
Fuse (electrical)
Encyclopedia

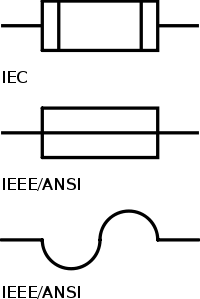
In electronics
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
and electrical engineering
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
, a fuse (from the French fusée, Italian. fuso, "spindle") is a type of low resistance resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
that acts as a sacrificial device to provide overcurrent
Overcurrent
In electricity supply, overcurrent or excess current is a situation where a larger than intended electric current exists through a conductor, leading to excessive generation of heat, and the risk of fire or damage to equipment. Possible causes for overcurrent include short circuits, excessive load,...
protection, of either the load or source circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows, which interrupts the circuit
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
in which it is connected. Short circuit
Short circuit
A short circuit in an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path, often where essentially no electrical impedance is encountered....
, overloading, mismatched loads or device failure are the prime reasons for excessive current.
A fuse interrupts excessive current (blows) so that further damage by overheating or fire
Fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material in the chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products. Slower oxidative processes like rusting or digestion are not included by this definition....
is prevented. Wiring regulations often define a maximum fuse current rating for particular circuits. Overcurrent protection devices are essential in electrical systems to limit threats to human life and property damage. Fuses are selected to allow passage of normal current plus a marginal percentage and to allow excessive current only for short periods. Slow blow fuses are designed to allow higher currents for a modest amount of time longer, and such considerations are and were commonly necessary when electronics devices or systems had electronic tube tech or a large number of incandescent lights were being powered such as in a large hall, theater or stadium. Tubes and incandescent lights each have reduced current needs as they heat up to operating temperatures for their internal resistance grows as they are heated— the same physics principle causes the fuse material to melt, disconnecting the circuit from power.
In 1847, Breguet
Louis-François-Clement Breguet
Louis Francois Clement Breguet , was a French physicist and watchmaker, noted for his work in the early days of telegraphy...
recommended use of reduced-section conductors to protect telegraph stations from lightning strikes; by melting, the smaller wires would protect apparatus and wiring inside the building. A variety of wire or foil fusible elements were in use to protect telegraph cables and lighting installations as early as 1864.
A fuse was patented by Thomas Edison
Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices that greatly influenced life around the world, including the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and a long-lasting, practical electric light bulb. In addition, he created the world’s first industrial...
in 1890 as part of his successful electric distribution system.
Operation
A fuse consists of a metal strip or wire fuse element, of small cross-section compared to the circuit conductors, mounted between a pair of electrical terminals, and (usually) enclosed by a non-combustible housing. The fuse is arranged in series
Series and parallel circuits
Components of an electrical circuit or electronic circuit can be connected in many different ways. The two simplest of these are called series and parallel and occur very frequently. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the...
to carry all the current passing through the protected circuit. The resistance of the element generates heat due to the current flow. The size and construction of the element is (empirically) determined so that the heat produced for a normal current does not cause the element to attain a high temperature. If too high a current flows, the element rises to a higher temperature and either directly melts, or else melts a solder
Solder
Solder is a fusible metal alloy used to join together metal workpieces and having a melting point below that of the workpiece.Soft solder is what is most often thought of when solder or soldering are mentioned and it typically has a melting range of . It is commonly used in electronics and...
ed joint within the fuse, opening the circuit.
The fuse element is made of zinc, copper, silver, aluminum, or alloys to provide stable and predictable characteristics. The fuse ideally would carry its rated current indefinitely, and melt quickly on a small excess. The element must not be damaged by minor harmless surges of current, and must not oxidize or change its behavior after possibly years of service.
The fuse elements may be shaped to increase heating effect. In large fuses, current may be divided between multiple strips of metal. A dual-element fuse may contain a metal strip that melts instantly on a short-circuit, and also contain a low-melting solder joint that responds to long-term overload of low values compared to a short-circuit. Fuse elements may be supported by steel or nichrome wires, so that no strain is placed on the element, but a spring may be included to increase the speed of parting of the element fragments.
The fuse element may be surrounded by air, or by materials intended to speed the quenching of the arc. Silica sand or non-conducting liquids may be used.
Rated current IN
A maximum current that the fuse can continuously conduct without interrupting the circuit.Speed
The speed at which a fuse blows depends on how much current flows through it and the material of which the fuse is made. The operating time is not a fixed interval, but decreases as the current increases. Fuses have different characteristics of operating time compared to current, characterized as fast-blow, slow-blow, or time-delay, according to time required to respond to an overcurrent condition. A standard fuse may require twice its rated current to open in one second, a fast-blow fuse may require twice its rated current to blow in 0.1 seconds, and a slow-blow fuse may require twice its rated current for tens of seconds to blow.Fuse selection depends on the load's characteristics. Semiconductor devices may use a fast or ultrafast fuse since semiconductor devices heat rapidly when excess current flows. The fastest blowing fuses are designed for the most sensitive electrical equipment, where even a short exposure to an overload current could be very damaging. Normal fast-blow fuses are the most general purpose fuses. The time delay fuse (also known as anti-surge, or slow-blow) are designed to allow a current which is above the rated value of the fuse to flow for a short period of time without the fuse blowing. These types of fuse are used on equipment such as motors, which can draw larger than normal currents for up to several seconds while coming up to speed.
The I2t value
A measure of energy required to blow the fuse element and so a measure of the damaging effect of overcurrent on protected devices; sometimes known as the let-through energy. Unique I2t parameters are provided by charts in manufacturer data sheets for each fuse family. The energy is mainly dependent on current and time for fuses.Breaking capacity
The breaking capacity is the maximum current that can safely be interrupted by the fuse. Generally, this should be higher than the prospective short circuit current. Miniature fuses may have an interrupting rating only 10 times their rated current. Some fuses are designated High Rupture Capacity (HRC) and are usually filled with sand or a similar material. Fuses for small, low-voltageLow voltage
Low voltage when used as an electrical engineering term concerning an electricity supply grid or industrial use, broadly identifies safety considerations of the system based on the voltage used. The meaning of the term "low voltage" is somewhat different when used with regard to a more typical end...
, usually residential, wiring systems are commonly rated, in North American practice, to interrupt 10,000 amperes. Fuses for larger power systems must have higher interrupting ratings, with some low-voltage current-limiting high interrupting fuses rated for 300,000 amperes. Fuses for high-voltage equipment, up to 115,000 volts, are rated by the total apparent power (megavolt-amperes, MVA
Volt-ampere
A volt-ampere is the unit used for the apparent power in an electrical circuit, equal to the product of root-mean-square voltage and RMS current. In direct current circuits, this product is equal to the real power in watts...
) of the fault level on the circuit.
Rated voltage
Voltage rating of the fuse must be greater than or equal to what would become the open circuit voltageOpen-circuit voltage
Open-circuit voltage is the difference of electrical potential between two terminals of a device when there is no external load connected, i.e. the circuit is broken or open. Under these conditions there is no external electric current between the terminals, even though there may be current...
. For example, a glass tube fuse rated at 32 volts would not reliably interrupt current from a voltage source
Voltage source
In electric circuit theory, an ideal voltage source is a circuit element where the voltage across it is independent of the current through it. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. In analysis, a voltage source supplies a constant DC or AC potential between its terminals for any current...
of 120 or 230 V. If a 32 V fuse attempts to interrupt the 120 or 230 V source, an arc
Electric arc
An electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on...
may result. Plasma
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
inside that glass tube fuse may continue to conduct current until current eventually so diminishes that plasma reverts to an insulating gas. Rated voltage should be larger than the maximum voltage source
Voltage source
In electric circuit theory, an ideal voltage source is a circuit element where the voltage across it is independent of the current through it. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. In analysis, a voltage source supplies a constant DC or AC potential between its terminals for any current...
it would have to disconnect. This requirement applies to every type of fuse.
Rated voltage remains same for any one fuse, even when similar fuses are connected in series. Connecting fuses in series does not increase the rated voltage of the combination (nor of any one fuse).
Medium-voltage fuses rated for a few thousand volts are never used on low voltage circuits, because of their cost and because they cannot properly clear the circuit when operating at very low voltages.
Voltage drop
A voltage drop across the fuse is usually provided by its manufacturer. Resistance may change when a fuse becomes hot due to energy dissipation while conducting higher currents. This resulting voltage drop should be taken into account, particularly when using a fuse in low-voltage applications. Voltage drop often is not significant in more traditional wire type fuses, but can be significant in other technologies such as resettable fuseResettable fuse
A polymeric positive temperature coefficient device is a passive electronic component used to protect against overcurrent faults in electronic circuits...
(PPTC) type fuses.
Temperature derating
Ambient temperature will change a fuse's operational parameters. A fuse rated for 1 A at 25 °C may conduct up to 10% or 20% more current at −40 °C and may open at 80% of its rated value at 100 °C. Operating values will vary with each fuse family and are provided in manufacturer data sheets.Markings

Conformance mark
Much equipment and tools have conformance marks stamped, inscribed, moulded, or printed on them to indicate that the tool or equipment in question meets the standards set by the body indicated by the mark or marks in question....
on the body or end caps with markings that indicate their ratings. Surface-mount technology
Surface-mount technology
Surface mount technology is a method for constructing electronic circuits in which the components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards . An electronic device so made is called a surface mount device...
"chip type" fuses feature few or no markings, making identification very difficult.
Similar appearing fuses may have significantly different properties, identified by their markings. Fuse markings will generally convey the following information, either explicitly as text, or else implicit with the approval agency marking for a particular type:
- AmpereAmpereThe ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
rating of the fuse. - VoltVoltThe volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
age rating of the fuse. - TimeTimeTime is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
-currentAmpereThe ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
characteristic; i.e. fuse speed. - ApprovalProduct certificationProduct certification or product qualification is the process of verifying that a certain product has passed performance tests and quality assurance tests or qualification requirements stipulated in contracts, regulations, or specifications...
s by national and international standards agencies. - ManufacturerManufacturingManufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
/part numberPart numberA part number is an identifier of a particular part design used in a particular industry. Its purpose is to simplify referencing to that part...
/series. - Breaking capacityBreaking capacityBreaking capacity or interrupting capacity is the current that a fuse, circuit breaker, or other electrical apparatus is able to interrupt without being destroyed or causing an electric arc with unacceptable duration. The prospective short circuit current which can occur under short circuit...
Packages and materials
Fuses come in a vast array of sizes and styles to serve in many applications, manufactured in standardised package layouts to make them easily interchangeable. Fuse bodies may be made of ceramicCeramic
A ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
, glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
, plastic
Plastic
A plastic material is any of a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic organic solids used in the manufacture of industrial products. Plastics are typically polymers of high molecular mass, and may contain other substances to improve performance and/or reduce production costs...
, fiberglass
Fiberglass
Glass fiber is a material consisting of numerous extremely fine fibers of glass.Glassmakers throughout history have experimented with glass fibers, but mass manufacture of glass fiber was only made possible with the invention of finer machine tooling...
, molded mica laminates, or molded compressed fibre depending on application and voltage class.

Ferrule
A ferrule is a name for types of metal objects, generally used for fastening, joining, or reinforcement...
) fuses have a cylindrical body terminated with metal end caps. Some cartridge fuses are manufactured with end caps of different sizes to prevent accidental insertion of the wrong fuse rating in a holder, giving them a bottle shape.
Fuses for low voltage power circuits may have bolted blade or tag terminals which are secured by screws to a fuseholder. Some blade-type terminals are held by spring clips. Blade type fuses often require the use of a special purpose extractor tool to remove them from the fuse holder.
Renewable fuses have replaceable fuse elements, allowing the fuse body and terminals to be reused if not damaged after a fuse operation.
Fuses designed for soldering
Soldering
Soldering is a process in which two or more metal items are joined together by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint, the filler metal having a lower melting point than the workpiece...
to a printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
have radial or axial wire leads. Surface mount fuses
Surface-mount technology
Surface mount technology is a method for constructing electronic circuits in which the components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards . An electronic device so made is called a surface mount device...
have solder pads instead of leads.
High-voltage fuses of the expulsion type have fiber or glass-reinforced plastic tubes and an open end, and can have the fuse element replaced.
Semi-enclosed fuses are fuse wire carriers in which the fusible wire itself can be replaced. The exact fusing current is not as well controlled as an enclosed fuse, and it is exremely important to use the correct diameter and material when replacing the fuse wire,
and for these reasons these fuses are slowly falling from favour.
(Current ratings from Table 53A of BS 7671: 1992)
| Fuse wire rating (A) | Cu Wire diameter (mm) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 0.15 |
| 5 | 0.20 |
| 10 | 0.35 |
| 15 | 0.50 |
| 20 | 0.60 |
| 25 | 0.75 |
| 30 | 0.85 |
| 45 | 1.25 |
| 60 | 1.53 |
| 80 | 1.8 |
| 100 | 2.0 |
These are still used in consumer unit
Consumer unit
A consumer unit is a box of fuses or breakers, usually arranged in a single row. This is unlike a distribution board which has multiple rows of fuses or breakers and usually serves two or more locations, which may be split phase, two phase, two phases taken from three phase, or three phases.A...
s in some parts of the world, but are becoming less common.
While glass fuses have the advantage of a fuse element visible for inspection purposes, they have a low breaking capacity
Breaking capacity
Breaking capacity or interrupting capacity is the current that a fuse, circuit breaker, or other electrical apparatus is able to interrupt without being destroyed or causing an electric arc with unacceptable duration. The prospective short circuit current which can occur under short circuit...
which generally restricts them to applications of 15 A or less at 250 VAC. Ceramic fuses have the advantage of a higher breaking capacity, facilitating their use in circuits with higher current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
and voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
. Filling a fuse body with sand
Sand
Sand is a naturally occurring granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles.The composition of sand is highly variable, depending on the local rock sources and conditions, but the most common constituent of sand in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal...
provides additional cooling of the arc and increases the breaking capacity of the fuse. Medium-voltage fuses may have liquid-filled envelopes to assist in the extinguishing of the arc. Some types of distribution switchgear use fuse links immersed in the oil
Transformer oil
Transformer oil or insulating oil is usually a highly-refined mineral oil that is stable at high temperatures and has excellent electrical insulating properties. It is used in oil-filled transformers, some types of high voltage capacitors, fluorescent lamp ballasts, and some types of high voltage...
that fills the equipment.
Fuse packages may include a rejection feature such as a pin, slot, or tab, which prevents interchange of otherwise similar appearing fuses. For example, fuse holders for North American class RK fuses have a pin that prevents installation of similar-appearing class H fuses, which have a much lower breaking capacity and a solid blade terminal that lacks the slot of the RK type.
Dimensions
Fuses can be built with different sized enclosures to prevent interchange of different ratings or types of fuse. For example, bottle style fuses distinguish between ratings with different cap diameters. Automotive glass fuses were made in different lengths, to prevent high-rated fuses being installed in a circuit intended for a lower rating.Special features
Glass cartridge and plug fuses allow direct inspection of the fusible element. Other fuses have other indication methods including:- Indicating pin or striker pin — extends out of the fuse cap when the element is blown.
- Indicating disc — a coloured disc (flush mounted in the end cap of the fuse) falls out when the element is blown.
- Element window — a small window built into the fuse body to provide visual indication of a blown element.
- External trip indicator — similar function to striker pin, but can be externally attached (using clips) to a compatible fuse.
Some fuses allow a special purpose micro switch or relay unit to be fixed to the fuse body. When the fuse element blows, the indicating pin extends to activate the micro switch
Micro switch
A miniature snap-action switch, also trademarked and frequently known as a micro switch, is an electric switch that is actuated by very little physical force, through the use of a tipping-point mechanism, sometimes called an "over-center" mechanism. Switching happens reliably at specific and...
or relay, which, in turn, triggers an event.
Some fuses for medium-voltage applications use two separate barrels and two fuse elements in parallel.
IEC 60269 fuses
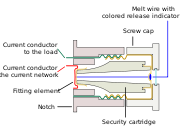
The International Electrotechnical Commission
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission is a non-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology"...
publishes standard 60269 for low-voltage power fuses. The standard is in four volumes, which describe general requirements, fuses for industrial and commercial applications, fuses for residential applications, and fuses to protect semiconductor devices. The IEC standard unifies several national standards, thereby improving the interchangeability of fuses in international trade. All fuses of different technologies tested to meet IEC standards will have similar time-current characteristics, which simplifies design and maintenance.
UL 248 fuses (North America)
In the United States and Canada, low-voltage fuses to 1 kV AC rating are made in accordance with Underwriters LaboratoriesUnderwriters Laboratories
Underwriters Laboratories Inc. is an independent product safety certification organization. Established in 1894, the company has its headquarters in Northbrook, Illinois. UL develops standards and test procedures for products, materials, components, assemblies, tools and equipment, chiefly dealing...
standard UL 248 or the harmonized Canadian Standards Association
Canadian Standards Association
The Canadian Standards Association, also known as the CSA, is a not-for-profit Standards organization with the stated aim of developing standards for use in 57 different areas of specialisation...
standard C22.2 No. 248. This standard applies to fuses rated 1 kV or less, AC or DC, and with breaking capacity
Breaking capacity
Breaking capacity or interrupting capacity is the current that a fuse, circuit breaker, or other electrical apparatus is able to interrupt without being destroyed or causing an electric arc with unacceptable duration. The prospective short circuit current which can occur under short circuit...
up to 200 kA. These fuses are intended for installations following Canadian Electrical Code, Part I (CEC), or the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70 (NEC).
IEC and UL nomenclature varies slightly. IEC standards refer to a "fuse" as the assembly of a fuse link and fuse holder. In North American standards, the fuse is the replaceable portion of the assembly, and a fuse link would be a bare metal element for installation in a fuse.
Automotive fuses
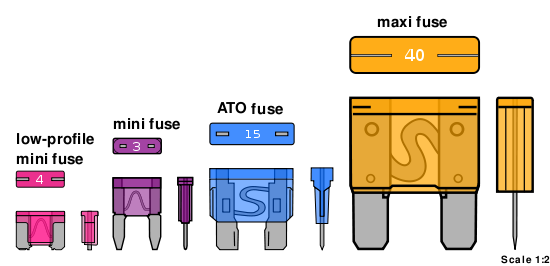
Automotive fuses are used to protect the wiring and electrical equipment for vehicles. There are several different types of automotive fuses and their usage is dependant upon the specific application, voltage, and current demands of the electrical circuit. Automotive fuses can be mounted in fuse blocks, inline fuse holders, or fuse clips. Some automotive fuses are occasionally used in non-automotive electrical applications. Standards for automotive fuses are published by SAE International
SAE International
SAE International is an organization for engineering professionals in the aerospace, automotive, and commercial vehicle industries. The Society is a standards development organization for the engineering of powered vehicles of all kinds, including cars, trucks, boats, aircraft, and others.SAE...
(formerly known as the Society of Automotive Engineers).
Automotive fuses can be classified into four distinct categories:
- Blade fuses
- Glass tube or Bosch type
- Fusible linkFusible linkFusible links include mechanical and electrical devices.A mechanical fusible link is a device consisting of two strips of metal soldered together with a fusible alloy that is designed to melt at a specific temperature, thus allowing the two pieces to separate...
s - Fuse limiters
Most automotive fuses rated at 32 volts are used on circuits rated 24 volts DC and below. Some vehicles use a dual 12/42 V DC electrical system
42-volt electrical system
In automobiles, a 42-volt electrical system was a proposed electrical power standard in the late 1990s intended to allow more powerful electrically driven accessories, and lighter automobile wiring harnesses...
that will require a fuse rated at 58 V DC.
High voltage fuses

Cutout (electric power distribution)
In electrical distribution, a fuse cutout or cut-out fuse is a combination of a fuse and a switch, used in primary overhead feeder lines and taps to protect distribution transformers from current surges and overloads. An overcurrent caused by a fault in the transformer or customer circuit will...
are used to protect instrument transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
s used for electricity metering, or for small power transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
s where the expense of a circuit breaker
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
is not warranted. For example, in distribution systems, a power fuse may be used to protect a transformer serving 1–3 houses. A circuit breaker at 115 kV may cost up to five times as much as a set of power fuses, so the resulting saving can be tens of thousands of dollars. Pole-mounted distribution transformers are nearly always protected by a fusible cutout
Cutout (electric power distribution)
In electrical distribution, a fuse cutout or cut-out fuse is a combination of a fuse and a switch, used in primary overhead feeder lines and taps to protect distribution transformers from current surges and overloads. An overcurrent caused by a fault in the transformer or customer circuit will...
, which can have the fuse element replaced using live-line maintenance tools.
Large power fuses use fusible elements made of silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
, copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
or tin
Tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4...
to provide stable and predictable performance. High voltage expulsion fuses surround the fusible link with gas-evolving substances, such as boric acid
Boric acid
Boric acid, also called hydrogen borate or boracic acid or orthoboric acid or acidum boricum, is a weak acid of boron often used as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, as a neutron absorber, and as a precursor of other chemical compounds. It exists in the form of colorless crystals or a...
. When the fuse blows, heat from the arc causes the boric acid to evolve large volumes of gases. The associated high pressure (often greater than 100 atmospheres) and cooling gases rapidly quench the resulting arc. The hot gases are then explosively expelled out of the end(s) of the fuse. Such fuses can only be used outdoors.


High-power fuse means that these fuses can interrupt several kiloamperes. Some manufacturers have tested their fuses for up to 63 kA cut-off current.
Fuses compared with circuit breakers
Fuses have the advantages of often being less costly and simpler than a circuit breakerCircuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
for similar ratings. The blown fuse must be replaced with a new device which is less convenient than simply resetting a breaker and therefore likely to discourage people from ignoring faults. On the other hand, replacing a fuse without isolating the circuit first (most building wiring designs do not provide individual isolation switches for each fuse) can be dangerous in itself, particularly if the fault is a short circuit.
High rupturing capacity fuses can be rated to safely interrupt up to 300,000 amperes at 600 V AC. Special current-limiting fuses are applied ahead of some molded-case breakers to protect the breakers in low-voltage power circuits with high short-circuit levels.
Current-limiting fuses operate so quickly that they limit the total "let-through" energy that passes into the circuit, helping to protect downstream equipment from damage. These fuses open in less than one cycle of the AC power frequency; circuit breakers cannot match this speed.
Some types of circuit breaker
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
s must be maintained on a regular basis to ensure their mechanical operation during an interruption. This is not the case with fuses, which rely on melting processes where no mechanical operation is required for the fuse to operate under fault conditions.
In a multi-phase power circuit, if only one fuse opens, the remaining phases will have higher than normal currents, and unbalanced voltages, with possible damage to motors. Fuses only sense overcurrent, or to a degree, over-temperature, and cannot usually be used independently with protective relaying to provide more advanced protective functions, for example, ground fault detection.
Some manufacturers of medium-voltage distribution fuses combine the overcurrent protection characteristics of the fusible element with the flexibility of relay protection by adding a pyrotechnic device to the fuse operated by external protective relay
Protective relay
In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a complex electromechanical apparatus, often with more than one coil, designed to calculate operating conditions on an electrical circuit and trip circuit breakers when a fault is detected...
s.
Fuse boxes
In the UK, older electrical consumer unitConsumer unit
A consumer unit is a box of fuses or breakers, usually arranged in a single row. This is unlike a distribution board which has multiple rows of fuses or breakers and usually serves two or more locations, which may be split phase, two phase, two phases taken from three phase, or three phases.A...
s (also called fuse boxes) are fitted either with semi-enclosed (rewirable) fuses (BS 3036) or cartridge fuses (BS 1361). (Fuse wire is commonly supplied to consumers as short lengths of 5 A-, 15 A- and 30 A-rated wire wound on a piece of cardboard.) Modern consumer units usually contain miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) instead of fuses, though cartridge fuses are sometimes still used, as MCBs are prone to nuisance tripping.
Renewable fuses (rewirable or cartridge) allow user replacement, but this can be hazardous as it is easy to put a higher-rated or double fuse element (link or wire) into the holder (overfusing), or simply fitting it with copper wire or even a totally different type of conducting object (hairpins, paper clips, nails, etc.) to the existing carrier. Such tampering will not be visible without full inspection of the fuse. Fuse wire was never used in North America for this reason, although renewable fuses continue to be made for distribution boards.
The fuse boxes pictured in this section are (right) a MEM consumer unit with four rewirable fuse holders (two 30 A and two 15 A) installed c. 1957 (cover removed); a Wylex standard unit with eight rewirable fuse holders.
The Wylex standard consumer unit was very popular in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
until the wiring regulations started demanding residual-current device
Residual-current device
A Residual Current Device is a generic term covering both RCCBs and RCBOs.A Residual-Current Circuit Breaker is an electrical wiring device that disconnects a circuit whenever it detects that the electric current is not balanced between the energized conductor and the return neutral conductor...
s (RCDs) for sockets that could feasibly supply equipment outside the equipotential zone. The design does not allow for fitting of RCDs or RCBOs. Some Wylex standard models were made with an RCD instead of the main switch, but (for consumer units supplying the entire installation) this is no longer compliant with the wiring regulations
BS 7671
British Standard BS 7671 "Requirements for electrical installations" is the national standard in the United Kingdom for low voltage electrical installations....
as alarm systems should not be RCD-protected. There are two styles of fuse base that can be screwed into these units: one designed for rewirable fusewire carriers and one designed for cartridge fuse carriers. Over the years MCBs have been made for both styles of base. In both cases, higher rated carriers had wider pins, so a carrier couldn't be changed for a higher rated one without also changing the base. Cartridge fuse carriers are also now available for DIN-rail enclosures.
In North America, fuses were used in buildings wired before 1960. These Edison Base fuses would screw into a fuse socket similar to Edison-base incandescent lamps. Ratings were 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 amperes. To prevent installation of fuses with an excessive current rating, later fuse boxes included rejection features in the fuseholder socket. Some installations use resettable miniature thermal circuit breaker
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
s, which screw into a fuse socket.
One form of fuse box abuse was to put a penny
Penny
A penny is a coin or a type of currency used in several English-speaking countries. It is often the smallest denomination within a currency system.-Etymology:...
in the socket, which defeated overcurrent protection and resulted in a dangerous condition.
In the 1950s, fuses in new residential or industrial construction for branch circuit protection were superseded by low voltage circuit breaker
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
s.
Coordination of fuses in series
Where several fuses are connected in series at the various levels of a power distribution system, it is desirable to blow (clear) only the fuse (or other overcurrent device) electrically closest to the fault. This process is called "coordination" and may require the time-current characteristics of two fuses to be plotted on a common current basis. Fuses are selected so that the minor, branch, fuse disconnects its circuit well before the supplying, major, fuse starts to melt. In this way, only the faulty circuit is interrupted with minimal disturbance to other circuits fed by a common supplying fuse.Where the fuses in a system are of similar types, simple rule-of-thumb ratios between ratings of the fuse closest to the load and the next fuse towards the source can be used.
Resettable fuses
So-called self-resettingResettable fuse
A polymeric positive temperature coefficient device is a passive electronic component used to protect against overcurrent faults in electronic circuits...
fuses use a thermoplastic conductive element known as a Polymeric Positive Temperature Coefficient (or PPTC) thermistor
Thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word is a portmanteau of thermal and resistor...
that impedes the circuit during an overcurrent condition (by increasing device resistance). The PPTC thermistor is self-resetting in that when current is removed, the device will cool and revert back to low resistance. These devices are often used in aerospace/nuclear applications where replacement is difficult, or on a computer motherboard so that a shorted mouse or keyboard does not cause motherboard damage.
Thermal fuses
A thermal fuse is often found in consumer equipment such as coffee makers or hair dryers or transformerTransformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
s powering small consumer electronics devices. They contain a fusible, temperature-sensitive alloy which holds a spring contact mechanism normally closed. When the surrounding temperature gets too high, the alloy melts and allows the spring contact mechanism to break the circuit. The device can be used to prevent a fire in a hair dryer for example, by cutting off the power supply to the heater elements when the air flow is interrupted (e.g., the blower motor stops or the air intake becomes accidentally blocked). Thermal fuses are a 'one shot', non-resettable device which must be replaced once they have been activated (blown).
See also
- AntifuseAntifuseAn antifuse is an electrical device that performs the opposite function to a fuse. Whereas a fuse starts with a low resistance and is designed to permanently break an electrically conductive path , an antifuse starts with a high resistance and is designed to permanently create an electrically...
- AutorecloserAutorecloserIn electric power distribution, a recloser, or autorecloser, is a circuit breaker equipped with a mechanism that can automatically close the breaker after it has been opened due to a fault. Reclosers are used on overhead distribution systems to detect and interrupt momentary faults...
- Circuit breakerCircuit breakerA circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
- Electronic Components
- Protective Device Coordination
- Programmable read-only memoryProgrammable read-only memoryA programmable read-only memory or field programmable read-only memory or one-time programmable non-volatile memory is a form of digital memory where the setting of each bit is locked by a fuse or antifuse. Such PROMs are used to store programs permanently...
- Semiconductor fuseSemiconductor fuseSemiconductor fuses are used to protect against over-current conditions in semiconductors devices. Because of their fast action, semiconductor fuses help to limit the short circuit current significantly....
External links
- edn.com/archives/1996/092696 Len Lundy, "The fuse-selection checklist: a quick update" EDN Magazine 26 Sept 1996 p121
- littelfuse.com/data/en/Product_Catalogs/ Information on circuit protection, surface mount fuses, axial lead & cartridge fuses, blade terminal & special mount fuses, fuseholders, fuse blocks & clips and military fuses and fuseholders
- bussmann.com/2/ApplicationTools for the Bussmann manual of fuse selection
- wiki.diyfaq.org.uk - Fuses vs MCBs

