is sometimes intentionally used as an effect, see also overdrive and distortion synthesis
. Other forms of audio distortion that may be referred to are non-flat frequency response
, compression
, modulation
, aliasing
, quantization noise, wow
and flutter from analog media such as vinyl records and magnetic tape
. The human ear cannot hear phase distortion
, except that it may affect the stereo imaging
. (See also: Audio system measurements
.)
In most fields, distortion is characterized as unwanted change to a signal.
, image/optical distortion is a divergence from rectilinear projection caused by a change in magnification
with increasing distance from the optical axis
of an optical system.
, a distortion is the misrepresentation of the area or shape of a feature. The Mercator projection
, for example, distorts by exaggerating the size of regions at high latitude
.
The addition of noise
Electronic noise
Electronic noise is a random fluctuation in an electrical signal, a characteristic of all electronic circuits. Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly, as it can be produced by several different effects...
or other extraneous signals (hum
Mains hum
Mains hum, electric hum, or power line hum is an audible oscillation of alternating current at the frequency of the mains electricity, which is usually 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the local power line frequency...
, interference
Interference (communication)
In communications and electronics, especially in telecommunications, interference is anything which alters, modifies, or disrupts a signal as it travels along a channel between a source and a receiver. The term typically refers to the addition of unwanted signals to a useful signal...
) is not considered to be distortion, though the effects of quantization distortion are sometimes considered noise. A quality measure that explicitly reflects both the noise and the distortion is the Signal-to-noise-and-distortion (SINAD) ratio.
Electronic signals
In telecommunicationTelecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
and signal processing
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, a noise-free "system
System
System is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
" can be characterised by a transfer function
Transfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
, such that the output
 can be written as a function of the input
can be written as a function of the input  as
asWhen the transfer function comprises only a perfect gain
Gain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
constant A and perfect delay
Propagation delay
Propagation delay is a technical term that can have a different meaning depending on the context. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics...
T
the output is undistorted. Distortion occurs when the transfer function F is more complicated than this. If F is a linear function, for instance a filter whose gain and/or delay varies with frequency, then the signal will experience linear distortion. Linear distortion will not change the shape of a single sinuosoid, but will usually change the shape of a multi-tone signal.
This diagram shows the behaviour of a signal (made up of a square wave
Square wave
A square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels...
followed by a sine wave
Sine wave
The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields...
) as it is passed through various distorting functions.
- The first trace (in black) shows the input. It also shows the output from a non-distorting transfer function (straight line).
- A high-pass filterHigh-pass filterA high-pass filter is a device that passes high frequencies and attenuates frequencies lower than its cutoff frequency. A high-pass filter is usually modeled as a linear time-invariant system...
(green trace) will distort the shape of a square wave by reducing its low frequency components. This is the cause of the "droop" seen on the top of the pulses. This "pulse distortion" can be very significant when a train of pulses must pass through an AC-coupled (high-pass filtered) amplifier. As the sine wave contains only one frequency, its shape is unaltered. - A low-pass filterLow-pass filterA low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
(blue trace) will round the pulses by removing the high frequency components. All systems are low pass to some extent. Note that the phasePhase (waves)Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
of the sine wave is different for the lowpass and the highpass cases, due to the phase distortion of the filters. - A slightly non-linear transfer function (purple), this one is gently compressing as may be typical of a tube audio amplifier, will compress the peaks of the sine wave. This will cause small amounts of low order harmonics to be generated.
- A hard-clippingClipping (audio)Clipping is a form of waveform distortion that occurs when an amplifier is overdriven and attempts to deliver an output voltage or current beyond its maximum capability...
transfer function (red) will generate high order harmonics. Parts of the transfer function are flat, which indicates that all information about the input signal has been lost in this region.
The transfer function of an ideal amplifier, with perfect gain and delay, is only an approximation. The true behavior of the system is usually different. Nonlinearities in the transfer function of an active device (such as vacuum tube
Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
s, transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s, and operational amplifier
Operational amplifier
An operational amplifier is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output...
s) are a common source of non-linear distortion; in passive components
Electronic component
An electronic component is a basic electronic element and may be available in a discrete form having two or more electrical terminals . These are intended to be connected together, usually by soldering to a printed circuit board, in order to create an electronic circuit with a particular function...
(such as a coaxial cable
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
or optical fiber
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
), linear distortion can be caused by inhomogeneities, reflections, and so on in the propagation
Wave propagation
Wave propagation is any of the ways in which waves travel.With respect to the direction of the oscillation relative to the propagation direction, we can distinguish between longitudinal wave and transverse waves....
path.
Amplitude distortion
Amplitude distortion is distortion occurring in a systemSystem
System is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
, subsystem, or device when the output
Output
Output is the term denoting either an exit or changes which exit a system and which activate/modify a process. It is an abstract concept, used in the modeling, system design and system exploitation.-In control theory:...
amplitude is not a linear function
Linear function
In mathematics, the term linear function can refer to either of two different but related concepts:* a first-degree polynomial function of one variable;* a map between two vector spaces that preserves vector addition and scalar multiplication....
of the input amplitude under specified conditions.
Harmonic distortion
Harmonic distortion adds overtoneOvertone
An overtone is any frequency higher than the fundamental frequency of a sound. The fundamental and the overtones together are called partials. Harmonics are partials whose frequencies are whole number multiples of the fundamental These overlapping terms are variously used when discussing the...
s that are whole number
Whole number
Whole number is a term with inconsistent definitions by different authors. All distinguish whole numbers from fractions and numbers with fractional parts.Whole numbers may refer to:*natural numbers in sense — the positive integers...
multiples of a sound wave's frequencies. Nonlinearities that give rise to amplitude distortion in audio systems are most often measured in terms of the harmonic
Harmonic
A harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
s (overtones) added to a pure sinewave fed to the system. Harmonic distortion may be expressed in terms of the relative strength of individual components, in decibels
DB
DB may refer to:In science and technology:*Decibel , a logarithmic unit of measurement in acoustics and electronics*Dubnium , a chemical element*DB connector, a size of D-subminiature electrical connector...
, or the Root Mean Square
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
of all harmonic components: Total harmonic distortion
Total harmonic distortion
The total harmonic distortion, or THD, of a signal is a measurement of the harmonic distortion present and is defined as the ratio of the sum of the powers of all harmonic components to the power of the fundamental frequency...
(THD), as a percentage. The level at which harmonic distortion becomes audible is not straightforward. Different types of distortion (like crossover distortion) are more audible than others (like soft clipping) even if the THD measurements are identical. Harmonic distortion in RF
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
applications is rarely expressed as THD.
Frequency response distortion
Non-flat frequency response is a form of distortion that occurs when different frequencies are amplified by different amounts, caused by filters. For example, the non-uniform frequency response curve of AC-coupled cascade amplifierCascade amplifier
A cascade amplifier is any amplifier constructed from a series of amplifiers, where each amplifier sends its output to the input of the next amplifier in a daisy chain....
is an example of frequency distortion. In the audio case, this is mainly caused by room acoustics, poor loudspeakers and microphones, long loudspeaker cables in combination with frequency dependent loudspeaker impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
, etc.
Phase distortion
This form of distortion mostly occurs due to the reactive component, such as capacitive reactance or inductive reactance. Here, all the components of the input signal are not amplified with the same phase shift, hence causing some parts of the output signal to be out of phase with the rest of the output.Group delay distortion
Can be found only in dispersive mediaDispersion (optics)
In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...
.
In a waveguide
Waveguide
A waveguide is a structure which guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound waves. There are different types of waveguides for each type of wave...
, propagation velocity
Wave velocity
Wave velocity is a wave property, which may refer to:*phase velocity, the velocity at which a wave phase propagates at a certain frequency*pulse wave velocity, the velocity at which a pulse travels through a medium, usually applied to arteries as a measure of arterial stiffness*group velocity, the...
varies with frequency.
In a filter, group delay tends to peak near the cut-off frequency, resulting in pulse distortion. When analog long distance trunks were commonplace, for example in 12 channel carrier, group delay distortion had to be corrected in repeaters.
Correction of distortion
As the system output is given by y(t) = F(x(t)), then if the inverse function F−1 can be found, and used intentionally to distort either the input or the output of the system, then the distortion will be corrected.An example of such correction is where LP/vinyl
Gramophone record
A gramophone record, commonly known as a phonograph record , vinyl record , or colloquially, a record, is an analog sound storage medium consisting of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove...
recordings or FM audio
FM broadcasting
FM broadcasting is a broadcasting technology pioneered by Edwin Howard Armstrong which uses frequency modulation to provide high-fidelity sound over broadcast radio. The term "FM band" describes the "frequency band in which FM is used for broadcasting"...
transmissions are deliberately pre-emphasised by a linear filter
Linear filter
Linear filters in the time domain process time-varying input signals to produce output signals, subject to the constraint of linearity.This results from systems composed solely of components classified as having a linear response....
, the reproducing system applies an inverse filter to make the overall system undistorted.
Correction is not possible if the inverse does not exist, for instance if the transfer function
Transfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
has flat spots (the inverse would map multiple input points to a single output point). This results in a loss of information, which is uncorrectable. Such a situation can occur when an amplifier is overdriven, resulting in clipping
Clipping
-Words:* Clipping , the cutting-out of articles from a paper publication* Clipping , shortening the articulation of a speech sound, usually a vowel* Clipping , the formation of a new word by shortening it, e.g...
or slew rate
Slew rate
In electronics, the slew rate represents the maximum rate of change of a signal at any point in a circuit.Limitations in slew rate capability can give rise to non linear effects in electronic amplifiers...
distortion, when for a moment the output is determined by the characteristics of the amplifier alone, and not by the input signal.
Teletypewriter or modem signaling
In binary signaling such as FSKFSK
FSK can have alternative meanings:* Federal Counterintelligence Service, , Federal Counterintelligence Service of Russia)...
, distortion is the shifting of the significant instants of the signal pulses from their proper positions relative to the beginning of the start pulse
Pulse
In medicine, one's pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the heartbeat by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed against a bone, such as at the neck , at the wrist , behind the knee , on the inside of the elbow , and near the...
. The magnitude of the distortion is expressed in percent of an ideal unit pulse
Pulse
In medicine, one's pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the heartbeat by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed against a bone, such as at the neck , at the wrist , behind the knee , on the inside of the elbow , and near the...
length. This is sometimes called 'bias' distortion.
Telegraphic distortion is a similar older problem, distorting the ratio between "mark" and "space" intervals. http://www.freepatentsonline.com/3725787.html
In this context, distortion refers to any kind of deformation of a waveform, compared to an input, usually Clipping, harmonic distortion and intermodulation distortion (mixing
Mixing (physics)
In physics, a dynamical system is said to be mixing if the phase space of the system becomes strongly intertwined, according to at least one of several mathematical definitions. For example, a measure-preserving transformation T is said to be strong mixing ifwhenever A and B are any measurable...
phenomena) caused by non-linear behavior of electronic components and power supply limitations. Terms for specific types of nonlinear audio distortion include: crossover distortion
Crossover distortion
Crossover distortion is a type of distortion which is caused by switching between devices driving a load, most often when the devices are matched...
, slew-Induced Distortion
Slew-induced distortion
Slew-induced Distortion is caused when an amplifier or transducer is required to change output , i.e. slew, faster than it is able to do so without error. At such times any other signals may suffer considerable gain distortion, leading to Intermodulation distortion...
(SID) and transient intermodulation (TIM).
Distortion in music is sometimes intentionally used as an effect, see also overdrive and distortion synthesis
Distortion synthesis
Distortion synthesis is a group of sound synthesis techniques which modify existing sounds to produce more complex sounds , usually by using non-linear circuits or mathematics....
. Other forms of audio distortion that may be referred to are non-flat frequency response
Frequency response
Frequency response is the quantitative measure of the output spectrum of a system or device in response to a stimulus, and is used to characterize the dynamics of the system. It is a measure of magnitude and phase of the output as a function of frequency, in comparison to the input...
, compression
Audio level compression
Dynamic range compression, also called DRC or simply compression reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds by narrowing or "compressing" an audio signal's dynamic range...
, modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
, aliasing
Aliasing
In signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing refers to an effect that causes different signals to become indistinguishable when sampled...
, quantization noise, wow
Wow (recording)
Wow is a relatively slow form of flutter which can affect both gramophone records and tape recorders. In the latter, the collective expression wow and flutter is commonly used.-Gramophone records:...
and flutter from analog media such as vinyl records and magnetic tape
Magnetic tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic recording, made of a thin magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic. It was developed in Germany, based on magnetic wire recording. Devices that record and play back audio and video using magnetic tape are tape recorders and video tape recorders...
. The human ear cannot hear phase distortion
Phase distortion
In signal processing, phase distortion or phase-frequency distortion is distortion that occurs when a filter's phase response is not linear over the frequency range of interest, that is, the phase shift introduced by a circuit or device is not directly proportional to frequency, or the...
, except that it may affect the stereo imaging
Stereo imaging
Stereo imaging is an audio jargon term used for the aspect of sound recording and reproduction concerning spatial locations of the sound source, both laterally and in depth. An image is 'good' if the performers can be effortlessly located; 'bad' if there is no hope of doing so...
. (See also: Audio system measurements
Audio system measurements
Audio system measurements are made for several purposes. Designers take measurements so that they can specify the performance of a piece of equipment. Maintenance engineers make them to ensure equipment is still working to specification, or to ensure that the cumulative defects of an audio path are...
.)
In most fields, distortion is characterized as unwanted change to a signal.
Optics
In opticsOptics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, image/optical distortion is a divergence from rectilinear projection caused by a change in magnification
Magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not in physical size. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification"...
with increasing distance from the optical axis
Optical axis
An optical axis is a line along which there is some degree of rotational symmetry in an optical system such as a camera lens or microscope.The optical axis is an imaginary line that defines the path along which light propagates through the system...
of an optical system.
Map projections
In cartographyCartography
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
, a distortion is the misrepresentation of the area or shape of a feature. The Mercator projection
Mercator projection
The Mercator projection is a cylindrical map projection presented by the Belgian geographer and cartographer Gerardus Mercator, in 1569. It became the standard map projection for nautical purposes because of its ability to represent lines of constant course, known as rhumb lines or loxodromes, as...
, for example, distorts by exaggerating the size of regions at high latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
.
See also
- AliasingAliasingIn signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing refers to an effect that causes different signals to become indistinguishable when sampled...
- Amplitude distortionAmplitude distortionAmplitude distortion is distortion occurring in a system, subsystem, or device when the output amplitude is not a linear function of the input amplitude under specified conditions....
- Attenuation distortionAttenuation DistortionAttenuation distortion is the distortion of an analog signal that occurs during transmission when the transmission medium does not have a flat frequency response across the bandwidth of the medium or the frequency spectrum of the signal....
- Bias distortionBias distortionIn telecommunication, the term bias distortion has the following meanings:#Signal distortion resulting from a shift in the bias.#In digital signaling, distortion of the signal in which all the significant intervals have uniformly longer or shorter durations than their theoretical durations.Bias...
- Crossover distortionCrossover distortionCrossover distortion is a type of distortion which is caused by switching between devices driving a load, most often when the devices are matched...
- Degree of isochronous distortionDegree of isochronous distortionThe degree of isochronous distortion, in data transmission, is the ratio of the absolute value of the maximum measured difference between the actual and the theoretical intervals separating any two significant instants of modulation , to the unit interval. These instants are not necessarily...
- Degree of start-stop distortionDegree of start-stop distortionIn telecommunication, the term degree of start-stop distortion has the following meanings:# In asynchronous data transmission, the ratio of the absolute value of the maximum measured difference between the actual and theoretical intervals separating any significant instant of modulation from the...
- Delay distortion
- Distortion-limited operationDistortion-limited operationIn telecommunication, distortion-limited operation is the condition prevailing when distortion of a received signal, rather than its attenuated amplitude , limits performance under stated operational conditions and limits....
- Distortion (music)
- Distortion power factor
- Frequency-selective fading
- Image warpingImage warpingImage warping is the process of digitally manipulating an image such that any shapes portrayed in the image have been significantly distorted. Warping may be used for correcting image distortion as well as for creative purposes...
- Intermodulation distortion
- Lossy compression
- Minimum Resolvable ContrastMinimum Resolvable ContrastMinimum resolvable contrast is a subjective measure of a visible spectrum sensor’s or camera's sensitivity and ability to resolve data. A snapshot image of a series of three bar targets of selected spatial frequencies and various contrast coatings captured by the UUT are used to determine the...
- Overdrive (music)
- Total harmonic distortionTotal harmonic distortionThe total harmonic distortion, or THD, of a signal is a measurement of the harmonic distortion present and is defined as the ratio of the sum of the powers of all harmonic components to the power of the fundamental frequency...
— a measurement of the amount of distortion in a sinusoidal waveform - Valve sound