
Taskbar
Encyclopedia
In computing
, a taskbar is a bar displayed on a full edge of a GUI
desktop that is used to launch and monitor running applications. Microsoft
incorporated a taskbar in Windows 95
and it has been a defining aspect of Microsoft Windows
's graphical user interface
ever since. Some desktop environment
s, such as KDE
and old versions of GNOME
, include a more configurable taskbar. Other operating systems may use different methods for task management or application launching such as a panel
or a dock
.
place it at the bottom of the screen and includes from left to right the Start menu button, Quick Launch bar, taskbar buttons, and notification area. The Quick Launch toolbar was added with the Internet Explorer 4 shell update, and is not enabled by default in Windows XP
. Windows 7 removed the Quick Launch feature in favor of pinning applications to the taskbar itself.
The taskbar was originally developed as a feature of Windows 95, but it was based on a similar user interface feature called the tray that was developed as part of Microsoft's Cairo
project.
With the release of Windows XP, Microsoft changed the behavior of the taskbar to take advantage of Fitts' law
.
allow it to span multiple displays. When the taskbar is displayed vertically on versions of Windows prior to Windows Vista, the Start menu button will only display the text "Start" or translated equivalent if the taskbar is wide enough to show the full text. However, the edge of the taskbar (in any position) can be dragged to control its height (width for a vertical taskbar); this is especially useful for a vertical taskbar to show window titles next to the window icons.
Users can resize the height (or width when displayed vertically) of the taskbar up to half of the display area. To avoid inadverdent resizing or repositioning of the taskbar, Windows XP and later lock the taskbar by default. When unlocked, "grips" are displayed next to the movable elements which allow grabbing with the mouse to move and size. These grips slightly decrease amount of available space in the taskbar.
The taskbar as a whole can be hidden until the mouse pointer is moved to the display edge, or has keyboard focus..
In addition to deskbands, Windows supports "Application Desktop Toolbars" (also called "appbands") that supports creating additional toolbars that can dock to any side of the screen, and cannot be overlaid by other applications.
Users can add additional toolbars that display the contents of folders. The display for toolbars that represent folder items (such as Links, Desktop and Quick Launch) can be changed to show large icons and the text for each item. Prior to Windows Vista, the Desktop Toolbars could be dragged off the taskbar and float independently, or docked to a display edge. Windows Vista greatly limited
, but did not eliminate the ability to have desktop toolbar not attached to the taskbar. Windows 7 has deprecated the use of Floating Deskbands altogether: they only appear pinned into the Taskbar.
1987 Arthur operating system, for their Acorn Archimedes
computer. It is called the Icon bar
and remains an essential part of Arthur's succeeding RISC OS
operating system. The Iconbar holds icons which represent mounted disc drives and RAM discs, running applications and system utilities. These icons have their own context-sensitive menus and support drag and drop behaviour.
, MorphOS
. There could be AppIcons (Quick Launch Icons) lying on the windows manager desktop of Amiga (called Workbench
) since AmigaOS 2.04 (in 1991); also very appreciated in Amiga are "dock" utilities, just as like as in MacOS. For example Amidock born as third party utility, has then being integrated into AmigaOS 3.9 (1999), and an enhanced PPC
Amidock version runs into AmigaOS 4.0.. As long as AmigaOS interface is highly customizable, it could also being integrated with taskbar utilities whose aspect could be more or less similar in aspect to the taskbars of Windows. For example AmiKit
is a freeware compilation of more than 300 Amiga programs. It could be used to enhance experience of native Amigaos 3.9 or any version of AmigaOS 3.5 or 3.9 running into Windows Amiga Emulator WinUAE. Amikit features a windows-like taskbar utility (called Amistart) that is being loaded by default at startup . AROS
operating system has its version of Amistart too that is provided with the OS and free to be installed by the users, while MorphOS
has being equipped with a docking utility just as like as AmigaOS or MacOS.
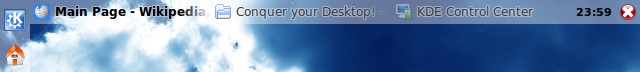
distributions, the taskbar is run by the Kicker
program, which shows rectangular panels that can contain applets, one of which is the taskbar. Applets can be arbitrarily relocated, for instance, the notification area can be moved away from the taskbar. The bar can be placed not only at the bottom, but also at the top or (vertically) at the left or the right and its size can be altered (from 24 to 256 pixels), as well as the length in % of the screen size. And several other bars with various specific functions can be added in different locations, e.g., one bar at the left and one at the right or even overlapping (one fixed and one with automatic hiding).
Since KDE 4, the taskbar is implemented as a Plasma
widget.
desktop environment uses its own type of taskbar, known as panels (the program responsible for them is therefore called gnome-panel
). By default, GNOME usually contains two full-width panels at the top and bottom of the screen. The top panel usually contains navigation menus labelled Applications, Places, and System in that order. These menus hold links to common applications, areas of the file system, and system preferences and administration utilities, respectively. The top panel usually contains a clock and notification area, which can double as a sort of dock, as well.
The bottom panel is commonly empty by default, other than a set of buttons to navigate between desktops and a button to minimize all windows and show the desktop, due to its use in the navigation between windows (windows minimize to the bottom panel by default).
These panels can be populated with other customizable menus and buttons, including new menus, search boxes, and icons to perform quick-launch like functions. Other applications can also be attached to the panels, and the contents of the panels can be moved, removed, or configured in other ways.
s or window manager
s without one. Example include pypanel, fbpanel, perlpanel, tint2, and others.
and its predecessor NeXTSTEP
, is also a kind of taskbar. The Mac OS X Dock is application-oriented instead of window-oriented. Each running application is represented by one icon in the Dock regardless of how many windows it has on screen. A textual menu can be opened by right-clicking on the dock icon that gives access to an application's windows, among other functions determined by the app. Minimized windows also appear in the dock, in the rightmost section, represented by a graphical thumbnail. The trash can is also represented in the Dock, as a universal metaphor for deletion. For example, dragging selected text to the trash should remove the text from the document and create a clipping file in the trash.
The right side of Mac OS X's Menu bar
also contains several notification widgets and quick access functions, called Menu extra
s.
Computing
Computing is usually defined as the activity of using and improving computer hardware and software. It is the computer-specific part of information technology...
, a taskbar is a bar displayed on a full edge of a GUI
Gui
Gui or guee is a generic term to refer to grilled dishes in Korean cuisine. These most commonly have meat or fish as their primary ingredient, but may in some cases also comprise grilled vegetables or other vegetarian ingredients. The term derives from the verb, "gupda" in Korean, which literally...
desktop that is used to launch and monitor running applications. Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
incorporated a taskbar in Windows 95
Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented graphical user interface-based operating system. It was released on August 24, 1995 by Microsoft, and was a significant progression from the company's previous Windows products...
and it has been a defining aspect of Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
's graphical user interface
Graphical user interface
In computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
ever since. Some desktop environment
Desktop environment
In graphical computing, a desktop environment commonly refers to a style of graphical user interface derived from the desktop metaphor that is seen on most modern personal computers. These GUIs help the user in easily accessing, configuring, and modifying many important and frequently accessed...
s, such as KDE
KDE
KDE is an international free software community producing an integrated set of cross-platform applications designed to run on Linux, FreeBSD, Microsoft Windows, Solaris and Mac OS X systems...
and old versions of GNOME
GNOME
GNOME is a desktop environment and graphical user interface that runs on top of a computer operating system. It is composed entirely of free and open source software...
, include a more configurable taskbar. Other operating systems may use different methods for task management or application launching such as a panel
Gnome-panel
GNOME Panel is a highly configurable launcher and taskbar for GNOME. It forms a core part of the GNOME desktop.It has been replaced in GNOME 3.x by default with GNOME Shell, which only works with the Mutter window manager...
or a dock
Dock (computing)
The Dock is a prominent feature of the graphical user interface of the Mac OS X operating system. It is used to launch applications and switch between running applications...
.
Microsoft Windows
The default settings for the taskbar in Microsoft WindowsMicrosoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
place it at the bottom of the screen and includes from left to right the Start menu button, Quick Launch bar, taskbar buttons, and notification area. The Quick Launch toolbar was added with the Internet Explorer 4 shell update, and is not enabled by default in Windows XP
Windows XP
Windows XP is an operating system produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops and media centers. First released to computer manufacturers on August 24, 2001, it is the second most popular version of Windows, based on installed user base...
. Windows 7 removed the Quick Launch feature in favor of pinning applications to the taskbar itself.
The taskbar was originally developed as a feature of Windows 95, but it was based on a similar user interface feature called the tray that was developed as part of Microsoft's Cairo
Cairo (operating system)
Cairo was the code name for a project at Microsoft from 1991 to 1996. Its charter was to build technologies for a next generation operating system that would fulfill Bill Gates' vision of "information at your fingertips." Cairo never shipped, although portions of its technologies have since...
project.
With the release of Windows XP, Microsoft changed the behavior of the taskbar to take advantage of Fitts' law
Fitts' law
Fitts's law is a model of human movement primarily used in human–computer interaction and ergonomics that predicts that the time required to rapidly move to a target area is a function of the distance to the target and the size of the target...
.
Taskbar elements
- The Start menuStart menuThe Start Menu and Start Button are user interface elements used in the later versions of the Microsoft Windows operating systems and in some X window managers...
, which is accessed by a button on the taskbar, contains commands that can access programs, documents, and settings. - The Quick Launch bar, introduced with Windows 98Windows 98Windows 98 is a graphical operating system by Microsoft. It is the second major release in the Windows 9x line of operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on 15 May 1998 and to retail on 25 June 1998. Windows 98 is the successor to Windows 95. Like its predecessor, it is a hybrid...
(also for separate download for Windows 95Windows 95Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented graphical user interface-based operating system. It was released on August 24, 1995 by Microsoft, and was a significant progression from the company's previous Windows products...
and Windows NT 4.0Windows NT 4.0Windows NT 4.0 is a preemptive, graphical and business-oriented operating system designed to work with either uniprocessor or symmetric multi-processor computers. It was the next release of Microsoft's Windows NT line of operating systems and was released to manufacturing on 31 July 1996...
with Windows Desktop UpdateWindows Desktop UpdateMicrosoft's Windows Desktop Update was an optional feature included with Internet Explorer 4 , which introduced several updated shell features to the Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 operating systems...
for Internet Explorer 4Internet Explorer 4Microsoft Internet Explorer 4 is a graphical web browser released in September 1997 by Microsoft, primarily for Microsoft Windows, but also with versions available for Apple Mac OS, Solaris, and HP-UX and marketed as "The Web the Way You Want It".It was one of the main participants of the first...
), contains shortcuts to applications. Windows provides default entries, such as Launch Internet ExplorerInternet ExplorerWindows Internet Explorer is a series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft and included as part of the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems, starting in 1995. It was first released as part of the add-on package Plus! for Windows 95 that year...
Browser, and the user or third-party software may add any further shortcuts that they choose. A single click on the application's icon in this area launches the application. This section may not always be present: for example it is turned off by default in Windows XPWindows XPWindows XP is an operating system produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops and media centers. First released to computer manufacturers on August 24, 2001, it is the second most popular version of Windows, based on installed user base...
and Windows 7. - The Windows shell places a taskbar button on the taskbar whenever an application creates an unowned window: that is, a window that doesn't have a parent and that is created according to normal Windows user interface guidelines. Typically all Single Document InterfaceSingle document interfaceIn graphical user interfaces, a single document interface or SDI is a method of organizing graphical user interface applications into individual windows that the operating system's window manager handles separately. Each window contains its own menu or tool bar, and does not have a "background"...
applications have a single taskbar button for each open window, although modal windowModal windowIn user interface design, a modal window is a child window that requires users to interact with it before they can return to operating the parent application, thus preventing the workflow on the application main window...
s may also appear there.- Windows 98Windows 98Windows 98 is a graphical operating system by Microsoft. It is the second major release in the Windows 9x line of operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on 15 May 1998 and to retail on 25 June 1998. Windows 98 is the successor to Windows 95. Like its predecessor, it is a hybrid...
and Windows Desktop UpdateWindows Desktop UpdateMicrosoft's Windows Desktop Update was an optional feature included with Internet Explorer 4 , which introduced several updated shell features to the Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 operating systems...
for Windows 95 introduced the ability to minimize foreground windows by clicking their button on the taskbar. - Windows 2000Windows 2000Windows 2000 is a line of operating systems produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, business desktops, laptops, and servers. Windows 2000 was released to manufacturing on 15 December 1999 and launched to retail on 17 February 2000. It is the successor to Windows NT 4.0, and is the...
introduced balloon notifications. - Windows MeWindows MeWindows Millennium Edition, or Windows Me , is a graphical operating system released on September 14, 2000 by Microsoft, and was the last operating system released in the Windows 9x series. Support for Windows Me ended on July 11, 2006....
added an option to disable moving or resizing the taskbar. - Windows XPWindows XPWindows XP is an operating system produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops and media centers. First released to computer manufacturers on August 24, 2001, it is the second most popular version of Windows, based on installed user base...
introduced taskbar grouping, which can group the taskbar buttons of several windows from the same application into a single button. This button pops up a menu listing all the grouped windows when clicked. This keeps the taskbar from being overcrowded when many windows are open at once. - Windows VistaWindows VistaWindows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
introduced window previews which show thumbnail views of the application in real-time. This capability is provided by the Desktop Window ManagerDesktop Window ManagerDesktop Window Manager is the window manager in Windows Vista and Windows 7 that enables the Windows Aero graphical user interface and visual theme. The Desktop Window Manager requires video cards supporting DirectX 9.0 and Shader Model 2.0. DWM is not included with Windows Vista Starter edition...
. Start menu tooltipTooltipThe tooltip or infotip is a common graphical user interface element. It is used in conjunction with a cursor, usually a mouse pointer. The user hovers the cursor over an item, without clicking it, and a tooltip may appear—a small "hover box" with information about the item being hovered...
no longer says "Click here to begin". Now, says simply "Start". - Windows 7 introduced jumplistsJumplistJumplist was a term used in the early years of the world wide web to describe a collection of links, which were individually referred to as jumps. The Jumplist database-driven web service was developed by i/us Corp. and launched in 1998 at jumplist.com...
which are menus that provide shortcuts to recently opened documents, frequently opened documents, folders paths (in case of Windows Explorer), or various options (called Tasks) which apply to that specific program or pinned website shortcut. Jump lists appear when the user right-clicks on an icon in the taskbar or drags the icon upwards with the mouse left click. Recent and frequent files and folders can be pinned inside the jump list. - Windows 7 introduced the ability to pin applications to the taskbar so that buttons for launching them appear when they are not running. Previously, the Quick launch was used to pin applications to the taskbar; however, running programs appeared as a separate button.
- Windows 7 removed several classic taskbar features.
- Windows 98
- Deskbands are minimized functional, long-running programs, such as Windows Media Player. Programs that minimize to deskbands aren't displayed in the taskbar.
- The notification area is the portion of the taskbar that displays icons for system and program features that have no presence on the desktop as well as the time and the volume icon. It contains mainly icons that show status information, though some programs, such as WinampWinampWinamp is a media player for Windows-based PCs and Android devices, written by Nullsoft, now a subsidiary of AOL. It is proprietary freeware/shareware, multi-format, extensible with plug-ins and skins, and is noted for its graphical sound visualization, playlist, and media library features.Winamp...
, use it for minimized windows. By default, this is located in the bottom-right of the primary monitor (or bottom-left on languages of Windows that use right-to-left reading order), or at the bottom of the taskbar if docked vertically. The clock appears here, and applications can put icons in the notification area to indicate the status of an operation or to notify the user about an event. For example, an application might put a printer icon in the status area to show that a print job is under way, or a display driver application may provide quick access to various screen resolutions. The notification area is commonly referred to as the system tray, which Microsoft states is wrong, although the term is sometimes used in Microsoft documentation, articles, and software descriptions. Raymond Chen suggests the confusion originated with systray.exe, a small application that controlled some icons within the notification area in Windows 95. The notification area is also referred to as the status area by Microsoft.- In older versions of Windows the notification area icons were limited to 16 colors. Windows MeWindows MeWindows Millennium Edition, or Windows Me , is a graphical operating system released on September 14, 2000 by Microsoft, and was the last operating system released in the Windows 9x series. Support for Windows Me ended on July 11, 2006....
added support for high color notification area icons. - Starting with Windows XP, the user can choose to always show or hide some icons, or hide them if inactive for some time. A button allows the user to reveal all the icons.
- Starting with Windows Vista, the taskbar notification area is split into two areas; one reserved for system icons including clock, volume, network and power. The other is for applications.
- In older versions of Windows the notification area icons were limited to 16 colors. Windows Me
Customization
The Windows taskbar can be modified by users in several ways. The position of the taskbar can be changed to appear on any edge of the primary display. Up to and including Windows Server 2008, the taskbar is constrained to single display, although third-party utilities such as UltraMonUltramon
UltraMon is a commercial application for Microsoft Windows users who use multiple displays. UltraMon is developed by Realtime Soft, a small software development company based in Bern, Switzerland.UltraMon currently contains the following features:...
allow it to span multiple displays. When the taskbar is displayed vertically on versions of Windows prior to Windows Vista, the Start menu button will only display the text "Start" or translated equivalent if the taskbar is wide enough to show the full text. However, the edge of the taskbar (in any position) can be dragged to control its height (width for a vertical taskbar); this is especially useful for a vertical taskbar to show window titles next to the window icons.
Users can resize the height (or width when displayed vertically) of the taskbar up to half of the display area. To avoid inadverdent resizing or repositioning of the taskbar, Windows XP and later lock the taskbar by default. When unlocked, "grips" are displayed next to the movable elements which allow grabbing with the mouse to move and size. These grips slightly decrease amount of available space in the taskbar.
The taskbar as a whole can be hidden until the mouse pointer is moved to the display edge, or has keyboard focus..
Screenshots
Desktop toolbars
Other toolbars, known as "Deskbands", may be added to the taskbar. Windows includes the following deskbands but does not display them by default (except the Quick Launch toolbar in certain versions and configurations).- Address. Contains an address bar similar to what is found in Internet ExplorerInternet ExplorerWindows Internet Explorer is a series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft and included as part of the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems, starting in 1995. It was first released as part of the add-on package Plus! for Windows 95 that year...
. - Windows Media Player. Optionally shown when the Windows Media PlayerWindows Media PlayerWindows Media Player is a media player and media library application developed by Microsoft that is used for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as on Pocket PC and Windows Mobile-based devices...
is minimized. - Links. Shortcuts to items located in the users Links folder. Usually shortcuts to internet sites.
- Tablet PC Input Panel. Contains a button to show the Tablet PCTablet computerA tablet computer, or simply tablet, is a complete mobile computer, larger than a mobile phone or personal digital assistant, integrated into a flat touch screen and primarily operated by touching the screen...
input panel for ink text entry. - Desktop. Contains shortcuts to items contained on the users desktop. Since the taskbar is always shown, this provides easy access to desktop items without having to minimize applications.
- Quick Launch. Contains shortcuts to Internet Explorer, email applications and a link to display the desktop. Windows Vista adds a link to the Flip 3D feature.
- Language. Contains shortcuts to quickly change the desired language for the keyboard to follow.
In addition to deskbands, Windows supports "Application Desktop Toolbars" (also called "appbands") that supports creating additional toolbars that can dock to any side of the screen, and cannot be overlaid by other applications.
Users can add additional toolbars that display the contents of folders. The display for toolbars that represent folder items (such as Links, Desktop and Quick Launch) can be changed to show large icons and the text for each item. Prior to Windows Vista, the Desktop Toolbars could be dragged off the taskbar and float independently, or docked to a display edge. Windows Vista greatly limited
Features removed from Windows Vista
While Windows Vista contains many new features, a number of capabilities and certain programs that were a part of previous Windows versions up to Windows XP were removed or changed - some of which were later re-introduced in Windows 7....
, but did not eliminate the ability to have desktop toolbar not attached to the taskbar. Windows 7 has deprecated the use of Floating Deskbands altogether: they only appear pinned into the Taskbar.
- Upon opening the Taskbar properties on Windows 95Windows 95Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented graphical user interface-based operating system. It was released on August 24, 1995 by Microsoft, and was a significant progression from the company's previous Windows products...
and Windows 98Windows 98Windows 98 is a graphical operating system by Microsoft. It is the second major release in the Windows 9x line of operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on 15 May 1998 and to retail on 25 June 1998. Windows 98 is the successor to Windows 95. Like its predecessor, it is a hybrid...
whilst holding down the CTRL key, an extra tab for DeskBar Options is shown, but no part of it can be used. The DeskBar option was a feature that was never included within these versions of Windows.
Acorn Computers
An early implementation of the taskbar concept is seen in Acorn ComputersAcorn Computers
Acorn Computers Ltd. was a British computer company established in Cambridge, England, in 1978. The company produced a number of computers which were especially popular in the UK. These included the Acorn Electron, the BBC Micro, and the Acorn Archimedes...
1987 Arthur operating system, for their Acorn Archimedes
Acorn Archimedes
The Acorn Archimedes was Acorn Computers Ltd's first general purpose home computer to be based on their own ARM architecture.Using a RISC design with a 32-bit CPU, at its launch in June 1987, the Archimedes was stated as running at 4 MIPS, with a claim of 18 MIPS during tests.The name is commonly...
computer. It is called the Icon bar
Icon bar
In computing, the icon bar is the name of the dock in Acorn's RISC OS operating system, and is fundamental to the OS. Its introduction in 1987 was a new concept in GUIs...
and remains an essential part of Arthur's succeeding RISC OS
RISC OS
RISC OS is a computer operating system originally developed by Acorn Computers Ltd in Cambridge, England for their range of desktop computers, based on their own ARM architecture. First released in 1987, under the name Arthur, the subsequent iteration was renamed as in 1988...
operating system. The Iconbar holds icons which represent mounted disc drives and RAM discs, running applications and system utilities. These icons have their own context-sensitive menus and support drag and drop behaviour.
AmigaOS
AmigaOS featured various implementations of taskbar concept, and this inheritance is present also in its successors (AmigaOS 4.0, AROSAros
Aros may refer to:*Aros , a river in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium*AROS Research Operating System, a free software implementation of AmigaOS* Aros, the original Viking name of Aarhus, the second largest city in Denmark...
, MorphOS
MorphOS
MorphOS is an Amiga-compatible computer operating system. It is a mixed proprietary and open source OS produced for the Pegasos PowerPC processor based computer, PowerUP accelerator equipped Amiga computers, and a series of Freescale development boards that use the Genesi firmware, including the...
. There could be AppIcons (Quick Launch Icons) lying on the windows manager desktop of Amiga (called Workbench
Workbench (AmigaOS)
-Overview:Commodore named their Amiga computer's first operating system Workbench 1.0 and continued with the Workbench name until version 3.1, when it was changed to AmigaOS, prompted by Apple renaming their propriety OS from "System" to "MacOS"...
) since AmigaOS 2.04 (in 1991); also very appreciated in Amiga are "dock" utilities, just as like as in MacOS. For example Amidock born as third party utility, has then being integrated into AmigaOS 3.9 (1999), and an enhanced PPC
PowerPC
PowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
Amidock version runs into AmigaOS 4.0.. As long as AmigaOS interface is highly customizable, it could also being integrated with taskbar utilities whose aspect could be more or less similar in aspect to the taskbars of Windows. For example AmiKit
AmiKit
AmiKit is a freeware compilation of more than 300 pre-installed Amiga programs. It enables user to experience the high-end AmigaOS environment under Windows or Linux system for free...
is a freeware compilation of more than 300 Amiga programs. It could be used to enhance experience of native Amigaos 3.9 or any version of AmigaOS 3.5 or 3.9 running into Windows Amiga Emulator WinUAE. Amikit features a windows-like taskbar utility (called Amistart) that is being loaded by default at startup . AROS
Aros
Aros may refer to:*Aros , a river in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium*AROS Research Operating System, a free software implementation of AmigaOS* Aros, the original Viking name of Aarhus, the second largest city in Denmark...
operating system has its version of Amistart too that is provided with the OS and free to be installed by the users, while MorphOS
MorphOS
MorphOS is an Amiga-compatible computer operating system. It is a mixed proprietary and open source OS produced for the Pegasos PowerPC processor based computer, PowerUP accelerator equipped Amiga computers, and a series of Freescale development boards that use the Genesi firmware, including the...
has being equipped with a docking utility just as like as AmigaOS or MacOS.
KDE
In various KDEKDE
KDE is an international free software community producing an integrated set of cross-platform applications designed to run on Linux, FreeBSD, Microsoft Windows, Solaris and Mac OS X systems...
distributions, the taskbar is run by the Kicker
Kicker (KDE)
Kicker is the main panel used in K Desktop Environment 3 and earlier. It can be customized by the user. By default, it has the K Menu, a Desktop Access button, a Home button, a Konqueror button, a Kontact button, and a Help button...
program, which shows rectangular panels that can contain applets, one of which is the taskbar. Applets can be arbitrarily relocated, for instance, the notification area can be moved away from the taskbar. The bar can be placed not only at the bottom, but also at the top or (vertically) at the left or the right and its size can be altered (from 24 to 256 pixels), as well as the length in % of the screen size. And several other bars with various specific functions can be added in different locations, e.g., one bar at the left and one at the right or even overlapping (one fixed and one with automatic hiding).
Since KDE 4, the taskbar is implemented as a Plasma
Plasma (KDE)
Plasma Workspaces is the umbrella term for all graphical environments provided by KDE.Three Plasma sub-projects are currently being developed: Plasma Desktop for traditional desktop PCs and notebooks, Plasma Netbook for netbooks, and Plasma Active for Tablet PCs, Nokia N900 style smartphones and...
widget.

GNOME
Similarly, the GNOMEGNOME
GNOME is a desktop environment and graphical user interface that runs on top of a computer operating system. It is composed entirely of free and open source software...
desktop environment uses its own type of taskbar, known as panels (the program responsible for them is therefore called gnome-panel
Gnome-panel
GNOME Panel is a highly configurable launcher and taskbar for GNOME. It forms a core part of the GNOME desktop.It has been replaced in GNOME 3.x by default with GNOME Shell, which only works with the Mutter window manager...
). By default, GNOME usually contains two full-width panels at the top and bottom of the screen. The top panel usually contains navigation menus labelled Applications, Places, and System in that order. These menus hold links to common applications, areas of the file system, and system preferences and administration utilities, respectively. The top panel usually contains a clock and notification area, which can double as a sort of dock, as well.
The bottom panel is commonly empty by default, other than a set of buttons to navigate between desktops and a button to minimize all windows and show the desktop, due to its use in the navigation between windows (windows minimize to the bottom panel by default).
These panels can be populated with other customizable menus and buttons, including new menus, search boxes, and icons to perform quick-launch like functions. Other applications can also be attached to the panels, and the contents of the panels can be moved, removed, or configured in other ways.
Window managers that provide an integrated taskbar
- fluxboxFluxboxFluxbox is a stacking window manager for the X Window System, which started as a fork of Blackbox 0.61.1, with the same aim to be lightweight. Its user interface has only a taskbar, a pop-up menu accessible by right-clicking on the desktop, and minimal support for graphical icons...
- fvwm95FVWM95FVWM95 is a window manager for the X Window System based on the popular FVWM 2 window manager. It is similar to the original FVWM, but is designed to closely resemble the look of Windows 95....
- icewmIceWMIceWM is a stacking window manager for the X Window System graphical infrastructure, written by Marko Maček. It was coded from scratch in C++ and is released under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License...
- jwmJWMJWM is a lightweight stacking window manager for the X Window System written by Joe Wingbermuehle. JWM is written in C and uses only Xlib at a minimum...
- qvwm
- windowlabWindowLabWindowLab is an X window manager for Unix-like systems. It is based on aewm and retains that window manager's small and lightweight nature. In many aspects, WindowLab has looked to the Amiga's user interface for inspiration without cloning it completely...
Other Unix environments
There are many programs that offer standalone taskbars for desktop environmentDesktop environment
In graphical computing, a desktop environment commonly refers to a style of graphical user interface derived from the desktop metaphor that is seen on most modern personal computers. These GUIs help the user in easily accessing, configuring, and modifying many important and frequently accessed...
s or window manager
Window manager
A window manager is system software that controls the placement and appearance of windows within a windowing system in a graphical user interface. Most window managers are designed to help provide a desktop environment...
s without one. Example include pypanel, fbpanel, perlpanel, tint2, and others.
Apple Macintosh computers
The Dock, as featured in Mac OS XMac OS X
Mac OS X is a series of Unix-based operating systems and graphical user interfaces developed, marketed, and sold by Apple Inc. Since 2002, has been included with all new Macintosh computer systems...
and its predecessor NeXTSTEP
NEXTSTEP
NeXTSTEP was the object-oriented, multitasking operating system developed by NeXT Computer to run on its range of proprietary workstation computers, such as the NeXTcube...
, is also a kind of taskbar. The Mac OS X Dock is application-oriented instead of window-oriented. Each running application is represented by one icon in the Dock regardless of how many windows it has on screen. A textual menu can be opened by right-clicking on the dock icon that gives access to an application's windows, among other functions determined by the app. Minimized windows also appear in the dock, in the rightmost section, represented by a graphical thumbnail. The trash can is also represented in the Dock, as a universal metaphor for deletion. For example, dragging selected text to the trash should remove the text from the document and create a clipping file in the trash.
The right side of Mac OS X's Menu bar
Menu bar
A menu bar is a region of a screen or application interface where drop down menus are displayed. The menu bar's purpose is to supply a common housing for window- or application-specific menus which provide access to such functions as opening files, interacting with an application, or displaying...
also contains several notification widgets and quick access functions, called Menu extra
Menu extra
A menu extra, menu item, menulet, or status item in Mac OS X is a small icon or sometimes a word that appears at the right of the menu bar. They often provide quick ways to use applications or display information , or control system-level variables...
s.

