
Timeline of the 2005 Pacific hurricane season
Encyclopedia
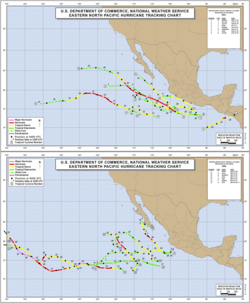
2005 Pacific hurricane season
The 2005 Pacific hurricane season officially began on May 15, 2005 in the eastern Pacific and on June 1, 2005 in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 2005. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean...
was the least active season since the 2001 season
2001 Pacific hurricane season
The 2001 Pacific hurricane season was an event in tropical cyclone meteorology. The most notable storm that year was Hurricane Juliette, which caused devastating floods in Baja California, leading to 12 fatalities and $400 million worth of damage...
, producing 16 tropical depressions; 15 of which became tropical storms
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
or hurricanes. The season officially started on May 15, 2005 in the eastern Pacific, designated as the area east of 140°W
Longitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
, and on June 1, 2005 in the central Pacific, which is between the International Date Line
International Date Line
The International Date Line is a generally north-south imaginary line on the surface of the Earth, passing through the middle of the Pacific Ocean, that designates the place where each calendar day begins...
and 140°W, and lasted until November 30, 2005. These dates typically limit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin
Pacific hurricane
A Pacific hurricane or tropical storm is a tropical cyclone that develops in the northeastern part of the Pacific Ocean. For organizational purposes, the northern Pacific Ocean is divided into three regions: the eastern, , central , and western...
. This timeline documents all the storm formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls
Landfall (meteorology)
Landfall is the event of a tropical cyclone or a waterspout coming onto land after being over water. When a waterspout makes landfall it is reclassified as a tornado, which can then cause damage inland...
, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipation. The timeline also includes information which was not operationally released, meaning that information from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center , located at Florida International University in Miami, Florida, is the division of the National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting weather systems within the tropics between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th...
, such as information on a storm that was not operationally warned on, has been included.
The first storm of the season, Hurricane Adrian
Hurricane Adrian (2005)
Hurricane Adrian was an early season hurricane which took an unusual southwest to northeast track, bringing it closer to El Salvador than any other hurricane since reliable records began in 1949. The first storm of the 2005 Pacific hurricane season, Adrian developed on May 17, just two days...
, formed off the southwest coast of El Salvador
El Salvador
El Salvador or simply Salvador is the smallest and the most densely populated country in Central America. The country's capital city and largest city is San Salvador; Santa Ana and San Miguel are also important cultural and commercial centers in the country and in all of Central America...
and made the closest approach of any hurricane to the country on record. Most of June was quiet until the end of the month, when two tropical storms developed. July remained inactive as well, as only two tropical storms formed. In August, the activity picked up somewhat; the Central Pacific had its first and only depression of the year and four tropical storms, two of which became hurricanes, forming in the Eastern Pacific. September was the most active month of the year; six tropical storms formed, four of which became hurricanes, and two of the hurricanes strengthened further to become the only major hurricanes of the year. The strongest storm of the season was Hurricane Kenneth
Hurricane Kenneth (2005)
Hurricane Kenneth was the strongest and longest-tracked hurricane of the 2005 Pacific hurricane season. The eleventh named storm and fifth hurricane of the season, Kenneth developed from a disturbance in the Intertropical Convergence Zone to the southwest of Mexico on September 14...
, whose remnants briefly threatened Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
near the end of the month. Activity sharply dropped off in October as only one tropical depression formed. No storms formed in November in both basins, and the season ended on November 30.
May
May 15
- The Eastern Pacific hurricane season officially begins.
May 17
- 11:00 a.m. PDTPacific Time ZoneThe Pacific Time Zone observes standard time by subtracting eight hours from Coordinated Universal Time . The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 120th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory. During daylight saving time, its time offset is UTC-7.In the United States...
(18:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression One-E forms 460 miles (740 km) west-southwest of El SalvadorEl SalvadorEl Salvador or simply Salvador is the smallest and the most densely populated country in Central America. The country's capital city and largest city is San Salvador; Santa Ana and San Miguel are also important cultural and commercial centers in the country and in all of Central America...
. - 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC May 18) – Tropical Depression One-E strengthens into Tropical Storm AdrianHurricane Adrian (2005)Hurricane Adrian was an early season hurricane which took an unusual southwest to northeast track, bringing it closer to El Salvador than any other hurricane since reliable records began in 1949. The first storm of the 2005 Pacific hurricane season, Adrian developed on May 17, just two days...
.
May 19
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Adrian strengthens into Hurricane Adrian.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC May 20) – Hurricane Adrian weakens to a tropical storm.
May 20
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Adrian weakens to a tropical depression.
- 2:00 p.m. PDT (21:00 UTC – Tropical Depression Adrian makes landfall on the Pacific coast of HondurasHondurasHonduras is a republic in Central America. It was previously known as Spanish Honduras to differentiate it from British Honduras, which became the modern-day state of Belize...
in the Gulf of FonsecaGulf of FonsecaThe Gulf of Fonseca , part of the Pacific Ocean, is a gulf in Central America, bordering El Salvador, Honduras and Nicaragua.-History:Fonseca Bay was discovered in 1522 by Gil Gonzalez de Avila, and named by him after his patron, Archbishop Juan Fonseca, the implacable enemy of Columbus.In 1849, E. G...
with winds of 25 mph (40 km/h).The figures for maximum sustained windMaximum sustained windThe maximum sustained winds associated with a tropical cyclone are a common indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, they are found within the eyewall at a distance defined as the radius of maximum wind, or RMW. Unlike gusts, the value of these winds are...
s and position estimates are rounded to the nearest 5 units (knots, miles, or kilometersKilometreThe kilometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one thousand metres and is therefore exactly equal to the distance travelled by light in free space in of a second...
), following the convention used in the National Hurricane CenterNational Hurricane CenterThe National Hurricane Center , located at Florida International University in Miami, Florida, is the division of the National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting weather systems within the tropics between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th...
's operational products for each storm. All other units are rounded to the nearest digit. - 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC May 21) – Tropical Depression Adrian dissipates.
June
June 1- The Central Pacific hurricane season officially begins.
June 21

- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Two-E forms 385 mi (620 km) south of Zihuatanejo, Mexico.
June 22
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Two-E strengthens into Tropical Storm BeatrizTropical Storm Beatriz (2005)Tropical Storm Beatriz was the second named storm of the 2005 Pacific hurricane season. The precursor to Beatriz was a tropical wave which formed off the east coast of Africa on June 8. The wave traversed the tropical Atlantic ocean for more than a week before entering the Pacific basin on June 17...
.
June 23
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC June 24) – Tropical Storm Beatriz weakens to a tropical depression.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC June 24) – Tropical Depression Beatriz degenerates into a remnant low-pressure areaLow pressure areaA low-pressure area, or "low", is a region where the atmospheric pressure at sea level is below that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence which occur in upper levels of the troposphere. The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as...
.
June 25
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC June 26) – Tropical Depression Three-E forms 330 mi (530 km) south-southeast of Acapulco, Mexico.
June 26
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – The remnants of Beatriz dissipate.
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Three-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Calvin.
June 28
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Calvin weakens to a tropical depression.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC June 29) – Tropical Depression Calvin degenerates into a remnant low-pressure area.
July
July 3
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – The remnants of Calvin dissipate.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC July 4) – Tropical Depression Four-E forms 145 mi (235 km) south of Acapulco, Mexico.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC July 4) – Tropical Depression Four-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Dora.
July 5
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Dora weakens to a tropical depression.
July 6
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Dora degenerates into a remnant low.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC July 7) – The remnants of Dora dissipate.
July 17
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC July 18) – Tropical Depression Five-E forms 305 mi (490 km) south of Manzanillo, Mexico.
July 18
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Five-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Eugene.
July 20
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Eugene weakens to a tropical depression.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC July 21) – Tropical Depression Eugene degenerates into a remnant low-pressure area.
July 21
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – The remnants of Eugene dissipate.
August
August 3
- 8:00 a.m. HSTHawaii-Aleutian time zoneThe Hawaii-Aleutian Time Zone observes Hawaii-Aleutian Standard Time , by subtracting ten hours from Coordinated Universal Time . The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 150th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory....
(18:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression One-C forms 1,000 mi (1,610 km) southeast of the Island of HawaiiHawaii (island)The Island of Hawaii, also called the Big Island or Hawaii Island , is a volcanic island in the North Pacific Ocean...
.
August 4
- 8:00 p.m. HST (06:00 UTC August 5) – Tropical Depression One-C dissipates.
August 9
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Six-E forms 945 mi (1,520 km) west-southwest of Acapulco, Mexico.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC August 10) – Tropical Depression Six-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Fernanda.
August 10
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC August 11) – Tropical Storm Fernanda strengthens into a hurricane.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC August 11) – Tropical Depression Seven-E forms 690 mi (1,110 km) south of Cabo San Lucas, Mexico.
August 11
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Seven-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Greg.
August 13
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC August 14) – Hurricane Fernanda weakens to a tropical storm.
August 14

- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Greg weakens to a tropical depression.
August 15
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Fernanda weakens to a tropical depression.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC August 16) – Tropical Depression Greg degenerates into a remnant low-pressure area.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC August 16) – Tropical Depression Fernanda degenerates into a remnant low-pressure area.
August 17
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – The remnants of Fernanda dissipate.
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – The remnants of Greg are absorbed into the Intertropical Convergence ZoneIntertropical Convergence ZoneThe Intertropical Convergence Zone , known by sailors as The Doldrums, is the area encircling the earth near the equator where winds originating in the northern and southern hemispheres come together....
.
August 19
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Eight-E forms 160 mi (260 km) south of Puerto Angel, Mexico.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC August 20) – Tropical Depression Eight-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Hilary.
August 20
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC August 21) – Tropical Storm Hilary strengthens into Hurricane Hilary.
August 21
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC August 22) – Hurricane Hilary reaches category two intensity.
August 22

- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC August 23) – Hurricane Hilary weakens to a category one hurricane.
August 24
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Hurricane Hilary weakens to a tropical storm.
August 25
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Nine-E forms 155 mi (250 km) south of Manzanillo, Mexico.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC August 26) – Tropical Depression Nine-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Irwin.
August 26
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Hilary weakens to a tropical depression.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC August 27) – Tropical Depression Hilary degenerates into a remnant low-pressure area.
August 27
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC August 28) – Tropical Storm Irwin weakens to a tropical depression.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC August 28) – The remnants of Hilary dissipate.
August 28
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Irwin degenerates into a remnant low-pressure area.
September
September 2- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC September 3) – The remnants of Irwin dissipate.
September 11

- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC September 12) – Tropical Depression Ten-E forms 630 mi (1,015 km) south-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California SurBaja California SurBaja California Sur , is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state on October 8, 1974, the area was known as the South Territory of Baja California. It has an area of , or 3.57% of the land mass of Mexico and comprises...
.
September 14
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Eleven-E forms 900 mi (1,450 km) southwest of Cabo San Lucas, Mexico.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC September 15) – Tropical Depression Ten-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Jova.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC September 15) – Tropical Depression Eleven-E strengthens into Tropical Storm KennethHurricane Kenneth (2005)Hurricane Kenneth was the strongest and longest-tracked hurricane of the 2005 Pacific hurricane season. The eleventh named storm and fifth hurricane of the season, Kenneth developed from a disturbance in the Intertropical Convergence Zone to the southwest of Mexico on September 14...
.
September 15
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC September 16) – Tropical Storm Kenneth strengthens into Hurricane Kenneth.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC September 16) – Tropical Storm Jova strengthens into Hurricane Jova.
September 16
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC September 17) – Hurricane Kenneth reaches category two intensity.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC September 17) – Hurricane Jova reaches category two intensity.
- 11:00 p.m PDT (06:00 UTC September 17) – Hurricane Kenneth reaches category three intensity, becoming the first major hurricane of the season.
September 17
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Twelve-E forms 760 mi (1,225 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California Sur.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Twelve-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Lida.
September 18

- approximately 2:00 a.m. HST (12:00 UTC) – Hurricane Jova, while a category two storm, crosses the 140°WLongitudeLongitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
boundary and moves into the Central Pacific Hurricane CenterCentral Pacific Hurricane CenterThe Central Pacific Hurricane Center of the United States National Weather Service is the official body responsible for tracking and issuing tropical cyclone warnings, watches, advisories, discussions, and statements for the Central North Pacific Basin...
's area of responsibility. - 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Hurricane Kenneth reaches category four intensity.
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Thirteen-E forms 575 mi (925 km) south-southwest of Cabo San Lucas, Mexico.
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Lida weakens to a tropical depression.
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Thirteen-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Max.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC September 19) – Hurricane Kenneth weakens to a category three hurricane.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC September 19) – Tropical Storm Lidia is absorbed by Tropical Storm Max.
September 19
- 2:00 a.m. HST (12:00 UTC) – Hurricane Jova reaches category three intensity.
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Hurricane Kenneth weakens to category two intensity.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC September 20) – Hurricane Kenneth weakens to category one intensity.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC September 20) – Tropical Storm Max strengthens into Hurricane Max.
September 20
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Hurricane Kenneth weakens to a tropical storm.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC September 21) – Hurricane Max weakens to a tropical storm.
September 21
- 2:00 p.m. HST (00:00 UTC September 22) – Hurricane Jova weakens to a category two hurricane.
September 22
- 2:00 a.m. HST (12:00 UTC) – Hurricane Jova weakens to a category one hurricane.
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Max weakens to a tropical depression.
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Max degenerates into a remnant low-pressure area.
- 2:00 p.m. HST (00:00 UTC September 23) – Hurricane Jova weakens to a tropical storm.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC September 23) – Tropical Depression Fourteen-E forms 590 mi (950 km) southwest of Acapulco, Mexico.
September 23
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Fourteen-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Norma.
- 2:00 p.m. HST (00:00 UTC September 24) – Tropical Storm Jova weakens to a tropical depression.
September 24

- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC September 25) – Tropical Storm Kenneth re-strengthens into a hurricane.
- 8:00 p.m. HST (06:00 UTC September 25) – Tropical Depression Jova dissipates.
- approximately 8:00 p.m. HST (06:00 UTC September 25) – Hurricane Kenneth, while a category one storm, crosses the 140°W boundary and moves into the Central Pacific Hurricane Center's area of responsibility.
September 25
- 2:00 a.m. HST (12:00 UTC) – Hurricane Kenneth weakens to a tropical storm.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC September 26) – The remnants of Max dissipate.
September 26
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Norma weakens to a tropical depression.
September 27
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Norma degenerates into a remnant low-pressure area.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC September 28) – Tropical Depression Fifteen-E forms 140 mi (225 km) south of Manzanillo, Mexico.
September 28
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC September 29) – Tropical Depression Fifteen-E strengthens to Tropical Storm OtisHurricane Otis (2005)Hurricane Otis was a moderate hurricane that threatened the Baja California Peninsula but dissipated before landfall. Otis developed on September 28, 2005, off the western coast of Mexico, from a tropical wave that emerged from the western coast of Africa and traversed the Atlantic Ocean during the...
.
September 29
- 2:00 a.m HST (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Kenneth weakens to a tropical depression.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC September 30) – Tropical Storm Otis strengthens into Hurricane Otis.
September 30

- 8:00 a.m. HST (18:00 UTC) – Tropical Depression Kenneth dissipates.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC October 1) – The remnants of Norma dissipate.
- 11:00 p.m. PDT (06:00 UTC October 1) – Hurricane Otis reaches category two intensity.
October
October 1- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – Hurricane Otis weakens to a category one hurricane.
October 2
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Hurricane Otis weakens to a tropical storm.
October 3
- 5:00 a.m. PDT (12:00 UTC) – Tropical Storm Otis weakens to a tropical depression.
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC October 4) – Tropical Depression Otis degenerates into a remnant low-pressure area.
October 5
- 11:00 a.m. PDT (18:00 UTC) – The remnants of Otis dissipate.
October 14
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC October 15) – Tropical Depression Sixteen-E forms 415 mi (670 km) south of Acapulco, Mexico.
October 17
- 5:00 p.m. PDT (00:00 UTC October 18) – Tropical Depression Sixteen-E degenerates into a remnant low-pressure area.
October 19

- 5:00 a.m. (12:00 UTC) – The remnants of Sixteen-E regenerate into a tropical depression.
October 20
- 5:00 a.m. (00:00 UTC October 21) – Tropical Depression Sixteen-E degenerates into a remnant low-pressure area again.
October 21
- 5:00 a.m. (12:00 UTC) – The remnants of Sixteen-E are absorbed into the Intertropical Convergence Zone.
See also
- 2005 Pacific hurricane season2005 Pacific hurricane seasonThe 2005 Pacific hurricane season officially began on May 15, 2005 in the eastern Pacific and on June 1, 2005 in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 2005. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean...
- List of Pacific hurricane seasons
- Timeline of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane seasonTimeline of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane seasonThe timeline of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season documents the formations, strengthenings, weakenings, landfalls, extratropical transitions, and dissipations of the season's tropical and subtropical storms. The 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was the most active Atlantic hurricane season in...
- Timeline of the 2005 Pacific typhoon seasonTimeline of the 2005 Pacific typhoon seasonThe 2005 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it runs year-round in 2005, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December...

