.gif)
History of Canada (1945-1960)
Encyclopedia
Prosperity returned to Canada during the Second World War. With continued Liberal
governments, national policies increasingly turned to social welfare, including universal health care
, old-age pensions, and veterans' pensions.
The financial crisis of the Great Depression
, soured by rampant corruption, had led Newfoundlanders to relinquish responsible government in 1934 and become a crown colony ruled by a British governor. Prosperity returned when the U.S. military arrived in 1941 with over 10,000 soldiers and huge investments in air and naval bases. Popular sentiment grew favourable toward the United States, alarming the Canadian government, which now wanted Newfoundland to enter into confederation instead of joining with the U.S. In 1948, the British government gave voters three Referendum
choices: remaining a crown colony, returning to Dominion status (that is, independence), or joining Canada. Joining the U.S. was not made an option. After bitter debate Newfoundlanders voted to join Canada in 1949 as a province.
 The Second World War brought many changes to Canada; the government was necessarily more centralized during the war, and it remained so afterwards. The federal government also began to adopt social welfare policies, often borrowed from the Co-operative Commonwealth Federation
The Second World War brought many changes to Canada; the government was necessarily more centralized during the war, and it remained so afterwards. The federal government also began to adopt social welfare policies, often borrowed from the Co-operative Commonwealth Federation
, which had introduced such policies in the western provinces even before the war. Federally, these included hospital insurance, old-age pensions, and veterans' pensions. Once the war ended, divisions in the Armed Forces were disbanded, and women would not be recruited again until the Korean War
in 1951. Free child-care and tax concessions were rescinded to encourage women to leave the workforce, and an act providing a family allowance
or "baby bonus" was passed to help families recover from the cost of war and the wartime wage freeze. Parents of children under 16 years old were given monthly payments between $5 and $8, depending on the age of the children. The economy had prospered because of the war, and in Alberta
, there was an economic boom due to the discovery of new oil fields in 1947.
Mackenzie King won the election of 1945, but retired in 1948 and was succeeded by Louis St. Laurent. St. Laurent succeeded in extending the welfare state, and helped bring Newfoundland into Confederation as Canada's 10th province in 1949.
to decide the future of the independent Dominion of Newfoundland
. The Convention voted to hold a referendum to decide between continuing the direct rule of the Commission of Government
or restoring responsible government
. Joseph R. Smallwood, the leader of the confederates, moved that a third option of confederation with Canada should be included. Although his motion was defeated by the convention, Smallwood did not give up, but instead gathered more than 5000 petitions from the people within a fortnight which he sent to London through the Governor. The United Kingdom, insisting that it would not give Newfoundland any further financial assistance, added a third option of having Newfoundland join Canada to the ballot.
 After much debate, an initial referendum was held on June 3, 1948 to decide between continuing with the Commission of Government, reverting to dominion
After much debate, an initial referendum was held on June 3, 1948 to decide between continuing with the Commission of Government, reverting to dominion
status, or joining Canadian Confederation
. The referendum was fought by three parties, Smallwood's Confederate Association
campaigned for the Confederation option while the anti-Confederation campaign was split amongst Peter Cashin's Responsible Government League
and Chesley Crosbie
's Party for Economic Union with the United States, both of which called for a vote for responsible government
. No party advocated continuing the Commission of Government.
The result was inconclusive, with 44.6% supporting the restoration of dominion status, 41.1% for confederation with Canada, and 14.3% for continuing the Commission of Government. Between the first and second referendums, rumours had it that Catholic bishops were using their religious influence to alter the outcome of the votes. The Orange Order
was incensed and called on all its members to vote for confederation, as the Catholics voted for responsible government. The Protestants of Newfoundland outnumbered the Catholics at a ratio of 2:1. This was believed to have greatly influenced the outcome of the second referendum. A second referendum on July 22, 1948, which asked Newfoundlanders to choose between confederation and dominion status, was decided by a vote of 52% to 48% for confederation with Canada. Newfoundland joined Canada on March 31, 1949.
Not everyone was satisfied with the results, however. Peter Cashin, an outspoken anti-Confederate, questioned the validity of the votes. He claimed that it was the unholy union between London and Ottawa that brought about confederation.
 Meanwhile, Canadian foreign relations were beginning to focus on the United States, which had eclipsed Britain as a world power. During World War II, Canada was a minor partner in the alliance between the United States and Britain, and the US had pledged to help defend Canada if necessary. Canada was one of the founding members of the United Nations
Meanwhile, Canadian foreign relations were beginning to focus on the United States, which had eclipsed Britain as a world power. During World War II, Canada was a minor partner in the alliance between the United States and Britain, and the US had pledged to help defend Canada if necessary. Canada was one of the founding members of the United Nations
in 1945, and also of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in 1949, but was largely overshadowed in world affairs by the United States. Canada remained a close ally of the United States throughout the Cold War
.
When Igor Gouzenko
, a cipher
clerk for the Soviet Embassy to Canada in Ottawa
, defected in 1945, fears of Soviet espionage
led to a red scare
and the arrest and conviction of a 18 people, including Communist
Member of Parliament
Fred Rose
.
 Canada participated, under the United Nations
Canada participated, under the United Nations
, in the Korean War
. Minister of External Affairs in St. Laurent's Cabinet
, Lester Bowles Pearson, was involved in the diplomatic side of the conflict, and became more active in diplomacy with the United Nations after the war ended. In 1956 Pearson suggested a solution to the Suez Crisis
- the creation of an international peacekeeping force. For his efforts, Pearson won the Nobel Peace Prize
in 1957.
St. Laurent attempted to create a new, highly advanced jet fighter
, the Avro Arrow. This controversial aircraft was cancelled by St. Laurent's successor, John George Diefenbaker, in 1959, although Diefenbaker did help establish a missile defence system with the United States, NORAD
.
from northern Quebec
to barren Cornwallis Island, Nunavut
. The first group of people were relocated in 1953 from Inukjuak, Quebec
(then known as Port Harrison ) and from Pond Inlet, Nunavut
. They were promised homes and game to hunt, but the relocated people discovered no buildings and very little familiar wildlife. They also had to endure weeks of 24 hour darkness during the winter, and 24 hour sunlight during the summer, something that does not occur in northern Quebec. They were told that they would be returned home after a year if they wished, but this offer was later withdrawn as it would damage Canada's claims to sovereignty in the area and the Inuit were forced to stay. Eventually, the Inuit learned the local beluga whale migration routes and were able to survive in the area, hunting over a range of 18,000 km2 (6,950 mi2) each year.
Liberal Party of Canada
The Liberal Party of Canada , colloquially known as the Grits, is the oldest federally registered party in Canada. In the conventional political spectrum, the party sits between the centre and the centre-left. Historically the Liberal Party has positioned itself to the left of the Conservative...
governments, national policies increasingly turned to social welfare, including universal health care
Universal health care
Universal health care is a term referring to organized health care systems built around the principle of universal coverage for all members of society, combining mechanisms for health financing and service provision.-History:...
, old-age pensions, and veterans' pensions.
The financial crisis of the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
, soured by rampant corruption, had led Newfoundlanders to relinquish responsible government in 1934 and become a crown colony ruled by a British governor. Prosperity returned when the U.S. military arrived in 1941 with over 10,000 soldiers and huge investments in air and naval bases. Popular sentiment grew favourable toward the United States, alarming the Canadian government, which now wanted Newfoundland to enter into confederation instead of joining with the U.S. In 1948, the British government gave voters three Referendum
Newfoundland referendums, 1948
The Newfoundland Referendums of 1948 were a series of two referendums to decide the political future of the Dominion of Newfoundland. Before the referendums, Newfoundland was in debt and went through several delegations to determine whether the country would join Canada, remain under British rule...
choices: remaining a crown colony, returning to Dominion status (that is, independence), or joining Canada. Joining the U.S. was not made an option. After bitter debate Newfoundlanders voted to join Canada in 1949 as a province.
The Post-war world

Co-operative Commonwealth Federation
The Co-operative Commonwealth Federation was a Canadian political party founded in 1932 in Calgary, Alberta, by a number of socialist, farm, co-operative and labour groups, and the League for Social Reconstruction...
, which had introduced such policies in the western provinces even before the war. Federally, these included hospital insurance, old-age pensions, and veterans' pensions. Once the war ended, divisions in the Armed Forces were disbanded, and women would not be recruited again until the Korean War
Korean War
The Korean War was a conventional war between South Korea, supported by the United Nations, and North Korea, supported by the People's Republic of China , with military material aid from the Soviet Union...
in 1951. Free child-care and tax concessions were rescinded to encourage women to leave the workforce, and an act providing a family allowance
Child benefit
Child benefit is a social security payment disbursed to the parents or guardians of children. Child benefit is means-tested in some countries.-Australia:...
or "baby bonus" was passed to help families recover from the cost of war and the wartime wage freeze. Parents of children under 16 years old were given monthly payments between $5 and $8, depending on the age of the children. The economy had prospered because of the war, and in Alberta
Alberta
Alberta is a province of Canada. It had an estimated population of 3.7 million in 2010 making it the most populous of Canada's three prairie provinces...
, there was an economic boom due to the discovery of new oil fields in 1947.
Mackenzie King won the election of 1945, but retired in 1948 and was succeeded by Louis St. Laurent. St. Laurent succeeded in extending the welfare state, and helped bring Newfoundland into Confederation as Canada's 10th province in 1949.
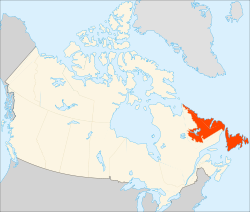
Newfoundland Joins the Country
Following the Second World War, in 1946, an election was held for the Newfoundland National ConventionNewfoundland National Convention
The Newfoundland National Convention of 1946 was a forum established to decide the constitutional future of Newfoundland-Nominations:On 11 December 1945 the Government of Britain announced that there would be an election to a National Convention, which would debate constitutional options and make a...
to decide the future of the independent Dominion of Newfoundland
Dominion of Newfoundland
The Dominion of Newfoundland was a British Dominion from 1907 to 1949 . The Dominion of Newfoundland was situated in northeastern North America along the Atlantic coast and comprised the island of Newfoundland and Labrador on the continental mainland...
. The Convention voted to hold a referendum to decide between continuing the direct rule of the Commission of Government
Commission of Government
The Commission of Government was a non-elected body that governed Newfoundland from 1934 to 1949...
or restoring responsible government
Responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability which is the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy...
. Joseph R. Smallwood, the leader of the confederates, moved that a third option of confederation with Canada should be included. Although his motion was defeated by the convention, Smallwood did not give up, but instead gathered more than 5000 petitions from the people within a fortnight which he sent to London through the Governor. The United Kingdom, insisting that it would not give Newfoundland any further financial assistance, added a third option of having Newfoundland join Canada to the ballot.

Dominion
A dominion, often Dominion, refers to one of a group of autonomous polities that were nominally under British sovereignty, constituting the British Empire and British Commonwealth, beginning in the latter part of the 19th century. They have included Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland,...
status, or joining Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation was the process by which the federal Dominion of Canada was formed on July 1, 1867. On that day, three British colonies were formed into four Canadian provinces...
. The referendum was fought by three parties, Smallwood's Confederate Association
Confederate Association
The Confederate Association was a political party formed and led by Joey Smallwood and Gordon Bradley to advocate that the Dominion of Newfoundland join Canadian Confederation. The party was formed on February 21, 1948 prior to the launch of the 1948 Newfoundland referendums on Confederation...
campaigned for the Confederation option while the anti-Confederation campaign was split amongst Peter Cashin's Responsible Government League
Responsible Government League
The Responsible Government League was a political movement in the Dominion of Newfoundland.The Responsible Government League of Newfoundland, led by Peter Cashin, was formed in February 1947 by anti-Confederation delegates to the Newfoundland National Convention on the future of the colony...
and Chesley Crosbie
Chesley Crosbie
Chesley A. Crosbie was a Newfoundland businessman and politician.Crosbie belonged to a prominent St. John's family involved in hotels, fish exporting, insurance, shipping and manufactring...
's Party for Economic Union with the United States, both of which called for a vote for responsible government
Responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability which is the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy...
. No party advocated continuing the Commission of Government.
The result was inconclusive, with 44.6% supporting the restoration of dominion status, 41.1% for confederation with Canada, and 14.3% for continuing the Commission of Government. Between the first and second referendums, rumours had it that Catholic bishops were using their religious influence to alter the outcome of the votes. The Orange Order
Orange Institution
The Orange Institution is a Protestant fraternal organisation based mainly in Northern Ireland and Scotland, though it has lodges throughout the Commonwealth and United States. The Institution was founded in 1796 near the village of Loughgall in County Armagh, Ireland...
was incensed and called on all its members to vote for confederation, as the Catholics voted for responsible government. The Protestants of Newfoundland outnumbered the Catholics at a ratio of 2:1. This was believed to have greatly influenced the outcome of the second referendum. A second referendum on July 22, 1948, which asked Newfoundlanders to choose between confederation and dominion status, was decided by a vote of 52% to 48% for confederation with Canada. Newfoundland joined Canada on March 31, 1949.
Not everyone was satisfied with the results, however. Peter Cashin, an outspoken anti-Confederate, questioned the validity of the votes. He claimed that it was the unholy union between London and Ottawa that brought about confederation.
The Cold War

United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
in 1945, and also of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in 1949, but was largely overshadowed in world affairs by the United States. Canada remained a close ally of the United States throughout the Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
.
When Igor Gouzenko
Igor Gouzenko
Igor Sergeyevich Gouzenko was a cipher clerk for the Soviet Embassy to Canada in Ottawa, Ontario. He defected on September 5, 1945, with 109 documents on Soviet espionage activities in the West...
, a cipher
Cipher
In cryptography, a cipher is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption — a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure. An alternative, less common term is encipherment. In non-technical usage, a “cipher” is the same thing as a “code”; however, the concepts...
clerk for the Soviet Embassy to Canada in Ottawa
Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital of Canada, the second largest city in the Province of Ontario, and the fourth largest city in the country. The city is located on the south bank of the Ottawa River in the eastern portion of Southern Ontario...
, defected in 1945, fears of Soviet espionage
History of Soviet espionage
Coming to power as a clandestine organization, having been schooled in the secret police tactics of the Czarist Okhrana the new Soviet government of the Soviet Union tended to overestimate the degree to which the other European powers of the day, especially the United Kingdom, were plotting its...
led to a red scare
Red Scare
Durrell Blackwell Durrell Blackwell The term Red Scare denotes two distinct periods of strong Anti-Communism in the United States: the First Red Scare, from 1919 to 1920, and the Second Red Scare, from 1947 to 1957. The First Red Scare was about worker revolution and...
and the arrest and conviction of a 18 people, including Communist
Labour-Progressive Party
For the Labour-Progressive Coalition Government in New Zealand see the Fifth Labour Government of New ZealandThe Labor-Progressive Party was the legal political organization of the Communist Party of Canada between 1943 and 1959....
Member of Parliament
Canadian House of Commons
The House of Commons of Canada is a component of the Parliament of Canada, along with the Sovereign and the Senate. The House of Commons is a democratically elected body, consisting of 308 members known as Members of Parliament...
Fred Rose
Fred Rose (politician)
Fred Rose was a Communist politician and trade union organizer in Canada. He was born in Lublin in what is now Poland, part of Russia at the time. He emigrated to Canada as a child in 1916. He became involved with the Young Communist League of Canada, and then joined the Communist Party of Canada...
.

United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
, in the Korean War
Korean War
The Korean War was a conventional war between South Korea, supported by the United Nations, and North Korea, supported by the People's Republic of China , with military material aid from the Soviet Union...
. Minister of External Affairs in St. Laurent's Cabinet
Cabinet of Canada
The Cabinet of Canada is a body of ministers of the Crown that, along with the Canadian monarch, and within the tenets of the Westminster system, forms the government of Canada...
, Lester Bowles Pearson, was involved in the diplomatic side of the conflict, and became more active in diplomacy with the United Nations after the war ended. In 1956 Pearson suggested a solution to the Suez Crisis
Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, also referred to as the Tripartite Aggression, Suez War was an offensive war fought by France, the United Kingdom, and Israel against Egypt beginning on 29 October 1956. Less than a day after Israel invaded Egypt, Britain and France issued a joint ultimatum to Egypt and Israel,...
- the creation of an international peacekeeping force. For his efforts, Pearson won the Nobel Peace Prize
Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes bequeathed by the Swedish industrialist and inventor Alfred Nobel.-Background:According to Nobel's will, the Peace Prize shall be awarded to the person who...
in 1957.
St. Laurent attempted to create a new, highly advanced jet fighter
Fighter aircraft
A fighter aircraft is a military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat with other aircraft, as opposed to a bomber, which is designed primarily to attack ground targets...
, the Avro Arrow. This controversial aircraft was cancelled by St. Laurent's successor, John George Diefenbaker, in 1959, although Diefenbaker did help establish a missile defence system with the United States, NORAD
North American Aerospace Defense Command
North American Aerospace Defense Command is a joint organization of Canada and the United States that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and defense for the two countries. Headquarters NORAD is located at Peterson AFB, Colorado Springs, Colorado...
.
High Arctic relocation
Efforts to assert sovereignty in the High Arctic during the Cold War, i.e. the area's strategic geopolitical position, were part of the reasons that led the federal government to forcibly relocate InuitInuit
The Inuit are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic regions of Canada , Denmark , Russia and the United States . Inuit means “the people” in the Inuktitut language...
from northern Quebec
Nunavik
Nunavik comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, Canada. Covering a land area of 443,684.71 km² north of the 55th parallel, it is the homeland of the Inuit of Quebec...
to barren Cornwallis Island, Nunavut
Cornwallis Island, Nunavut
Cornwallis Island is one of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, part of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut in the Canadian Arctic. It lies to the west of Devon Island and at its greatest length is about . At ) in size, it is the 96th largest island in the world, and...
. The first group of people were relocated in 1953 from Inukjuak, Quebec
Inukjuak, Quebec
Inukjuak , alternatively spelled Inoucdjouac, former name and current postal name Port Harrison, is an Inuit settlement located on Hudson Bay at the mouth of the Innuksuak River in the Nunavik region of northern Quebec, Canada. Its population is 1,294...
(then known as Port Harrison ) and from Pond Inlet, Nunavut
Pond Inlet, Nunavut
Pond Inlet is a small, predominantly Inuit community in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada and is located at the top of Baffin Island. As of the 2006 census the population was 1,315, an increase of 7.8% from the 2001 census making it the largest of the four hamlets above the 72nd parallel...
. They were promised homes and game to hunt, but the relocated people discovered no buildings and very little familiar wildlife. They also had to endure weeks of 24 hour darkness during the winter, and 24 hour sunlight during the summer, something that does not occur in northern Quebec. They were told that they would be returned home after a year if they wished, but this offer was later withdrawn as it would damage Canada's claims to sovereignty in the area and the Inuit were forced to stay. Eventually, the Inuit learned the local beluga whale migration routes and were able to survive in the area, hunting over a range of 18,000 km2 (6,950 mi2) each year.
Further reading
- Adam Chapnick. The Middle Power Project: Canada and the Founding of the United Nations University of British Columbia Press, 2005. ISBN 0-7748-1247-8.
- Bothwell, Robert, Ian Drummond, and John English. Canada since 1945 2d. ed. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1989.

