
Residual-current device
Encyclopedia

A Residual-Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) is an electrical wiring
Electrical wiring
Electrical wiring in general refers to insulated conductors used to carry electricity, and associated devices. This article describes general aspects of electrical wiring as used to provide power in buildings and structures, commonly referred to as building wiring. This article is intended to...
device that disconnects a circuit whenever it detects that the electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
is not balanced between the energized conductor and the return neutral
Ground and neutral
Since the neutral point of an electrical supply system is often connected to earth ground, ground and neutral are closely related. Under certain conditions, a conductor used to connect to a system neutral is also used for grounding of equipment and structures...
conductor. Such an imbalance may indicate current leakage through the body of a person who is grounded and accidentally touching the energized part of the circuit. A lethal shock
Electric shock
Electric Shock of a body with any source of electricity that causes a sufficient current through the skin, muscles or hair. Typically, the expression is used to denote an unwanted exposure to electricity, hence the effects are considered undesirable....
can result from these conditions. RCCBs are designed to disconnect quickly enough to prevent injury caused by such shocks. They are not intended to provide protection against overcurrent
Overcurrent
In electricity supply, overcurrent or excess current is a situation where a larger than intended electric current exists through a conductor, leading to excessive generation of heat, and the risk of fire or damage to equipment. Possible causes for overcurrent include short circuits, excessive load,...
(overload) or short-circuit conditions.
In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, a residual current device is most commonly known as a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI), ground fault interrupter (GFI) or an appliance leakage current interrupter (ALCI). In Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
they are sometimes known as "safety switches" or simply "RCD" and in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, along with circuit breakers
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
, they can be referred to as "trips" or "trip switches".
A Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overload protection (RCBO) combines the functions of overcurrent protection and leakage detection. An earth leakage circuit breaker
Earth leakage circuit breaker
An Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker is a safety device used in electrical installations with high earth impedance to prevent shock. It detects small stray voltages on the metal enclosures of electrical equipment, and interrupts the circuit if a dangerous votlage is detected...
(ELCB) may be a residual-current device, although an older type of voltage-operated earth leakage circuit breaker exists.
Purpose and operation
RCDs are designed to prevent electrocutionElectric shock
Electric Shock of a body with any source of electricity that causes a sufficient current through the skin, muscles or hair. Typically, the expression is used to denote an unwanted exposure to electricity, hence the effects are considered undesirable....
by detecting the leakage current, which can be far smaller (typically 5–30 milliamperes) than the currents needed to operate conventional circuit breakers or fuses (several amperes). RCDs are intended to operate within 25-40 milliseconds, before electric shock can drive the heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
into ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation is a condition in which there is uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart, making them quiver rather than contract properly. Ventricular fibrillation is a medical emergency and most commonly identified arrythmia in cardiac arrest...
, the most common cause of death through electric shock. In Europe, the commonly used RCDs have trip currents of 10–300 mA.
RCDs operate by measuring the current balance between two conductors using a differential current transformer
Current transformer
In electrical engineering, a current transformer is used for measurement of electric currents. Current transformers, together with voltage transformers , are known as instrument transformers...
. This measures the difference between the current flowing out the live conductor
Live wire (electricity)
The live wire in an AC electrical circuit refers to the wire which carries an oscillating voltage with respect to the earth...
and that returning through the neutral conductor. If these do not sum to zero, there is a leakage of current to somewhere else (to earth/ground, or to another circuit), and the device will open its contacts.
Residual current detection is complementary to over-current detection. Residual current detection cannot provide protection for overload or short-circuit currents, except for the special case of a short circuit from live to ground (not live to neutral).
For a RCD used with three-phase power, all live conductors and the neutral must pass through the current transformer.
Typical features
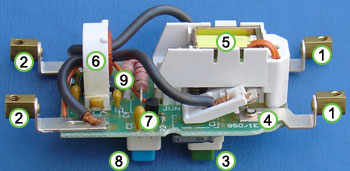
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
s and is designed to trip on a leakage current of 30 mA. This is an active RCD; that is, it latches mechanically and therefore trips on power failure, a useful feature for equipment that could be dangerous on unexpected re-energisation.
The incoming supply and the neutral conductors are connected to the terminals at (1) and the outgoing load conductors are connected to the terminals at (2). The earth conductor (not shown) is connected through from supply to load uninterrupted.
When the reset button (3) is pressed the contacts
Electrical connector
An electrical connector is an electro-mechanical device for joining electrical circuits as an interface using a mechanical assembly. The connection may be temporary, as for portable equipment, require a tool for assembly and removal, or serve as a permanent electrical joint between two wires or...
((4) and hidden behind (5)) close, allowing current to pass. The solenoid
Solenoid
A solenoid is a coil wound into a tightly packed helix. In physics, the term solenoid refers to a long, thin loop of wire, often wrapped around a metallic core, which produces a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it. Solenoids are important because they can create...
(5) keeps the contacts closed when the reset button is released.
The sense coil (6) is a differential current transformer which surrounds (but is not electrically connected to) the live and neutral conductors. In normal operation, all the current down the live conductor returns up the neutral conductor. The currents in the two conductors are therefore equal and opposite and cancel each other out.
Any fault to earth (for example caused by a person touching a live component in the attached appliance) causes some of the current to take a different return path which means there is an imbalance (difference) in the current in the two conductors (single phase case), or, more generally, a nonzero sum of currents from among various conductors (for example, three phase conductors and one neutral conductor).
This difference causes a current in the sense coil (6) which is picked up by the sense circuitry (7). The sense circuitry then removes power from the solenoid (5) and the contacts (4) are forced apart by a spring
Spring (device)
A spring is an elastic object used to store mechanical energy. Springs are usually made out of spring steel. Small springs can be wound from pre-hardened stock, while larger ones are made from annealed steel and hardened after fabrication...
, cutting off the electricity supply to the appliance.
The device is designed so that the current is interrupted in milliseconds, greatly reducing the chances of a dangerous electric shock
Electric shock
Electric Shock of a body with any source of electricity that causes a sufficient current through the skin, muscles or hair. Typically, the expression is used to denote an unwanted exposure to electricity, hence the effects are considered undesirable....
being received.
The test button (8) allows the correct operation of the device to be verified by passing a small current through the orange test wire (9). This simulates a fault by creating an imbalance in the sense coil. If the RCD does not trip when this button is pressed then the device must be replaced.
Form factors
A Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI in USA) and Residual Current Breaker with Overload (RCBO in Europe) are devices which combines Residual Current Device (RCD) with a Circuit BreakerCircuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
or miniature circuit breaker (MCB) which both detects supply imbalance and limits the current that may supplied.
In Europe RCDs can fit on the same DIN rail
DIN rail
A DIN rail is a metal rail of a standard type widely used for mounting circuit breakers and industrial control equipment inside equipment racks...
as the MCBs, however the busbar arrangements in consumer unit
Consumer unit
A consumer unit is a box of fuses or breakers, usually arranged in a single row. This is unlike a distribution board which has multiple rows of fuses or breakers and usually serves two or more locations, which may be split phase, two phase, two phases taken from three phase, or three phases.A...
s and distribution board
Distribution board
A distribution board is a component of an electricity supply system which divides an electrical power feed into subsidiary circuits, while providing a protective fuse or circuit breaker for each circuit, in a common enclosure...
s can make it awkward to use them in this way. If it is desired to protect an individual circuit an RCBO (Residual-current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent protection) can be used. This incorporates an RCD and a miniature circuit breaker in one device.
Electrical plugs which incorporate an RCD are sometimes installed on appliances which might be considered to pose a particular safety hazard, for example long extension leads which might be used outdoors or garden equipment or hair dryers which may be used near a tub or sink. Occasionally an in-line RCD may be used to serve a similar function to one in a plug. By putting the RCD in the extension lead protection is provided at whatever outlet is used even if the building has old wiring.
Electrical sockets with included RCDs are becoming common.
Combined with over current devices
Residual current and overcurrent protection may be combined in one device for installation into the service panel; this device is known as a GFCI breaker (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) in USA/Canada and as an RCBO (Residual current circuit breaker with overload protection) in Europe. In the US, RCBOs are more expensive than RCD outlets.As well as requiring both line and neutral (or 3-phase) input and output, GFCI/RCBO devices require a functional earth (FE) connection. For reasons of space some devices use flying leads rather than screw terminals, especially for the neutral input and FE connections.
More than one RCD feeding another is unnecessary, provided they have been wired properly. One exception is the case of a TT earthing system where the earth loop impedance may be high, meaning that a ground fault might not cause sufficient current to trip an ordinary circuit breaker or fuse. In this case a special 100 mA (or greater) trip current time-delayed RCD is installed covering the whole installation and then more sensitive RCDs should be installed downstream of it for sockets and other circuits which are considered high risk.
Testing
RCDs can be tested with the built-in test button to confirm functionality on a regular basis. RCDs if wired improperly may not operate correctly and are generally tested by the installer to verify correct operation. Use of a solenoid voltmeterSolenoid voltmeter
A solenoid voltmeter is a specific type of voltmeter used by electricians in the testing of electrical power circuits.Wiggy is the registered trademark for a common solenoid voltmeter used in North America derived from a device patented in 1918 by George P. Wigginton...
from live to earth provides an external path and can test the wiring to the RCD. Such a test may be performed on installation of the device and at any "downstream" outlet.
Limitations
A residual current circuit breaker cannot remove all risk of electric shock or fire. In particular, an RCD alone will not detect overload conditions, phase to neutral short circuits or phase-to-phase short circuits (see three phase electric power). Over-current protection (fuseFuse (electrical)
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is a type of low resistance resistor that acts as a sacrificial device to provide overcurrent protection, of either the load or source circuit...
s or circuit breaker
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
s) must be provided. Circuit breakers that combine the functions of an RCD with overcurrent protection respond to both types of fault. These are known as RCBOs, and are available in 1, 2, 3 and 4 pole configurations. RCBOs will typically have separate circuits for detecting current imbalance and for overload current but will have a common interrupting mechanism.
An RCD will help to protect against electric shock where current flows through a person from a phase (live / line / hot) to earth. It cannot protect against electric shock where current flows through a person from phase to neutral or phase to phase, for example where a finger touches both live and neutral contacts in a light fitting; a device can not differentiate between current flow through an intended load from flow through a person.
Whole installations on a single RCD, common in the UK, are prone to nuisance trips that can cause safety problems with loss of lighting and defrosting of food. RCDs also cause nuisance trips with appliances where earth leakage is common and not a cause of injury or mortality, such as water heaters.
A dangerous condition can arise if the neutral wire is broken or switched off before the RCD while its live wire is not interrupted. In this situation the tripping circuitry of the RCD that needs power to be supplied will cease to work. The circuit will look like it is switched off, but if someone touches the live wire thinking that it is de-energized, the RCD will not trip. For this reason circuit breakers must be installed in a way that ensures that the neutral wire is turned off only at the moment when the live wire is also turned off. Separate single-pole circuit breakers must never be used for live and neutral, only two or four pole breakers must be used in cases there is a need for switching off the neutral wire.
Number of poles
RCDs may comprise two poles for use on single phase supplies (two current paths), three poles for use on three phase supplies (three current paths) or four poles for use on three phase & neutral supplies (four current paths).Rated current
The rated current of an RCD is chosen according to the maximum sustained load current it will carry (if the RCD is connected in series with, and downstream of a circuit-breaker, the rated current of both items shall be the same).Sensitivity
RCD sensitivity is expressed as the rated residual operating current, noted IΔn. Preferred values have been defined by the IEC, thus making it possible to divide RCDs into three groups according to their IΔn value.- High sensitivity (HS): 6 – 10 – 30 mA (for direct-contact / life injury protection)
- Medium sensitivity (MS): 100 – 300 – 500 – 1000 mA (for fire protection)
- Low sensitivity (LS): 3 – 10 – 30 A (typically for protection of machine)
Type
Standard IEC 60755 (General requirements for residual current operated protective devices) defines three types of RCD depending on the characteristics of the fault current.- Type AC: RCD for which tripping is ensured for residual sinusoidal alternating currents
- Type A: RCD for which tripping is ensured
- for residual sinusoidal alternating currents
- for residual pulsating direct currentPulsating direct currentA pulsating direct current is a direct current that changes in value at regular or irregular intervals.A pulsating direct current may change in value, i.e., be always present but at different levels, or it may be a current that is interrupted completely at regular or irregular intervals, but when...
s - for residual pulsating direct currents superimposed by a smooth direct current of 0.006 A, with or without phase-angle control, independent of the polarity
- Type B: RCD for which tripping is ensured
- as for type A
- for residual sinusoidal currents up to 1000 Hz
- for residual sinusoidal currents superposed by a pure direct current
- for pulsating direct currents superposed by a pure direct current
- for residual currents which may result from rectifying circuits
- three pulse star connection or six pulse bridge connection
- two pulse bridge connection line-to-line with or without phase-angle monitoring, independently of the polarity
Break time
There are two groups of devices:- G (general use) for instantaneous RCDs (i.e. without a time delay)
- Minimum break time: immediate
- Maximum break time: 200 ms for 1x IΔn, 150 ms for 2x IΔn, and 40 ms for 5x IΔn
- S (selective) or T (time delayed) for RCDs with a short time delay (typically used in circuits containing surge suppressors)
- Minimum break time: 130 ms for 1x IΔn, 60 ms for 2x IΔn, and 50 ms for 5x IΔn
- Maximum break time: 500 ms for 1x IΔn, 200 ms for 2x IΔn, and 150 ms for 5x IΔn
Surge current resistance
The surge current refers to the peak current an RCD is designed to withstand using a test impulse of specified characteristics ( an 8/20 µs impulse, named after the time constantTime constant
In physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek letter \tau , is the risetime characterizing the response to a time-varying input of a first-order, linear time-invariant system.Concretely, a first-order LTI system is a system that can be modeled by a single first order...
s of the rise and fall of current).
The IEC 61008 and IEC 61009 standards impose the use of a 0.5 µs/ 100 kHz damped oscillator wave (ring wave) to test the ability of residual current protection devices to withstand operational discharges with a peak current equal to 200 A. With regard to atmospheric discharges, IEC 61008 and 61009 standards establish the 8/20 µs surge current test with 3000 A peak current but limit the requirement to RCDs classified as Selective.
History and nomenclature
The world’s first high-sensitivity earth leakage protection system (i.e. a system capable of protecting people from the hazards of direct contact between a live conductor and earth), was a second-harmonic magnetic amplifier core-balance system, known as the magamp, developed in South AfricaSouth Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
by Henri Rubin. Electrical hazards were of great concern in South African gold mines, and Rubin, an engineer at the company F.W.J. Electrical Industries, initially developed a cold-cathode system in 1955 which operated at 525 V and had a tripping sensitivity of 250 mA. Prior to this, core balance earth leakage protection systems operated at sensitivities of about 10 A.
The cold cathode system was installed in a number of gold mines and worked reliably. However, Rubin began working on a completely novel system with greatly improved sensitivity, and by early 1956, he had produced a prototype second-harmonic magnetic amplifier-type core balance system (South African Patent No. 2268/56 and Australian Patent No. 218360). The prototype magamp was rated at 220V 60A and had an internally adjustable tripping sensitivity of 12.5 to 17.5 mA. Very rapid tripping times were achieved through a novel design, and this combined with the high sensitivity was well within the safe current-time envelope for ventricular fibrillation determined by Charles Dalziel
Charles Dalziel
Charles Dalziel was a professor of electrical engineering and computer sciencesat UC Berkeley. According to volume 54 of UCB's Blue and Gold, Dalziel graduated with a Mechanics degree in 1927 and was from Santa Maria, CA...
of the University of California, Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley , is a teaching and research university established in 1868 and located in Berkeley, California, USA...
, USA, who had estimated electrical shock hazards in humans. This system, with its associated circuit breaker, included overcurrent and short-circuit protection. In addition, the original prototype was able to trip at a lower sensitivity in the presence of an interrupted neutral, thus protecting against an important cause of electrical fire.
Following the accidental electrocution of a woman in a domestic accident at the Stilfontein gold mining village near Johannesburg
Johannesburg
Johannesburg also known as Jozi, Jo'burg or Egoli, is the largest city in South Africa, by population. Johannesburg is the provincial capital of Gauteng, the wealthiest province in South Africa, having the largest economy of any metropolitan region in Sub-Saharan Africa...
, a few hundred F.W.J. 20 mA magamp earth leakage protection units were installed in the homes of the mining village during 1957 and 1958. F.W.J. Electrical Industries, which later changed its name to FW Electrical Industries, continued to manufacture 20 mA single phase and three phase magamp units.
At the time that he worked on the magamp, Rubin also considered using transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s in this application, but concluded that the early transistors then available were too unreliable. However, with the advent of improved transistors, the company that he worked for and other companies later produced transistorized versions of earth leakage protection.
In 1961, Charles F. Dalziel, working with Rucker Manufacturing Co., developed a transistorized device for earth leakage protection which became known as a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI), sometimes colloquially shortened to Ground Fault Interrupter (GFI). This name for high-sensitivity earth leakage protection is still in common use in the U.S.A.
In the early 1970s most GFCI devices were of the circuit breaker type. However the most commonly used in the USA since the early 1980s are built into outlet receptacles. The problem with those of the circuit breaker type was that of many false trips due to the poor alternating current characteristics of 120 volt insulations, especially in circuits having longer cable lengths. So much current leaked along the length of the conductors' insulation that the breaker might trip with the slightest increase of current imbalance.
Regulation and adoption
Rules and regulations, as well as adoption and specific application, differ widely from country to country. In most countries, not all circuits in a home are protected by RCDs.If a single RCD is installed for an entire electrical installation, any fault will cut all power to the premises.
Australia
In Australia, they have been mandatory in all new houses since 1991 on all power and lighting circuits.Germany
Germany requires the use of RCDs on sockets up to 20A which are for general use. This rule was introduced in June 2007 (DINDin
DIN or Din or din can have several meanings:* A din is a loud noise.* Dīn, an Arabic term meaning "religion" or "way of life".* Din is one of the ten aspects of the Ein Sof in Kabbalah ....
VDE 0100-410 Nr. 411.3.3).
Norway
In Norway, it has been required in all new homes since 2002, and on all new sockets since 2006.United Kingdom
The UK has only mandated the use of RCDs in new installations since July 2008. In the 16th Edition of the IEE Electrical Wiring Regulations, they were used to add extra fault protection to socket outlets. The current edition (17th) of the regulations state that all new installations, as well as a change of distribution board or the installation of new circuits in a property wired to any previous installation, must have a split load distribution board with two RCDs covering the installation, with upstairs and downstairs lighting and power circuits spread across both RCDs in case of a fault on one RCD, therefore leaving power to at least one lighting and power circuit.Normal practice in domestic installations in the UK was to use a single RCD for all RCD protected circuits but to have some circuits that are not protected at all (sockets usually are on the RCD; lamp holders usually aren't; other circuits vary by who installed the system). Regulation introduced in 2008 dictate that on all new electrical installations in the UK, all circuits must be protected by an RCD however, this does not affect existing installations.
It is common to install an RCD in a consumer unit
Consumer unit
A consumer unit is a box of fuses or breakers, usually arranged in a single row. This is unlike a distribution board which has multiple rows of fuses or breakers and usually serves two or more locations, which may be split phase, two phase, two phases taken from three phase, or three phases.A...
in what is known as a split load configuration where one group of circuits is just on the main switch (or time delay RCD in the case of a TT earth) and another group is on the RCD.
North America
In North America, RCD (“GFCI”) sockets are usually of the DecoraLeviton
Leviton Manufacturing Company, Inc., is the largest privately held manufacturer of electrical wiring equipment in North America. It produces electrical products: light sockets, receptacles , dimmers and other lighting control systems, wire, power cables, power cords, wall and ceiling occupancy...
form (which harmonizes outlets and switches, so that there is no difference between an outlet cover and a switch cover). For example, using the decora size outlets, RCD outlets can be mixed with regular outlets or with switches in a multigang box with a standard cover plate.
In Canada and the United States, two-wire (ungrounded) outlets may be replaced with three-wire GFCIs to protect against electrocution, and a grounding wire does not need to be supplied to that GFCI. The outlet must be labeled as such. The GFCI manufacturers provide tags for the appropriate installation description.
United States
GFI receptacles in the USA have connections to protect downstream receptacles so that all outlets on a circuit may be protected by one GFI outlet.In the United States, the National Electrical Code requires GFCI devices intended to protect people to interrupt the circuit if the leakage current exceeds a range of 4–6 mA of current (the trip setting is typically 5 mA) within 25 ms. A GFCI device which protects equipment (not people) is allowed to trip as high as 30 mA of current; this is known as an Equipment Protective Device (EPD). "RCDs" with trip currents as high as 500 mA are sometimes deployed in environments (such as computing centers) where a lower threshold would carry an unacceptable risk of accidental trips. These high-current RCDs serve for equipment and fire protection instead of protection against the risks of electrical shocks.
GFCI outlets are required by law in wet areas (See National Electrical Code (US)
National Electrical Code (US)
The National Electrical Code , or NFPA 70, is a regionally adoptable standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment...
for details.)
In the U.S.
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, the National Electrical Code
National Electrical Code (US)
The National Electrical Code , or NFPA 70, is a regionally adoptable standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment...
requires GFCIs for underwater swimming pool lights (1968); construction sites (1974); bathrooms and outdoor areas (1975); garages (1978); near hot tubs or spas (1981); hotel bathrooms (1984); kitchen counter receptacles (1987, revised 1996 and specifically excluding the refrigerator outlet, which is usually on a dedicated circuit); crawl spaces and unfinished basements (1990); wet bar sinks (1993); laundry sinks (2005).
Related technologies
A related electrical safety device is the arc-fault circuit interrupterArc-fault circuit interrupter
An Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter is a circuit breaker designed to prevent fires by detecting a non-working electrical arc and disconnecting the power before the arc starts a fire...
(AFCI) which detects electrical arcing due to loose or corroded wiring connections, which can cause building fires.
See also
- Earth leakage circuit breakerEarth leakage circuit breakerAn Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker is a safety device used in electrical installations with high earth impedance to prevent shock. It detects small stray voltages on the metal enclosures of electrical equipment, and interrupts the circuit if a dangerous votlage is detected...
- Arc-fault circuit interrupterArc-fault circuit interrupterAn Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter is a circuit breaker designed to prevent fires by detecting a non-working electrical arc and disconnecting the power before the arc starts a fire...
— protects against electrical arcing due to bad wiring - Insulation monitoring deviceInsulation monitoring deviceAn insulation monitoring device monitors the ungrounded system between an active phase conductor and earth. It is intended to give an alert or disconnect the power supply when the impedance between the two conductors drops below a set value, usually 50 kΩ.The main advantage of the device that it...
- Circuit breakerCircuit breakerA circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
— protects against overload and short-circuit conditions - Fuse (electrical)Fuse (electrical)In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is a type of low resistance resistor that acts as a sacrificial device to provide overcurrent protection, of either the load or source circuit...
— protects against overload and short-circuit conditions - Domestic AC power plugs and socketsDomestic AC power plugs and socketsAC power plugs and sockets are devices for removably connecting electrically operated devices to the power supply. Electrical plugs and sockets differ by country in rating, shape, size and type of connectors...

