
Single-ended triode
Encyclopedia

Single-ended
Single-ended may refer to:* Single ended recuperative burner, a type of gas burner used in industrial furnaces* Single-ended signalling, the simplest commonly used method of transmitting electrical signals over wires* Single-ended triode, an audio amplifier...
triode
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplification device having three active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a vacuum tube with three elements: the filament or cathode, the grid, and the plate or anode. The triode vacuum tube was the first electronic amplification device...
(SET) vacuum tube
Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
electronic amplifier
Electronic amplifier
An electronic amplifier is a device for increasing the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude...
uses a single triode
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplification device having three active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a vacuum tube with three elements: the filament or cathode, the grid, and the plate or anode. The triode vacuum tube was the first electronic amplification device...
to produce an output, in contrast to a push-pull
Push-pull output
A push–pull output is a type of electronic circuit that can drive either a positive or a negative current into a load. Push–pull outputs are present in TTL and CMOS digital logic circuits and in some types of amplifiers, and are usually realized as a complementary pair of transistors, one...
amplifier which uses a pair of devices with antiphase inputs to generate an output with the wanted signals added and the distortion components subtracted. Single-ended amplifiers normally operate in Class A; the cancellation of distortion allows push-pull amplifiers also to operate in Classes AB or B without excessive net distortion. See power amplifier classes for a detailed discussion.
Most small-signal audio and radio frequency tube and discrete transistor amplifiers are single-ended, as distinct from balanced, class A.
The term single-ended triode amplifier is mainly used for output stages of audio
Sound recording and reproduction
Sound recording and reproduction is an electrical or mechanical inscription and re-creation of sound waves, such as spoken voice, singing, instrumental music, or sound effects. The two main classes of sound recording technology are analog recording and digital recording...
power amplifiers.
The phrase directly heated triode
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplification device having three active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a vacuum tube with three elements: the filament or cathode, the grid, and the plate or anode. The triode vacuum tube was the first electronic amplification device...
single-ended triode amplifier (abbreviated to DHT SET) is used when directly heated triodes are used.
There are also single-ended tetrode
Tetrode
A tetrode is an electronic device having four active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a two-grid vacuum tube. It has the three electrodes of a triode and an additional screen grid which significantly changes its behaviour.-Control grid:...
, beam tetrode
Beam tetrode
A beam tetrode is a type of vacuum tube specially designed to produce greater output power than a similar pentode...
/beam power tube/kinkless tetrode, and pentode
Pentode
A pentode is an electronic device having five active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a three-grid vacuum tube , which was invented by the Dutchman Bernhard D.H. Tellegen in 1926...
amplifiers with the same functionality and similar circuitry; e.g. this Mullard
Mullard
Mullard Limited was a British manufacturer of electronic components. The Mullard Radio Valve Co. Ltd. of Southfields, London, was founded in 1920 by Captain Stanley R. Mullard, who had previously designed valves for the Admiralty before becoming managing director of the Z Electric Lamp Co. The...
design.
An older, but quite different, use of the term single-ended was to distinguish tubes in which all pins were connected via the base from those that had a top cap for high-voltage (plate) or interference-susceptible (control grid
Control grid
The control grid is an electrode used in thermionic valves used to modulate the flow of electrons in the cathode to anode or plate circuit.- Operation :...
) electrodes.
Audio power amplifiers
A typical triodeTriode
A triode is an electronic amplification device having three active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a vacuum tube with three elements: the filament or cathode, the grid, and the plate or anode. The triode vacuum tube was the first electronic amplification device...
audio power amplifier will have a driver that provides voltage gain, coupled to a triode
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplification device having three active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a vacuum tube with three elements: the filament or cathode, the grid, and the plate or anode. The triode vacuum tube was the first electronic amplification device...
(like 2A3 and 300B
300B
The 300B is a directly heated power triode using a four pin base, introduced in 1937 to amplify telephone signals. It measures 6.4 inches high and 2.4 inches wide, and has a 40 watt anode dissipation. In the 1980s use of 300Bs by audiophiles had grown. The 300Bs used by these audiophiles...
) or a pentode or kinkless tetrode such as EL34
EL34
The EL34 is a thermionic valve or vacuum tube of the power pentode type. It has an international octal base and is found mainly in the final output stages of audio amplification circuits and was designed to be suitable as a series regulator by virtue of its high permissible voltage between heater...
or KT88
KT88
The KT88 is a beam tetrode/kinkless tetrode vacuum tube for audio amplification.- Features :The KT88 fits a standard eight-pin octal socket and has similar pinout and applications as the 6L6 and EL34. Specifically designed for audio amplification, the KT88 has similar ratings to the American 6550...
connected as a triode
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplification device having three active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a vacuum tube with three elements: the filament or cathode, the grid, and the plate or anode. The triode vacuum tube was the first electronic amplification device...
, connected to the loudspeaker
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
through an audio transformer in a common cathode arrangement. The triode
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplification device having three active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a vacuum tube with three elements: the filament or cathode, the grid, and the plate or anode. The triode vacuum tube was the first electronic amplification device...
is biased to Class A operation by applying a suitable negative bias voltage to its input grid
Grid
Grid or The Grid may refer to:In entertainment and media:* The Grid, an electronic dance group* Kevorkian Death Cycle, a music group formerly called Grid* The Grid , a 2001 third person shooter...
(see diagram), or by raising the cathode potential with biasing components.
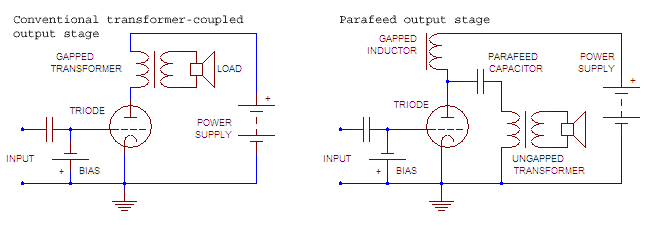
In traditional SET amp, the direct current of output triode
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplification device having three active electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a vacuum tube with three elements: the filament or cathode, the grid, and the plate or anode. The triode vacuum tube was the first electronic amplification device...
(from 30 mA for triode-strapped 6V6
6V6
The 6V6 is a beam-power tetrode, introduced by Radio Corporation of America RCA United States in late 1937, and still in use in niche applications.Similar to its predecessor the 6L6, the 6V6 was far more widely used...
to 250 mA for 6C33C) flows continuously through the primary winding of a transformer. This requires inserting a gap in the transformer core to prevent core saturation
Saturation (magnetic)
Seen in some magnetic materials, saturation is the state reached when an increase in applied external magnetizing field H cannot increase the magnetization of the material further, so the total magnetic field B levels off...
by DC current; adding a gap decreases primary inductance
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
and limits bass response; the inductance and bass response can be restored by using a larger transformer than if the DC were not present.
An alternative schematic, parafeed amplifier, solves bandwidth problem by blocking direct current from output transformer (which does not need to be gapped, thus improving its bass response). Power supply is reconfigured into a constant current source, usually with a massive, high-inductance anode choke (gapped inductor
Inductor
An inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in a magnetic field. An inductor's ability to store magnetic energy is measured by its inductance, in units of henries...
), so there is little, if any, gain in cost and weight of magnetic components.
A stereo class A single-ended design with KT88
KT88
The KT88 is a beam tetrode/kinkless tetrode vacuum tube for audio amplification.- Features :The KT88 fits a standard eight-pin octal socket and has similar pinout and applications as the 6L6 and EL34. Specifically designed for audio amplification, the KT88 has similar ratings to the American 6550...
kinkless tetrodes which produces 15W of output power per channel, and 5W when triode-connected, is the Antique Sound Lab MG-SI15DT. By comparison a pair of the same tubes in class AB push-pull claim to output about 50W at 1% distortion (higher powers at high distortion are quoted for guitar amplifier
Guitar amplifier
A guitar amplifier is an electronic amplifier designed to make the signal of an electric or acoustic guitar louder so that it will produce sound through a loudspeaker...
s).
Benefits
- Simplicity. An audio amplifier cannot be much simpler than a Class A single-ended.
- Overall low harmonic distortion with small signals. By nature Class A amplifiers do not suffer from crossover distortion.
- Small roaming of anode bias current does not do anything catastrophic.
Drawbacks
- Low efficiency. All Class A amplifiers consume power regardless of the signal amplitude.
- Second harmonic distortion at high signal level is a normal feature of single-ended amplifiers.
- Compared to the amplifier's low power the output transformer is heavy and expensive.
Speaker matching
Historically, negative feedback in single ended pentode amplifiers was quite common (for example, the Mullard 3-3 design built around EL84EL84
The EL84 is a vacuum tube of the power pentode type. It has a 9 pin Noval base and is found mainly in the final output stages of amplification circuits, most commonly now in guitar amplifiers, but originally in radios and many other devices of the pre-transistor era.It was developed to eliminate...
). Today negative feedback is less popular with SET amplifiers, with many having no overall feedback loop. Their frequency response, limited by transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
passband, is then modulated by irregularities in loudspeaker
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
. This, and the very low attainable power levels (3 Watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s for 2A3 to 20 Watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s for 6C33C), requires careful matching of amplifier to speakers; selection is usually limited to high-efficiency loudspeakers with a sensitivity
Sensitivity (electronics)
The sensitivity of an electronic device, such as a communications system receiver, or detection device, such as a PIN diode, is the minimum magnitude of input signal required to produce a specified output signal having a specified signal-to-noise ratio, or other specified criteria.Sensitivity is...
exceeding 90 dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
/Watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
.
Audio quality
Single-ended triode (SET) amplifiers are considered a classic design among certain audiophileAudiophile
An audiophile is a person who enjoys listening to recorded music, usually in a home. Some audiophiles are more interested in collecting and listening to music, while others are more interested in collecting and listening to audio components, whose "sound quality" they consider as important as the...
s and have achieved a cult status because of their excellent midband performance (argued to be the most important part of the audio spectrum in music reproduction), musicality, and directness. This perceived high sonic quality is mainly attributed to the simplicity and minimalistic approach of the circuits involved and the triode amplifying tubes that are typically used.
The configuration will generally provide higher measured distortion performance compared to high feedback amplifiers. This distortion is predominantly second harmonic which is not unpleasant to the ear (the second harmonic for an A on the musical scale at 440Hz is 880Hz which is, obviously, also an A i.e., the same note just an octave higher). In a push pull amplifier this second harmonic distortion is canceled in the output transformer. Several percent THD is not unusual at full power output, but will be much lower at normal music levels. Most builders and users have concluded that while global feedback reduces distortion across the harmonic range, it also reduces the dramatic dynamics associated with a SET amplifier and the highly efficient speaker needed to enjoy a low power amplifier.
Estimating power output for a Class A1 amplifier from valve specs
In class A, in order to produce a full sine wave, the tube must be exactly half-way on. Therefore the maximum current swing is +/- 50%. No actual amplifier will ever achieve this.Obtain the following parameters:
- Pa (or P[a+g2] for pentodes) (in watts).
- Rp in triode (in ohms),
- load resistance (Rl) (in ohms) (which may vary depending on the design.)
Compute maximum theoretical power output by P[ot] = Pa / 2.
While the valve can be driven all the way to shut-off fairly easily, the maximum current will be limited by the internal resistance of the valve as the grid reaches the voltage of the cathode and is not impeding electron flow. For this reason, valves that have a low Rp can yield more power in class A1 than other valves with similar Pa ratings.
Next, compute P[o] = P[ot] * (1 - Rp/Rl) to obtain an estimate of the maximum obtainable output power.
Deduct 10% from this figure to account for the relatively heavy distortion encountered as the valve approaches cut-off.
Class A2
Class A2 amplifiers can overcome a high Rp by driving the grid positive with respect to the cathode. Because this makes the grid a secondary anode, it too will draw current from the cathode while accelerating the remaining electrons towards the plate. Grid currents can place extreme demands on the driving circuitry, sometimes requiring as much as 8 watts input for larger tubes such as the 211.See also
- Valve sound
- High-end audioHigh-end audioHigh-end audio is a term used to describe a class of consumer home audio equipment marketed to audio enthusiasts on the basis of high price or quality, and esoteric or novel sound reproduction technologies. High-end audio can refer simply to the price, to the build quality of the components, or to...
- European triode festivalEuropean triode festivalSince 2000 each year the "European Triode Festival" has been held in various venues in Europe Since 2000 each year the "European Triode Festival" (ETF) has been held in various venues in Europe Since 2000 each year the "European Triode Festival" (ETF) has been held in various venues in Europe (the...
- List of vacuum tubes
External links
- www.pmillett.com A public domain depository for various audio designs and projects, including tubes and SET.
- www.enjoythemusic.com Article titled "Why The SET And Efficient Loudspeaker Approach Works".
- The Single-Ended Amplifier: Cary's Dennis Had in Stereophile, September, 1995

