
Hexateron
Encyclopedia
In five dimensional geometry
, a 5-simplex
is a self-dual regular
5-polytope
. It has 6 vertices
, 15 edge
s, 20 triangle faces
, 15 tetrahedral cells, and 6 pentachoron
facets. It has a dihedral angle
of cos−1(1/5), or approximately 78.46°.
and teron (with ter- being a corruption of tetra-) for having four-dimensional facets.
By Jonathan Bowers, a hexateron is given the acronym hix.
The Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of an origin-centered regular hexateron having edge length 2 are:
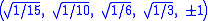
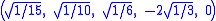
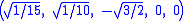
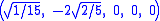
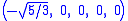
The vertices of the 5-simplex can be more simply positioned on a hyperplane
in 6-space as permutations of (0,0,0,0,0,1) or (0,1,1,1,1,1). These construction can be seen as facets of the hexacross
or rectified 6-cube
respectively.
, all shown here in A5 Coxeter plane orthographic projection
s. (Vertices are colored by projection overlap order, red, orange, yellow, green, cyan, blue, purple having progressively more vertices)
base in a 4-space hyperplane
, and an apex
point above the hyperplane. The five sides of the pyramid are made of pentachoral cells.
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, a 5-simplex
Simplex
In geometry, a simplex is a generalization of the notion of a triangle or tetrahedron to arbitrary dimension. Specifically, an n-simplex is an n-dimensional polytope which is the convex hull of its n + 1 vertices. For example, a 2-simplex is a triangle, a 3-simplex is a tetrahedron,...
is a self-dual regular
Regular polytope
In mathematics, a regular polytope is a polytope whose symmetry is transitive on its flags, thus giving it the highest degree of symmetry. All its elements or j-faces — cells, faces and so on — are also transitive on the symmetries of the polytope, and are regular polytopes of...
5-polytope
5-polytope
In five-dimensional geometry, a 5-polytope is a 5-dimensional polytope, bounded by facets. Each polyhedral cell being shared by exactly two polychoron facets. A proposed name for 5-polytopes is polyteron.-Definition:...
. It has 6 vertices
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex is a special kind of point that describes the corners or intersections of geometric shapes.-Of an angle:...
, 15 edge
Edge (geometry)
In geometry, an edge is a one-dimensional line segment joining two adjacent zero-dimensional vertices in a polygon. Thus applied, an edge is a connector for a one-dimensional line segment and two zero-dimensional objects....
s, 20 triangle faces
Face (geometry)
In geometry, a face of a polyhedron is any of the polygons that make up its boundaries. For example, any of the squares that bound a cube is a face of the cube...
, 15 tetrahedral cells, and 6 pentachoron
Pentachoron
In geometry, the 5-cell is a four-dimensional object bounded by 5 tetrahedral cells. It is also known as the pentachoron, pentatope, or hyperpyramid...
facets. It has a dihedral angle
Dihedral angle
In geometry, a dihedral or torsion angle is the angle between two planes.The dihedral angle of two planes can be seen by looking at the planes "edge on", i.e., along their line of intersection...
of cos−1(1/5), or approximately 78.46°.
Alternate names
It can also be called a hexateron, or hexa-5-tope, as a 6-facetted polytope in 5-dimensions. The name hexateron is derived from hexa- for having six facetsFacet (mathematics)
A facet of a simplicial complex is a maximal simplex.In the general theory of polyhedra and polytopes, two conflicting meanings are currently jostling for acceptability:...
and teron (with ter- being a corruption of tetra-) for having four-dimensional facets.
By Jonathan Bowers, a hexateron is given the acronym hix.
Regular hexateron cartesian coordinates
The hexateron can be constructed from a 5-cell by adding a 6th vertex such that it is equidistant from all the other vertices of the 5-cell.The Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of an origin-centered regular hexateron having edge length 2 are:
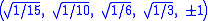
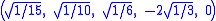
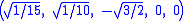
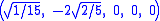
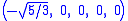
The vertices of the 5-simplex can be more simply positioned on a hyperplane
Hyperplane
A hyperplane is a concept in geometry. It is a generalization of the plane into a different number of dimensions.A hyperplane of an n-dimensional space is a flat subset with dimension n − 1...
in 6-space as permutations of (0,0,0,0,0,1) or (0,1,1,1,1,1). These construction can be seen as facets of the hexacross
Hexacross
In geometry, a 6-orthoplex, or 6-cross polytope, is a regular 6-polytope with 12 vertices, 60 edges, 160 triangle faces, 240 tetrahedron cells, 192 5-cell 4-faces, and 64 5-faces....
or rectified 6-cube
Rectified 6-cube
In six-dimensional geometry, a rectified 6-cube is a convex uniform 6-polytope, being a rectification of the regular 6-cube.There are unique 6 degrees of rectifications, the zeroth being the 6-cube, and the 6th and last being the 6-orthoplex. Vertices of the rectified 6-cube are located at the...
respectively.
Projected images
 Stereographic projection Stereographic projection The stereographic projection, in geometry, is a particular mapping that projects a sphere onto a plane. The projection is defined on the entire sphere, except at one point — the projection point. Where it is defined, the mapping is smooth and bijective. It is conformal, meaning that it... 4D to 3D of Schlegel diagram 5D to 4D of hexateron. |
Related uniform 5-polytopes
The regular 5-simplex is one of 19 uniform polytera based on the [3,3,3,3] Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
, all shown here in A5 Coxeter plane orthographic projection
Orthographic projection
Orthographic projection is a means of representing a three-dimensional object in two dimensions. It is a form of parallel projection, where all the projection lines are orthogonal to the projection plane, resulting in every plane of the scene appearing in affine transformation on the viewing surface...
s. (Vertices are colored by projection overlap order, red, orange, yellow, green, cyan, blue, purple having progressively more vertices)
Other forms
The hexateron can also be considered a pentachoral pyramid, constructed as a pentachoronPentachoron
In geometry, the 5-cell is a four-dimensional object bounded by 5 tetrahedral cells. It is also known as the pentachoron, pentatope, or hyperpyramid...
base in a 4-space hyperplane
Hyperplane
A hyperplane is a concept in geometry. It is a generalization of the plane into a different number of dimensions.A hyperplane of an n-dimensional space is a flat subset with dimension n − 1...
, and an apex
Apex (geometry)
In geometry, an apex is the vertex which is in some sense the highest of the figure to which it belongs.*In an isosceles triangle, the apex is the vertex where the two sides of equal length meet, opposite the unequal third side....
point above the hyperplane. The five sides of the pyramid are made of pentachoral cells.
External links
- Polytopes of Various Dimensions, Jonathan Bowers
- Multi-dimensional Glossary

