Stichodactyla toxin
Encyclopedia
Stichodactyla toxin is a peptide
toxin
that blocks the voltage-gated potassium channel
s: Kv1.1, Kv1.3
and Kv3.2
.
basic peptide first discovered in the sea anemone
Stichodactyla helianthus
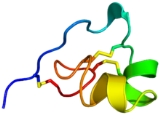
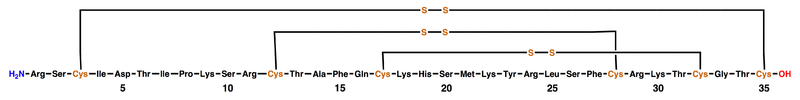
by Professor Olga Castaneda from the University of Havana, Cuba, and her collaborators in Sweden. It is cross-linked by three disulfide bridges: Cys3-Cys35, Cys12-Cys28, and Cys17-Cys32 (see figure below). The amino acid sequence of the ShK toxin is Arg-Ser-Cys-Ile-Asp-Thr-Ile-Pro-Lys-Ser-Arg-Cys-Thr-Ala-Phe-Gln-Cys-Lys-His-Ser-Met-Lys-Tyr-Arg-Leu-Ser-Phe-Cys-Arg-Lys-Thr-Cys-Gly-Thr-Cys. ShK is stabilized by three disulfide bridges and consists of two short α-helices
comprising residues 14-19 and 21-24. The N-terminal eight residues of ShK adopt an extended conformation, followed by a pair of interlocking turns that resemble a 310 helix, while its C-terminal Cys35 residue forms a nearly head-to-tail cyclic structure through a disulfide bond with Cys3. Protein domains with structural resemblance to ShK have been described in 402 proteins, most of them from C. elegans
. Other proteins containing domains with similar structures include the cysteine-rich secretory protein
snake toxins natrin, triflin
, and stecrisp, the Toxocara canis
mucin
s and the human protein Tpx-1
.
ShK blocks the Kv1.3 channel in T cells with a Kd of about 11 pM. It blocks the neuronal Kv1.1 and Kv1.6 channels with Kds of 16 pM and 200 pM respectively. The Kv3.2 and KCa3.1 channels are more than 1000 times less sensitive to the peptide.
Several ShK analogs have been generated to enhance specificity for the Kv1.3 channel over the Kv1.1, Kv1.6 and Kv3.2 channels. The first analog that showed some degree of specificity was ShK-Dap22. Attaching a fluorescein
to the N-terminus of the peptide via a hydrophilic AEEA linker (2-aminoethoxy-2-ethoxy acetic acid; mini-PEG) resulted in a peptide, ShK-F6CA, with 100-fold specificity for Kv1.3 over Kv1.1 and related channels. Based on this surprising finding additional analogs were made. ShK-170 [a.k.a ShK(L5)],contains a L-phosphotyrosine in place of the fluorescein in ShK-F6CA. It blocks Kv1.3 with a Kd of 69 pM and shows exquisite specificity for Kv1.3. However, it is chemically unstable. To improve stability a new analog, ShK-186 [a.k.a. SL5], was made with the C-terminal carboxyl of ShK-170 replaced by an amide; ShK-186 is otherwise identical to ShK-170. However, ShK-186 is also chemically unstable. ShK-192 is a new analog with increased stability. It contains norleucine
21 in place of methionine
21 to avoid methionine oxidation, and the terminal phosphotyrosine is replaced by a non-hydrolyzable para-phosphonophenylalanine (Ppa) group. The D-diasteromer of ShK is also stable but blocks Kv1.3 with 2800-fold potency than the L-form (Kd = 36 nM) and it only exhibits 2-fold specificity for Kv1.3 over Kv1.1.
Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 regulate membrane potential
and calcium signaling
of T cell
s. Calcium entry through the CRAC channel is promoted by potassium efflux through the Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 potassium channels. Blockade of Kv1.3 channels in effector-memory T cells by ShK-186 suppresses calcium signaling, cytokine
production (interferon-gamma
, interleukin 2
) and cell proliferation. In vivo, ShK-186 paralyzes effector-memory T cells at the sites of inflammation and prevent their reactivation in inflamed tissues. In contrast, ShK-186 does not affect the homing to and motility within lymph nodes of naive and central memory T cells, most likely because these cells express the KCa3.1 channel and are therefore protected from the effect of Kv1.3 blockade. In proof-of-concept studies, ShK and its analogs have prevented and treated disease in rat models of multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and delayed type hypersensitivity.
As ShK toxin binds to the synaptosomal membranes, it facilitates an acetylcholine
release at avian neuromuscular junctions while the Kv3.2 channels are expressed in neurons that fire at a high frequency (such as cortical GABAergic interneurons), due to their fast activation and deactivation rates. By blocking Kv3.2, ShK toxin depolarises the cortical GABAergic interneurons. Kv3.2 is also expressed in pancreatic
beta cell
s. These cells are thought to play a role in their delayed-rectifier current, which regulates glucose-dependent firing. Therefore, ShK, as a Kv3.2 blocker, might be useful in the treatment of type-2 diabetes, although inhibition of the delayed-rectifier current has not yet been observed in human cells even when very high ShK concentrations were used.
ShK-Dap22 is less toxic, even a dose of 1.0 mg dose did not cause hyperactivity, seizures or mortality. The median paralytic dose was 200 mg/kg body weight.
ShK-170 [a.k.a. ShK(L5)] does not cause significant toxicity in vitro. The peptide was not toxic to human and rat lymphoid cells incubated for 48 h with 100 nM of ShK-170 (>1200 times greater than the Kv1.3 half-blocking dose). The same high concentration of ShK-170 was negative in the Ames test
on tester strain TA97A, suggesting that it is not a mutagen. ShK-170 had no effect on heart rate or heart rate variability parameters in either the time or the frequency domain in rats. It does not block the hERG
(Kv11.1) channel that is associated with drug-associated cardiac arrhythmias. Repeated daily administration of the peptide by subcutaneous injection (10 µg/kg/day) for 2 weeks to rats does not cause any changes in blood counts, blood chemistry or in the proportion of thymocyte or lymphocyte subsets. Furthermore, the rats administered the peptide gain weight normally.
ShK-186 [a.k.a. SL5] is also safe. Repeated daily administration by subcutaneous injection of ShK-186 (100 µg/kg/day) for 4 weeks to rats does not cause any changes in blood counts, blood chemistry or histopathology. Furthermore, ShK-186 did not compromise the protective immune response to acute influenza viral infection or acute bacterial (Chlamydia) infection at concentrations that were effective in ameliorating autoimmune diseases in rat models. Interestingly, rats repeatedly administered ShK-186 for a month by subcutaneous injection (500 µg/kg/day) did not develop anti-ShK antibodies. The reason for the low immunogenicity of the peptide is not well understood.
Many groups are developing Kv1.3 blockers for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
s, and these or related analogs might have use as therapeutics for human autoimmune diseases.
Kv1.3 is also considered a therapeutic target for the treatment of obesity
, for enhancing peripheral insulin sensitivity in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus
, and for preventing bone resorption
in periodontal disease. Furthermore, because pancreatic beta cell
s, which have Kv3.2 channels, are thought to play a role in glucose-dependent firing, ShK, as a Kv3.2 blocker, might be useful in the treatment of type-2 diabetes, although inhibition of the delayed-rectifier current has not yet been observed in human cells even when very high ShK concentrations were used.
Peptide
Peptides are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. They are distinguished from proteins on the basis of size, typically containing less than 50 monomer units. The shortest peptides are dipeptides, consisting of two amino acids joined by a single peptide bond...
toxin
Toxin
A toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; man-made substances created by artificial processes are thus excluded...
that blocks the voltage-gated potassium channel
Voltage-gated potassium channel
Voltage-gated potassium channels are transmembrane channels specific for potassium and sensitive to voltage changes in the cell's membrane potential. During action potentials, they play a crucial role in returning the depolarized cell to a resting state....
s: Kv1.1, Kv1.3
KCNA3
Potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 3, also known as KCNA3 or Kv1.3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the KCNA3 gene....
and Kv3.2
KCNC2
Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily C member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNC2 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a voltage-gated potassium channel subunit.-Expression pattern:...
.
Structure
ShK is a 35-residueResidue (chemistry)
In chemistry, residue is the material remaining after a distillation or an evaporation, or to a portion of a larger molecule, such as a methyl group. It may also refer to the undesired byproducts of a reaction....
basic peptide first discovered in the sea anemone
Sea anemone
Sea anemones are a group of water-dwelling, predatory animals of the order Actiniaria; they are named after the anemone, a terrestrial flower. Sea anemones are classified in the phylum Cnidaria, class Anthozoa, subclass Zoantharia. Anthozoa often have large polyps that allow for digestion of larger...
Stichodactyla helianthus
Stichodactyla helianthus
Stichodactyla helianthus is a sea anemone of the family Stichodactylidae. Helianthus stems from the Greek words ἡλιος , and ἀνθος, meaning flower. S. helianthus is also referred to as the 'sun anemone'. S. helianthus is a large, green, sessile, carpet-like sea anemone, from the Caribbean...
by Professor Olga Castaneda from the University of Havana, Cuba, and her collaborators in Sweden. It is cross-linked by three disulfide bridges: Cys3-Cys35, Cys12-Cys28, and Cys17-Cys32 (see figure below). The amino acid sequence of the ShK toxin is Arg-Ser-Cys-Ile-Asp-Thr-Ile-Pro-Lys-Ser-Arg-Cys-Thr-Ala-Phe-Gln-Cys-Lys-His-Ser-Met-Lys-Tyr-Arg-Leu-Ser-Phe-Cys-Arg-Lys-Thr-Cys-Gly-Thr-Cys. ShK is stabilized by three disulfide bridges and consists of two short α-helices
Alpha helix
A common motif in the secondary structure of proteins, the alpha helix is a right-handed coiled or spiral conformation, in which every backbone N-H group donates a hydrogen bond to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid four residues earlier...
comprising residues 14-19 and 21-24. The N-terminal eight residues of ShK adopt an extended conformation, followed by a pair of interlocking turns that resemble a 310 helix, while its C-terminal Cys35 residue forms a nearly head-to-tail cyclic structure through a disulfide bond with Cys3. Protein domains with structural resemblance to ShK have been described in 402 proteins, most of them from C. elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans is a free-living, transparent nematode , about 1 mm in length, which lives in temperate soil environments. Research into the molecular and developmental biology of C. elegans was begun in 1974 by Sydney Brenner and it has since been used extensively as a model...
. Other proteins containing domains with similar structures include the cysteine-rich secretory protein
Cysteine-rich secretory protein
Cysteine-rich secretory proteins, often abbreviated as CRISPs, are a group of glycoproteins found exclusively in vertebrates. They are a subgroup of the CRISP, antigen 5 and Pr-1 protein superfamily and are substantially implicated in the functioning of the mammalian reproductive system...
snake toxins natrin, triflin
Triflin
Triflin is a cysteine-rich secretory protein , which is excreted by the venom gland of the Habu snake . Triflin reduces high potassium-induced smooth muscle contraction, suggesting a blocking effect on L-type calcium channels.- Source :Triflin is a toxin derived from snake venom...
, and stecrisp, the Toxocara canis
Toxocara canis
Toxocara canis is worldwide distributed helminth parasite of dogs and other canids. T. canis are gonochorists, adult worms measure from 9 to 18 cm, are yellow-white in color, and occur in the intestine of the definitive host. In adult dogs, the infection is usually asymptomatic. By the...
mucin
Mucin
Mucins are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins produced by epithelial tissues in most metazoans. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in most gel-like secretions, serving functions from lubrication to cell...
s and the human protein Tpx-1
CRISP2
Cysteine-rich secretory protein 2 is a cysteine-rich secretory protein that in humans is encoded by the CRISP2 gene.-Further reading:...
.

Target
ShK toxin blocks the K+ channels Kv1.1, Kv1.3, Kv1.6 and Kv3.2 The peptide binds to all four subunits in the Kv1.3 tetramer through its interaction with the shallow vestibule at the outer entrance of the ion conduction pathway. The peptide's Lysine22 residue occludes the channel pore like a "cork in a bottle". This blocks the entrance to the pore.ShK blocks the Kv1.3 channel in T cells with a Kd of about 11 pM. It blocks the neuronal Kv1.1 and Kv1.6 channels with Kds of 16 pM and 200 pM respectively. The Kv3.2 and KCa3.1 channels are more than 1000 times less sensitive to the peptide.
Several ShK analogs have been generated to enhance specificity for the Kv1.3 channel over the Kv1.1, Kv1.6 and Kv3.2 channels. The first analog that showed some degree of specificity was ShK-Dap22. Attaching a fluorescein
Fluorescein
Fluorescein is a synthetic organic compound available as a dark orange/red powder soluble in water and alcohol. It is widely used as a fluorescent tracer for many applications....
to the N-terminus of the peptide via a hydrophilic AEEA linker (2-aminoethoxy-2-ethoxy acetic acid; mini-PEG) resulted in a peptide, ShK-F6CA, with 100-fold specificity for Kv1.3 over Kv1.1 and related channels. Based on this surprising finding additional analogs were made. ShK-170 [a.k.a ShK(L5)],contains a L-phosphotyrosine in place of the fluorescein in ShK-F6CA. It blocks Kv1.3 with a Kd of 69 pM and shows exquisite specificity for Kv1.3. However, it is chemically unstable. To improve stability a new analog, ShK-186 [a.k.a. SL5], was made with the C-terminal carboxyl of ShK-170 replaced by an amide; ShK-186 is otherwise identical to ShK-170. However, ShK-186 is also chemically unstable. ShK-192 is a new analog with increased stability. It contains norleucine
Leucines
The leucines are primarily the four isomeric amino acids: leucine, isoleucine, tert-leucine and norleucine. Being compared with the four butanols, they could be classified as butyl-substituted glycines; they represent all four possible variations....
21 in place of methionine
Methionine
Methionine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2SCH3. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. This amino-acid is coded by the codon AUG, also known as the initiation codon, since it indicates mRNA's coding region where translation into protein...
21 to avoid methionine oxidation, and the terminal phosphotyrosine is replaced by a non-hydrolyzable para-phosphonophenylalanine (Ppa) group. The D-diasteromer of ShK is also stable but blocks Kv1.3 with 2800-fold potency than the L-form (Kd = 36 nM) and it only exhibits 2-fold specificity for Kv1.3 over Kv1.1.
Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 regulate membrane potential
Membrane potential
Membrane potential is the difference in electrical potential between the interior and exterior of a biological cell. All animal cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with a variety of types of proteins embedded in it...
and calcium signaling
Calcium signaling
Calcium is a common signaling mechanism, as once it enters the cytoplasm it exerts allosteric regulatory effects on many enzymes and proteins...
of T cell
T cell
T cells or T lymphocytes belong to a group of white blood cells known as lymphocytes, and play a central role in cell-mediated immunity. They can be distinguished from other lymphocytes, such as B cells and natural killer cells , by the presence of a T cell receptor on the cell surface. They are...
s. Calcium entry through the CRAC channel is promoted by potassium efflux through the Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 potassium channels. Blockade of Kv1.3 channels in effector-memory T cells by ShK-186 suppresses calcium signaling, cytokine
Cytokine
Cytokines are small cell-signaling protein molecules that are secreted by the glial cells of the nervous system and by numerous cells of the immune system and are a category of signaling molecules used extensively in intercellular communication...
production (interferon-gamma
Interferon-gamma
Interferon-gamma is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. This interferon was originally called macrophage-activating factor, a term now used to describe a larger family of proteins to which IFN-γ belongs...
, interleukin 2
Interleukin 2
Interleukin-2 is an interleukin, a type of cytokine immune system signaling molecule, which is a leukocytotrophic hormone that is instrumental in the body's natural response to microbial infection and in discriminating between foreign and self...
) and cell proliferation. In vivo, ShK-186 paralyzes effector-memory T cells at the sites of inflammation and prevent their reactivation in inflamed tissues. In contrast, ShK-186 does not affect the homing to and motility within lymph nodes of naive and central memory T cells, most likely because these cells express the KCa3.1 channel and are therefore protected from the effect of Kv1.3 blockade. In proof-of-concept studies, ShK and its analogs have prevented and treated disease in rat models of multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and delayed type hypersensitivity.
As ShK toxin binds to the synaptosomal membranes, it facilitates an acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
The chemical compound acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter in both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system in many organisms including humans...
release at avian neuromuscular junctions while the Kv3.2 channels are expressed in neurons that fire at a high frequency (such as cortical GABAergic interneurons), due to their fast activation and deactivation rates. By blocking Kv3.2, ShK toxin depolarises the cortical GABAergic interneurons. Kv3.2 is also expressed in pancreatic
Pancreas
The pancreas is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine system of vertebrates. It is both an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin, as well as a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist...
beta cell
Beta cell
Beta cells are a type of cell in the pancreas located in the so-called islets of Langerhans. They make up 65-80% of the cells in the islets.-Function:...
s. These cells are thought to play a role in their delayed-rectifier current, which regulates glucose-dependent firing. Therefore, ShK, as a Kv3.2 blocker, might be useful in the treatment of type-2 diabetes, although inhibition of the delayed-rectifier current has not yet been observed in human cells even when very high ShK concentrations were used.
Toxicity
Toxicity of ShK toxin in mice is quite low. The median paralytic dose is about 25 mg/kg bodyweight (which translates to 0.5 mg per 20 g mouse). In rats the therapeutic safety index was greater than 75-fold.ShK-Dap22 is less toxic, even a dose of 1.0 mg dose did not cause hyperactivity, seizures or mortality. The median paralytic dose was 200 mg/kg body weight.
ShK-170 [a.k.a. ShK(L5)] does not cause significant toxicity in vitro. The peptide was not toxic to human and rat lymphoid cells incubated for 48 h with 100 nM of ShK-170 (>1200 times greater than the Kv1.3 half-blocking dose). The same high concentration of ShK-170 was negative in the Ames test
Ames test
The Ames test is a biological assay to assess the mutagenic potential of chemical compounds. A positive test indicates that the chemical is mutagenic and therefore may act as a carcinogen, since cancer is often linked to mutation. However, a number of false-positives and false-negatives are known...
on tester strain TA97A, suggesting that it is not a mutagen. ShK-170 had no effect on heart rate or heart rate variability parameters in either the time or the frequency domain in rats. It does not block the hERG
HERG
hERG is a gene that codes for a protein known as Kv11.1 potassium ion channel...
(Kv11.1) channel that is associated with drug-associated cardiac arrhythmias. Repeated daily administration of the peptide by subcutaneous injection (10 µg/kg/day) for 2 weeks to rats does not cause any changes in blood counts, blood chemistry or in the proportion of thymocyte or lymphocyte subsets. Furthermore, the rats administered the peptide gain weight normally.
ShK-186 [a.k.a. SL5] is also safe. Repeated daily administration by subcutaneous injection of ShK-186 (100 µg/kg/day) for 4 weeks to rats does not cause any changes in blood counts, blood chemistry or histopathology. Furthermore, ShK-186 did not compromise the protective immune response to acute influenza viral infection or acute bacterial (Chlamydia) infection at concentrations that were effective in ameliorating autoimmune diseases in rat models. Interestingly, rats repeatedly administered ShK-186 for a month by subcutaneous injection (500 µg/kg/day) did not develop anti-ShK antibodies. The reason for the low immunogenicity of the peptide is not well understood.
Many groups are developing Kv1.3 blockers for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Use
Because ShK toxin is a specific inhibitor of Kv1.1, Kv1.3, Kv1.6, Kv3.2 and KCa3.1, it may serve as a useful pharmacological tool for studying these channels. The Kv1.3 specific ShK analogs, ShK-170, ShK-186 and ShK-192, have been demonstrated to be effective in rat models of autoimmune diseaseAutoimmune disease
Autoimmune diseases arise from an overactive immune response of the body against substances and tissues normally present in the body. In other words, the body actually attacks its own cells. The immune system mistakes some part of the body as a pathogen and attacks it. This may be restricted to...
s, and these or related analogs might have use as therapeutics for human autoimmune diseases.
Kv1.3 is also considered a therapeutic target for the treatment of obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
, for enhancing peripheral insulin sensitivity in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus type 2
Diabetes mellitus type 2formerly non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus or adult-onset diabetesis a metabolic disorder that is characterized by high blood glucose in the context of insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. Diabetes is often initially managed by increasing exercise and...
, and for preventing bone resorption
Bone resorption
Bone resorption is the process by which osteoclasts break down bone and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone fluid to the blood....
in periodontal disease. Furthermore, because pancreatic beta cell
Beta cell
Beta cells are a type of cell in the pancreas located in the so-called islets of Langerhans. They make up 65-80% of the cells in the islets.-Function:...
s, which have Kv3.2 channels, are thought to play a role in glucose-dependent firing, ShK, as a Kv3.2 blocker, might be useful in the treatment of type-2 diabetes, although inhibition of the delayed-rectifier current has not yet been observed in human cells even when very high ShK concentrations were used.

