
Casqui
Encyclopedia

Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
tribe discovered in 1541 by the Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (explorer)
Hernando de Soto was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who, while leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day United States, was the first European documented to have crossed the Mississippi River....
expedition. This tribe inhabited fortified villages
Palisade
A palisade is a steel or wooden fence or wall of variable height, usually used as a defensive structure.- Typical construction :Typical construction consisted of small or mid sized tree trunks aligned vertically, with no spacing in between. The trunks were sharpened or pointed at the top, and were...
in eastern Arkansas
Arkansas
Arkansas is a state located in the southern region of the United States. Its name is an Algonquian name of the Quapaw Indians. Arkansas shares borders with six states , and its eastern border is largely defined by the Mississippi River...
.
The tribe takes its name from the chieftain
Paramount chief
A paramount chief is the highest-level traditional chief or political leader in a regional or local polity or country typically administered politically with a chief-based system. This definition is used occasionally in anthropological and archaeological theory to refer to the rulers of multiple...
Casqui who ruled the tribe from its primary village thought to be located in present day Cross County, Arkansas near the town of Parkin
Parkin, Arkansas
Parkin is a city in Cross County, Arkansas, in the United States, along the St. Francis River. The population was 1,602 at the 2000 census.-Geography:Parkin is located at ....
. The suspected site is the focal point of the Parkin Archeological State Park
Parkin Archeological State Park
Parkin Archeological State Park, also known as Parkin Indian Mound, is an archeological site and state park in Parkin, Cross County, Arkansas. Around 1350–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed at the site, at the confluence of the St. Francis and Tyronza Rivers. Artifacts from this...
and it has been determined that the site was continuously occupied for at least 500 years.
Information about Chief Casqui and his people comes from journals made during the expedition of Hernando de Soto in 1541.
de Soto Expedition
When de Soto's expedition arrived in the area the Casqui walked over a mile from their village to greet the travelers and invite them to stay in the town. The travelers declined the offer and made camp outside of the village. The journals report that de Soto gave a speech to the Casqui about religion and baptized several of the villagers as Christians. The journals report that the villagers helped them erect a large wooden cross on the central moundPlatform mound
A platform mound is any earthwork or mound intended to support a structure or activity.-Eastern North America:The indigenous peoples of North America built substructure mounds for well over a thousand years starting in the Archaic period and continuing through the Woodland period...
.
When de Soto determined to press on and visit the nearby tribe called the Pacaha
Pacaha
Pacaha was a Native American tribe encountered in 1541 by the Hernando de Soto expedition. This tribe inhabited fortified villages in what is today the northeastern portion of the U.S. state of Arkansas...
many of the Casqui people followed him. The Casqui and the Pacaha had been at war for some time and the Casqui had raided the Pacaha on previous occasions. When de Soto and the Casqui approached, many of the Pacaha became afraid and attempted to flee to an island in the river
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
and drowned. The Casqui who had followed de Soto proceeded to sack the village, desecrate holy sites, and steal everything they could.
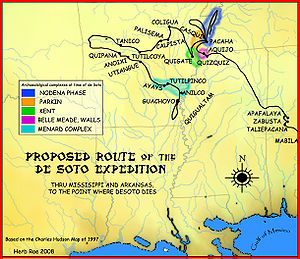
The Casqui received advance warning of the planned attack and returned the looted items to the Pacaha and issued an apology in order to stave off retribution. De Soto arranged a dinner for the two leaders and arranged a peace treaty between the tribes.
The Hernando de Soto expedition records are the only historical records of Chief Casqui and his tribe. Their later history is uncertain.
In recent years a Spanish trade bead
Slave beads
Trade beads were otherwise decorative glass beads used between the 16th and 20th century as a currency to exchange for goods, services and slaves . Made to ease the passage of European explorers and then traders mainly across the African continents, the beads were made throughout Europe although...
which matches descriptions of the seven-layer glass beads carried by the expedition has been found at the Parkin site as well as two Spanish falconer
Falconry
Falconry is "the taking of wild quarry in its natural state and habitat by means of a trained raptor". There are two traditional terms used to describe a person involved in falconry: a falconer flies a falcon; an austringer flies a hawk or an eagle...
's bells, and Spanish musket balls.
Controversy
The accepted path of de Soto's travels was established by the research of the de Soto Commission in 1939 led by Dr. John R. SwantonJohn R. Swanton
John Reed Swanton was an American anthropologist and linguist who worked with Native American peoples throughout the United States. Swanton achieved recognition in the fields of ethnology and ethnohistory...
and has been generally accepted by the United States government and most archaeologists as the actual route. Some detractors claim that de Soto instead travelled north into the states of Indiana
Indiana
Indiana is a US state, admitted to the United States as the 19th on December 11, 1816. It is located in the Midwestern United States and Great Lakes Region. With 6,483,802 residents, the state is ranked 15th in population and 16th in population density. Indiana is ranked 38th in land area and is...
and Illinois
Illinois
Illinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,...
and found the Ohio River
Ohio River
The Ohio River is the largest tributary, by volume, of the Mississippi River. At the confluence, the Ohio is even bigger than the Mississippi and, thus, is hydrologically the main stream of the whole river system, including the Allegheny River further upstream...
instead of the Mississippi River
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
.
Due to this controversy some claim that the town of Pacaha was actually located on the present day site of Terre Haute, Indiana
Terre Haute, Indiana
Terre Haute is a city and the county seat of Vigo County, Indiana, United States, near the state's western border with Illinois. As of the 2010 census, the city had a total population of 60,785 and its metropolitan area had a population of 170,943. The city is the county seat of Vigo County and...
with the Casqui tribe living near present-day Vincennes, Indiana
Vincennes, Indiana
Vincennes is a city in and the county seat of Knox County, Indiana, United States. It is located on the Wabash River in the southwestern part of the state. The population was 18,701 at the 2000 census...
. This route is not the officially accepted route but archaeological study and analysis continues.
Other sites and personages encountered by the De Soto Expedition
- List of sites and peoples visited by the Hernando de Soto Expedition
- PacahaPacahaPacaha was a Native American tribe encountered in 1541 by the Hernando de Soto expedition. This tribe inhabited fortified villages in what is today the northeastern portion of the U.S. state of Arkansas...
- Mississippian cultureMississippian cultureThe Mississippian culture was a mound-building Native American culture that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1500 CE, varying regionally....
- Southeastern Ceremonial ComplexSoutheastern Ceremonial ComplexThe Southeastern Ceremonial Complex is the name given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography, ceremonies, and mythology of the Mississippian culture that coincided with their adoption of maize agriculture and chiefdom-level complex social organization from...

