.gif)
Workbench (AmigaOS)
Encyclopedia
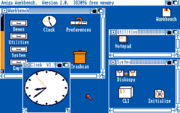
Overview
Commodore named their Amiga computer's first operating system Workbench 1.0 and continued with the Workbench name until version 3.1, when it was changed to AmigaOS, prompted by Apple renaming their propriety OS from "System" to "MacOS". Subsequently the AmigaAmiga
The Amiga is a family of personal computers that was sold by Commodore in the 1980s and 1990s. The first model was launched in 1985 as a high-end home computer and became popular for its graphical, audio and multi-tasking abilities...
computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
used the name Workbench to refer only to the native graphical interface
Gui
Gui or guee is a generic term to refer to grilled dishes in Korean cuisine. These most commonly have meat or fish as their primary ingredient, but may in some cases also comprise grilled vegetables or other vegetarian ingredients. The term derives from the verb, "gupda" in Korean, which literally...
file manager and application launcher of the Amiga's operating system typically presented to users upon booting the Amiga
Amiga
The Amiga is a family of personal computers that was sold by Commodore in the 1980s and 1990s. The first model was launched in 1985 as a high-end home computer and became popular for its graphical, audio and multi-tasking abilities...
. In that regard the Workbench GUI component was not required to boot the Amiga
Amiga
The Amiga is a family of personal computers that was sold by Commodore in the 1980s and 1990s. The first model was launched in 1985 as a high-end home computer and became popular for its graphical, audio and multi-tasking abilities...
or run other applications, but was a standalone application listed in the startup-sequence script.
The Amiga Workbench used the metaphor
Metaphor
A metaphor is a literary figure of speech that uses an image, story or tangible thing to represent a less tangible thing or some intangible quality or idea; e.g., "Her eyes were glistening jewels." Metaphor may also be used for any rhetorical figures of speech that achieve their effects via...
of a workbench
Workbench
A workbench is sturdy table at which manual work is done. They range from simple flat surfaces to very complex designs that may be considered tools in themselves. Workbenches vary in size from tiny jewelers benches to the huge benches used by staircase makers...
rather than the now standard desktop
Desktop metaphor
The desktop metaphor is an interface metaphor which is a set of unifying concepts used by graphical user interfaces to help users more easily interact with the computer. The desktop metaphor treats the monitor of a computer as if it is the user's desktop, upon which objects such as documents and...
for exposing file management and application launching functionality. The Workbench application appeared similar to other consumer Operating Systems of the era by utilizing a trash can, menu bar, and icons to represent files, folder and volumes (filesystem devices). The underlying AmigaOS was much more advanced allowing the Workbench to launch multiple applications that could execute at the same time and communicate with each other. The Amiga used a two button mouse for left click and right menu.
The Amiga did not use filename extensions to normally distinguish file types. Instead the Workbench used a separate file of the same name but followed by .info. That was the only file extension Workbench recognized. This file supplied information such as the icon graphic to display, the application to launch with, etc, similar in many ways to a Windows .pif file. Most files were human recognized by name (32 cased characters) or associated icon, or by applications using embedded metadata. The common format containing open metadata was the Interchange File Format
Interchange File Format
Interchange File Format , is a generic container file format originally introduced by the Electronic Arts company in 1985 in order to ease transfer of data between software produced by different companies....
which allowed applications to access the known parts of even a completely foreign IFF format file.
The Workbench utilized the underlying API to provide the GUI interface. The actual Workbench in its executable format (loadWB AmigaDOS command + Workbench.library) was quite small only taking a fraction of an Amiga floppy disc or other medium. Workbench.library in its first versions even occupied no space on system floppy discs, because it was part of the system ROM. Starting from 2.0 it became a shared library in Libs: and could be replaced by third-party GUIs.
The operating system library API
Application programming interface
An application programming interface is a source code based specification intended to be used as an interface by software components to communicate with each other...
's required by Workbench were stored in ROM
Read-only memory
Read-only memory is a class of storage medium used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be modified, or can be modified only slowly or with difficulty, so it is mainly used to distribute firmware .In its strictest sense, ROM refers only...
, or (on the earliest Amigas) loaded into WCS/WOM (Lockable/Write Once Memory) by the Kickstart
Kickstart (Amiga)
Kickstart is a commonly used term for the bootstrap firmware of the Amiga computers developed by Commodore.Most Amiga models were shipped with the Kickstart firmware stored on ROM chips...
system. Applications launched from either the CLI or Workbench executed equivalently, with both having full GUI functionality. Workbench launched applications were meant to report their successful launch back the Workbench, but this was not a requirement and few actually did. The CLI was entirely graphically based; the Amiga did not support character mapped displays.
Underlying Workbench is the Intuition.library
Intuition (Amiga)
Intuition is the windowing system and user interface engine of AmigaOS. It was developed almost entirely by RJ Mical. Intuition should not be confused with Workbench, the AmigaOS spatial file manager, which relies on Intuition for handling windows and input events.Users may remember the initial...
windowing system. This library controlled the logistics of clipping, rendering and preserving overlapping screens, windows and gadgets (graphical elements; equivalent to widgets.) The graphics.library provided software as well as hardware rendering. The exec.library handled low-level functions such as input from the keyboard and mouse, passing messages to programs, allocating memory and task switching.
Paradigm
The Amiga workbench follows the interface paradigm of a standard workbench of manual labour. The desktop itself is called Work-bench, the programs are called tools, program attributesAttribute (computing)
In computing, an attribute is a specification that defines a property of an object, element, or file. It may also refer to or set the specific value for a given instance of such....
(options) are called tooltypes, directories are called drawers (and there is a closet drawer icon representing directories on the screen of Workbench), data files are considered projects, etc. This may be considered somewhat unusual for a modern user, but in the early age of computer desktop GUIs, it was clear enough to users who approached a computer for the first time, and were generally unaccustomed to computer usage and computing science in general.
The only idiom of Amiga Workbench that is also found in other operating systems with more or less the same meaning is Utilities, which means the small programs that exist to enhance the computer's usability—for example the Calculator utility in Amiga, which is stored in the Utility drawer, similar to the Windows calculator.
Characteristics and main features
In comparison to the competing Mac OSMac OS
Mac OS is a series of graphical user interface-based operating systems developed by Apple Inc. for their Macintosh line of computer systems. The Macintosh user experience is credited with popularizing the graphical user interface...
and Atari
Atari
Atari is a corporate and brand name owned by several entities since its inception in 1972. It is currently owned by Atari Interactive, a wholly owned subsidiary of the French publisher Atari, SA . The original Atari, Inc. was founded in 1972 by Nolan Bushnell and Ted Dabney. It was a pioneer in...
, the Amiga Workbench featured, as the default, a 4 color blue desktop screen with color icons at NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
American standard or on European PAL
PAL
PAL, short for Phase Alternating Line, is an analogue television colour encoding system used in broadcast television systems in many countries. Other common analogue television systems are NTSC and SECAM. This page primarily discusses the PAL colour encoding system...
television sets. This is in contrast to the black and white interface presented by the Mac, and the Amiga user was also free to create and modify system and program icons, while, in the same time Atari TOS
Atari TOS
TOS is the operating system of the Atari ST range of computers. This range includes the 520 and 1040ST, their STF/M/FM and STE variants and the Mega ST/STE. Later, 32-bit machines were developed using a new version of TOS, called MultiTOS, which allowed multitasking...
featured only default system icons whose appearance could not be modified.
It was a deeply customizable interface. Users could customize all four colours and choose from two different resolutions ( or on NTSC, or or on PAL systems). In later revisions, the TV or TV-monitor overscan could be adjusted. User could change the aspect of program icons replacing it with newer ones with different color combination. Users could also take a "snapshot" of icons and windows so the icons will remain on the desktop at coordinates chosen by user and windows will open at the desired size.
This freedom of choice and the multitude of different desktop colors and aspects chosen by any single user was sometimes seen as chaotic interface by people new to the Amiga and its interface. It could present icons of unusual size, and quite different from the original system ones, depending only on personal choice and the taste of the user. There were also no obliged user interface design guidelines
User interface design
User interface design or user interface engineering is the design of computers, appliances, machines, mobile communication devices, software applications, and websites with the focus on the user's experience and interaction...
regarding fixed menu options for software in general (i.e. the user must learn the various orderings of basic commands like Load, Save, Open, Close, Quit, etc.). This fact was sometimes argued as a diminishing feature of Amiga by its detractors. Still today some historical GUI sites like guidebook gallery presented Amiga Workbench as:
"Unique (if slightly chaotic) GUI for Amiga machines".
Workbench 1.x
The 1.x series of Workbench defaults to a distinctive blue and orange color scheme, designed to give high contrast on even the worst of television screens (the colors can be changed by the user). Versions 1.1 consists mostly of bug fixes and, like version 1.0, was distributed only for the Amiga 1000Amiga 1000
The A1000, or Commodore Amiga 1000, was Commodore's initial Amiga personal computer, introduced on July 23, 1985 at the Lincoln Center in New York City....
.
- Color Desktop 4 colors out a palette of 4096
- Maximum resolution with interlace on PAL or on NTSC (640x256 and 640x200 without interlace)
- Gauge meter to show free space of removable devices
- Two states icons with images to represent quiet and activated state creating a pseudo-animation effect when clicked on
- Two button mouse with double functions. On icons: left mouse click activates icons, right mousebutton activates .info metadata. On desktop: right mousebutton activates Menus
- Busy pointer (sleeping buzzing mouse pointer with a comics ballon saying: "Zzz..." was active during loading/writing disk activities)
Workbench 2.x
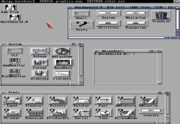
Look and feel
In software design, look and feel is a term used in respect of a graphical user interface and comprises aspects of its design, including elements such as colors, shapes, layout, and typefaces , as well as the behavior of dynamic elements such as buttons, boxes, and menus...
design standard - application developers had to write their own widgets (both buttons and menus) if they want to enhance standard basic widgets, with Intuition providing minimal support. With Workbench 2.0 gadtools.library was created, which provided standard widget sets, the Amiga User Interface Style Guide, which explained how applications should be laid out for consistency. Intuition was improved with BOOPSI
BOOPSI
BOOPSI is an object-oriented programming system for AmigaOS...
(Basic Object Oriented Programming system for Intuition) which enhanced the system with an object oriented interface with a system of classes in which every class individuate a single widget or describes an interface event. It can be used to program Object Oriented interfaces into Amiga at any level.
Workbench 2.0 also added support for public screens. Instead of the Workbench screen being the only shareable screen, applications could create their own named screens to share with other applications.
Workbench 2.0 introduced AmigaGuide
Amigaguide
AmigaGuide is a hypertext document file format designed for the Amiga, files are stored in ASCII so it is possible to read and edit a file without the need for special software.Since Workbench 2.1 an Amiga Guide system for O.S...
, a simple text-only hypertext
Hypertext
Hypertext is text displayed on a computer or other electronic device with references to other text that the reader can immediately access, usually by a mouse click or keypress sequence. Apart from running text, hypertext may contain tables, images and other presentational devices. Hypertext is the...
markup scheme and browser, for providing online help inside applications. It also introduced Installer, a standard software installation program, driven by a LISP
Lisp
A lisp is a speech impediment, historically also known as sigmatism. Stereotypically, people with a lisp are unable to pronounce sibilants , and replace them with interdentals , though there are actually several kinds of lisp...
-like scripting language.
Finally, Workbench 2.0 rectified the problem of applications hooking
Hooking
In computer programming, the term hooking covers a range of techniques used to alter or augment the behavior of an operating system, of applications, or of other software components by intercepting function calls or messages or events passed between software components...
directly into the input-events stream to capture keyboard and mouse movements, sometimes locking up the whole system. Workbench 2.0 provided Commodities, a standard interface for modifying or scanning input events. This included a standard method for specifying global "hotkey" key-sequences, and a Commodities Exchange registry for the user to see what commodities were running.
Workbench 3.0, 3.1
Version 3.0 was originally shipped with the Amiga 1200 and Amiga 4000 computers. Version 3.0 added datatypes support and Workbench could load any background image in any format if required datatype was installed. This feature was also used in Multiview. Its capabilities were directly related to the datatypes installed in Devs:Datatypes.Workbench 3.5, 3.9

Haage & Partner
Haage & Partner is a German company established in 1995. They distribute software products where they usually are the exclusive distributor. Products are aimed at Microsoft Windows and Mac OS. The primary destination countries are Germany, Austria, and Switzerland.Other areas include translations...
in 1999.
Workbench changed the complete look and feel
Look and feel
In software design, look and feel is a term used in respect of a graphical user interface and comprises aspects of its design, including elements such as colors, shapes, layout, and typefaces , as well as the behavior of dynamic elements such as buttons, boxes, and menus...
of its interface. A new blue desktop
Desktop environment
In graphical computing, a desktop environment commonly refers to a style of graphical user interface derived from the desktop metaphor that is seen on most modern personal computers. These GUIs help the user in easily accessing, configuring, and modifying many important and frequently accessed...
, resembling the first Amiga Workbench 1.0 was now available to users, but with many improvements over to the first AmigaOS desktop release, like presenting 2D icons that look isometric
Isometric projection
Isometric projection is a method for visually representing three-dimensional objects in two dimensions in technical and engineering drawings...
3D, with a high range of color schemes ready to use. It replaced the all-metal gray 4/8 colors interface that was used on AmigaOS from release 2.0 up to 3.1 with its embossed 3D icons.
Support for NewIcons
NewIcons
NewIcons is a third-party extension to the icon handling system for AmigaOS 2 and newer. NewIcons was first invented and developed by the Italian programmer Nicola Salmoria. Subsequent development was done by Eric Sauvageau.-History:...
and various other third party GUI enhancements to improve elder Amiga interfaces were made obsolete by integrating those patches into system.
The 3.9 version of Workbench was again developed by Haage&Partner and released in 2000. The main features in this Workbench version was the introduction of the AmiDOCK, a program start bar. Other new features were new preference tools and improved desktop watch clock.
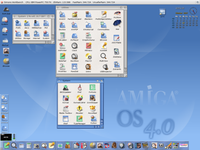
Workbench 4.0, 4.1
This new Workbench, called Workbench 4.0 has been rewritten to became fully PowerPCPowerPC
PowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
compatible. It was part of AmigaOS 4.0, and released in 2006. Some parts of AmigaOS and Workbench 3.5/3.9 could not be included into this new OS release as they belonged to Haage & Partner
Haage & Partner
Haage & Partner is a German company established in 1995. They distribute software products where they usually are the exclusive distributor. Products are aimed at Microsoft Windows and Mac OS. The primary destination countries are Germany, Austria, and Switzerland.Other areas include translations...
, and Amiga inc. did not acquire any license of it.
Since the fourth Developer Pre-Release Update a new technique is adopted and the screens are draggable in any direction. Drag and drop of Workbench icons between different screens is possible too.
Also in Workbench 4.0 were PowerPC
PowerPC
PowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
native version of Amidock, TrueType
TrueType
TrueType is an outline font standard originally developed by Apple Computer in the late 1980s as a competitor to Adobe's Type 1 fonts used in PostScript...
/OpenType
OpenType
OpenType is a format for scalable computer fonts. It was built on its predecessor TrueType, retaining TrueType's basic structure and adding many intricate data structures for prescribing typographic behavior...
fonts and movie player named "Action" with DivX
DivX
DivX is a brand name of products created by DivX, Inc. , including the DivX Codec which has become popular due to its ability to compress lengthy video segments into small sizes while maintaining relatively high visual quality.There are two DivX codecs; the regular MPEG-4 Part 2 DivX codec and the...
and MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
support.
In AmigaOS 4.1, a new Startup preferences feature was added which replaced WBStartup drawer. Additional enhancements were a new icon set to complement higher screen resolutions, new window themes including drop shadows, AmiDock with true transparency, scalable icons and Workbench with auto-update feature.
Workbench icons
The iconsIcon (computing)
A computer icon is a pictogram displayed on a computer screen and used to navigate a computer system or mobile device. The icon itself is a small picture or symbol serving as a quick, intuitive representation of a software tool, function or a data file accessible on the system. It functions as an...
that Workbench uses to represent the files in a volume or a drawer are stored in special
.info files, with the name of the .info file matching the name of the file it represents. For example, the icon for NotePad, a text editorText editor
A text editor is a type of program used for editing plain text files.Text editors are often provided with operating systems or software development packages, and can be used to change configuration files and programming language source code....
, is found in the file
NotePad.info.The
.info file includes the graphical representation of the icon and its position in the volume or drawer window. The icon also specifies the type of the file, as used by Workbench. Workbench recognises five different file types:
- Tool: An executable program.
- Project: A data file of an executable program. The program which created the file is named in the icon file, double-clicking on the icon loads the program that created it.
- Drawer: A directory containing files, and other drawers.
- Volume: A physical disk or a RAM diskRAM diskA RAM disk or RAM drive is a block of RAM that a computer's software is treating as if the memory were a disk drive...
. - Garbage: The Trashcan - a deleted file backup, which works in a similar way to the 'Recycle binRecycle bin (computing)In computing, the trash is temporary storage for files that have been deleted in a file manager by the user, but not yet permanently erased from the physical media...
' in Microsoft WindowsMicrosoft WindowsMicrosoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
.
An additional three file types are available and are intended for future expansion:
- Device: designed for displaying information about attached devices
- Kick: The icon of a bootable disk
- App Icon: An icon which will be used as (part of) the GUI for an application
Of these three file types, only "App Icons" currently are used by any part of Workbench/AmigaOS.
Tool files can include "tool types" in the
.info file. These are used as configuration options for the program. Each tool type is a single line of text, which can optionally include parameters, written after an = sign. Tool types can be commented out by writing them in parenthesesBracket
Brackets are tall punctuation marks used in matched pairs within text, to set apart or interject other text. In the United States, "bracket" usually refers specifically to the "square" or "box" type.-List of types:...
. For example, the tooltype "
CX_POPKEY=ctrl alt f1" says that the application (a Commodity) will pop up the user interface in response to the key sequence Ctrl-Alt-F1.The colours used in the icon are normally only stored as indices to the Amiga Workbench screen's current palette. Because of this, the icons' colour scheme is inherently tied to the chosen hues in the screen's palette, and choosing non-standard colours can give the icons an ugly appearance. This problem was party solved by a third-party system called NewIcons
NewIcons
NewIcons is a third-party extension to the icon handling system for AmigaOS 2 and newer. NewIcons was first invented and developed by the Italian programmer Nicola Salmoria. Subsequent development was done by Eric Sauvageau.-History:...
, which adds additional features to the standard
.info files. Unlike normal Workbench icons, NewIcons include actual RGB colour information, and the system tries its best to match the icons' colour hues to those in the screen palette.Since AmigaOS 3.5, Workbench supports icons with up to 256 colors. This release of AmigaOS features the GlowIcons icon set by Matt Chaput. With AmigaOS 3.5, a screen-palette-independent system is used. The 4.0 icons, designed by Martin Merz, can use a palette of 24 bit each.
Both AROS
Aros
Aros may refer to:*Aros , a river in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium*AROS Research Operating System, a free software implementation of AmigaOS* Aros, the original Viking name of Aarhus, the second largest city in Denmark...
and MorphOS
MorphOS
MorphOS is an Amiga-compatible computer operating system. It is a mixed proprietary and open source OS produced for the Pegasos PowerPC processor based computer, PowerUP accelerator equipped Amiga computers, and a series of Freescale development boards that use the Genesi firmware, including the...
support PNG icons natively. PNG allows using full 24-bit palette with alpha blending. On Amiga Workbench PNG icons are supported through plugins.
External links
- The Workbench Nostalgia Page
- Amiga University - Amiga Workbench Replacements
- All versions of Workbench explained on AmigaHistory site
- In the Beginning Was CAOS, by Andy Finkel (updated version of 1988 Amiga Transactor article)
- Name of the Amiga Operating System explained on Amiga Forever site

