2-Nitrobenzaldehyde
Encyclopedia
2-Nitrobenzaldehyde is an organic aromatic compound containing a nitro
group
ortho to formyl. 2-Nitrobenzaldehyde once was produced as an intermediate in the synthesis of the popular dye Indigo
.
followed by the conversions of the resulting 2-nitrostyrene and 2-nitrocinnamic acids. Cinnamaldehyde
can also be nitrated
, e.g. in a solution of acetic anhydride
in acetic acid
, in high-yield to 2-nitrocinnamaldehyde
. This compound is then oxidized to 2-nitrocinnamic acid, which is decarboxylated to the 2-nitrostyrene. The vinyl
group can be oxidized in a number of different ways to yield 2-nitrobenzaldehyde.
In one synthetic process, toluene
is mono-nitrated at cold temperatures to 2-nitrotoluene
, with about 58% being converted to the ortho- isomer, the remaining forming meta- and para- isomers. The 2-nitrotoluene can then be oxidized to yield 2-nitrobenzaldehyde.
Alternatively, 2-nitrotoluene as formed above can be halogenated
to a 2-nitrobenzyl halide followed by oxidation with DMSO
and sodium bicarbonate
to yield 2-nitrobenzaldehyde, which is subsequently purified with the creation of a bisulfite
adduct.
The nitration of benzaldehyde
produces mostly 3-nitrobenzaldehyde
, with yields being about 19% for the ortho-, 72% for the meta- and 9% for the para isomer. For this reason, the nitration of benzaldehyde to yield 2-nitrobenzaldehyde is not cost-effective.
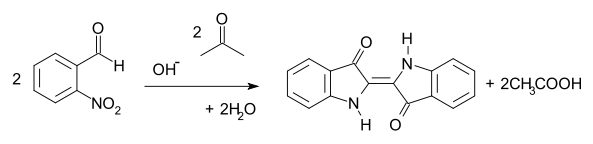
, a water-insoluble dye commonly used to dye jeans and other fabrics. In the Baeyer-Drewson indigo synthesis
, 2-nitrobenzaldehyde condenses with acetone
in basic aqueous solution to yield indigo in a one-pot synthesis. The method was abandoned in the early part of the 20th century, being replaced by routes from aniline
.
Given its two relatively reactive groups, 2-nitrobenzaldehyde is a potential starting material for other compounds. Substituted 2-nitrobenzaldehydes can also be used to yield other important compounds based on indigo, such as Indigo carmine
.
2-Nitrobenzaldehyde has been shown to be a useful photoremovable protecting group for various funcionalities.
Nitro
-Chemistry:*Nitroglycerin, an explosive chemical compound*Nitromethane, the simplest organic nitro compound; also used to fuel high-performance internal-combustion engines*Nitrous oxide, "laughing gas", used in some dental procedures as an anaesthetic...
group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
ortho to formyl. 2-Nitrobenzaldehyde once was produced as an intermediate in the synthesis of the popular dye Indigo
Indigo dye
Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive blue color . Historically, indigo was a natural dye extracted from plants, and this process was important economically because blue dyes were once rare. Nearly all indigo dye produced today — several thousand tons each year — is synthetic...
.
Synthesis
The main routes to nitrobenzaldehyde begin with the nitration of styrene and cinnamic acidCinnamic acid
Cinnamic acid is a white crystalline organic acid, which is slightly soluble in water.It is obtained from oil of cinnamon, or from balsams such as storax. It is also found in shea butter and is the best indication of its environmental history and post-extraction conditions...
followed by the conversions of the resulting 2-nitrostyrene and 2-nitrocinnamic acids. Cinnamaldehyde
Cinnamaldehyde
Cinnamaldehyde is the organic compound that gives cinnamon its flavor and odor. This pale yellow viscous liquid occurs naturally in the bark of cinnamon trees and other species of the genus Cinnamomum...
can also be nitrated
Nitration
Nitration is a general chemical process for the introduction of a nitro group into a chemical compound. The dominant application of nitration is for the production of nitrobenzene, the precursor to methylene diphenyl diisocyanate...
, e.g. in a solution of acetic anhydride
Acetic anhydride
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula 2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolatable acid anhydride and is a widely used reagent in organic synthesis...
in acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
, in high-yield to 2-nitrocinnamaldehyde
2-Nitrocinnamaldehyde
2-Nitrocinnamaldehyde, ortho-nitrocinnamaldehyde or o-nitrocinnamaldehyde is an organic aromatic compound containing a nitro group ortho- to the 1-position of cinnamaldehyde.-Synthesis:...
. This compound is then oxidized to 2-nitrocinnamic acid, which is decarboxylated to the 2-nitrostyrene. The vinyl
Gramophone record
A gramophone record, commonly known as a phonograph record , vinyl record , or colloquially, a record, is an analog sound storage medium consisting of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove...
group can be oxidized in a number of different ways to yield 2-nitrobenzaldehyde.
In one synthetic process, toluene
Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
is mono-nitrated at cold temperatures to 2-nitrotoluene
Mononitrotoluene
Mononitrotoluene, or methylnitrobenzene or nitrotoluene , is a group of 3 organic compounds, a nitro derivative of toluene...
, with about 58% being converted to the ortho- isomer, the remaining forming meta- and para- isomers. The 2-nitrotoluene can then be oxidized to yield 2-nitrobenzaldehyde.
Alternatively, 2-nitrotoluene as formed above can be halogenated
Halogenation
Halogenation is a chemical reaction that incorporates a halogen atom into a molecule in substitution of hydrogen atom. Halogenation takes place in the gas phase. There are four types of halogenation: fluorination, chlorination, bromination, and iodination...
to a 2-nitrobenzyl halide followed by oxidation with DMSO
Dimethyl sulfoxide
Dimethyl sulfoxide is an organosulfur compound with the formula 2SO. This colorless liquid is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is miscible in a wide range of organic solvents as well as water...
and sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate is the chemical compound with the formula Na HCO3. Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda . The natural mineral form is...
to yield 2-nitrobenzaldehyde, which is subsequently purified with the creation of a bisulfite
Bisulfite
Bisulfite ion is the ion HSO3−. Salts containing the HSO3− ion are termed bisulfites also known as sulfite lyes...
adduct.
The nitration of benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is the simplest aromatic aldehyde and one of the most industrially useful. This colorless liquid has a characteristic pleasant almond-like odor...
produces mostly 3-nitrobenzaldehyde
3-Nitrobenzaldehyde
3-Nitrobenzaldehyde, meta-nitrobenzaldehyde or m-nitrobenzaldehyde is an organic aromatic compound containing a nitro group meta-substituted to an aldehyde...
, with yields being about 19% for the ortho-, 72% for the meta- and 9% for the para isomer. For this reason, the nitration of benzaldehyde to yield 2-nitrobenzaldehyde is not cost-effective.
Uses
2-Nitrobenzaldehyde is an intermediate in an early route to IndigoIndigo dye
Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive blue color . Historically, indigo was a natural dye extracted from plants, and this process was important economically because blue dyes were once rare. Nearly all indigo dye produced today — several thousand tons each year — is synthetic...
, a water-insoluble dye commonly used to dye jeans and other fabrics. In the Baeyer-Drewson indigo synthesis
Baeyer-Drewson indigo synthesis
The Baeyer–Drewson indigo synthesis is an organic reaction in which indigo is prepared from 2-nitrobenzaldehyde and acetone The reaction is classified as a Aldol condensation...
, 2-nitrobenzaldehyde condenses with acetone
Acetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
in basic aqueous solution to yield indigo in a one-pot synthesis. The method was abandoned in the early part of the 20th century, being replaced by routes from aniline
Aniline
Aniline, phenylamine or aminobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the prototypical aromatic amine. Being a precursor to many industrial chemicals, its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane...
.
Given its two relatively reactive groups, 2-nitrobenzaldehyde is a potential starting material for other compounds. Substituted 2-nitrobenzaldehydes can also be used to yield other important compounds based on indigo, such as Indigo carmine
Indigo carmine
Indigo carmine, or 5,5'-indigodisulfonic acid sodium salt, also known as indigotine or FD&C Blue #2 is a pH indicator with the chemical formula C16H8N2Na2O8S2. It is approved for use as a food colorant in the USA and the EU and has the E number E132.-Uses:The primary use of Indigo carmine is as a...
.
2-Nitrobenzaldehyde has been shown to be a useful photoremovable protecting group for various funcionalities.