
Metal-induced gap states
Encyclopedia
In bulk semiconductor
band structure calculations, it is assumed that the crystal lattice (which features a periodic potential due to the atomic structure) of the material is infinite. When the finite size of a crystal is taken into account, the wavefunctions of electrons are altered and states that are forbidden within the bulk semiconductor gap are allowed at the surface. Similarly, when a metal
is deposited onto a semiconductor (by thermal evaporation (deposition)
, for example), the wavefunction of an electron in the semiconductor must match that of an electron in the metal at the interface. Since the Fermi level
s of the two materials must match at the interface, there exists gap states that decay deeper into the semiconductor.
is deposited onto a semiconductor
, even when the metal film is smaller than a single atomic layer, the Fermi levels of the metal and semiconductor must match. This pins the Fermi level
in the semiconductor to a position in the bulk gap. Shown to the right is a diagram of band-bending interfaces between two different metals (high and low work function
s) and two different semiconductors (n-type and p-type).
Volker Heine
was one of the first to respect the length of the tail end of metal electron
states extending into the semiconductor's energy gap. He calculated the variation in surface state energy by matching wavefunctions of a free-electron metal to gapped states in an undoped semiconductor, showing that in most cases the position of the surface state energy is quite stable regardless of the metal used.
states that leak into the semiconductor
. Since the mid-gap states do exist within some depth of the semiconductor, they must be a mixture (a Fourier series
) of valence
and conduction band states from the bulk. The resulting positions of these states, as calculated by J. Tersoff , must be closer to either the valence- or conduction- band thus acting as acceptor or donor dopants, respectively. The point that divides these two types of MIGS is called the branching point, E_B. Tersoff argued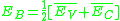
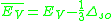 , where
, where 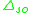 is the spin orbit splitting of
is the spin orbit splitting of 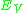 at the
at the 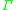 point.
point.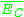 is the indirect conduction band minimum.
is the indirect conduction band minimum.
and semiconductor
. The amount of charge transfer was formulated by Linus Pauling and later revised to be:
where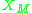 and
and 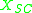 are the electronegativities of the metal and semiconductor, respectively. The charge transfer produces a dipole
are the electronegativities of the metal and semiconductor, respectively. The charge transfer produces a dipole
at the interface and thus a potential barrier called the Schottky barrier
height. In the same derivation of the branching point mentioned above, Tersoff derives the barrier height to be: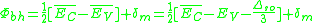
where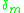 is a parameter adjustable for the specific metal, dependent mostly on its electronegativity,
is a parameter adjustable for the specific metal, dependent mostly on its electronegativity, 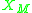 . Tersoff showed that the experimentally measured phi_bp fits his theoretical model for Au
. Tersoff showed that the experimentally measured phi_bp fits his theoretical model for Au
in contact with 10 common semiconductors, including Si
, Ge
, GaP
, and GaAs
.
Another derivation of the contact barrier height in terms of experimentally measurable parameters was worked out by Federico Garcia-Moliner who considered the density of states
and dipole
contributions more rigorously .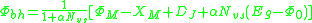
 is dependent on the charge densities of the both materials
is dependent on the charge densities of the both materials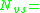 density of surface states
density of surface states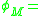 work function of metal
work function of metal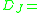 sum of dipole contributions considering dipole corrections to the jellium model
sum of dipole contributions considering dipole corrections to the jellium model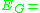 semiconductor gap
semiconductor gap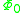 Ef – Ev in semiconductor
Ef – Ev in semiconductor
Thus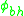 can be calculated by theoretically deriving or experimentally measuring each parameter. Garcia-Moliner also discusses two limits
can be calculated by theoretically deriving or experimentally measuring each parameter. Garcia-Moliner also discusses two limits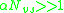 (The Bardeen Limit), where the high density of interface states pins the Fermi level at that of the semiconductor regardless of
(The Bardeen Limit), where the high density of interface states pins the Fermi level at that of the semiconductor regardless of 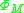 .
.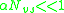 (The Schottky
(The Schottky
Limit)where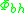 varies with strongly with the characteristics of the metal, including the particular lattice structure as accounted for in
varies with strongly with the characteristics of the metal, including the particular lattice structure as accounted for in 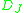 .
.
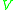 is applied across the interface of an n-type semiconductor and a metal, the Fermi level in the semiconductor is shifted with respect to the metal's and the band bending decreases. In effect, the capacitance across the depletion layer in the semiconductor is bias voltage dependent and goes as
is applied across the interface of an n-type semiconductor and a metal, the Fermi level in the semiconductor is shifted with respect to the metal's and the band bending decreases. In effect, the capacitance across the depletion layer in the semiconductor is bias voltage dependent and goes as 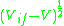 . This makes the metal/semiconductor junction useful in varactor devices used frequently in electronics.
. This makes the metal/semiconductor junction useful in varactor devices used frequently in electronics.
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
band structure calculations, it is assumed that the crystal lattice (which features a periodic potential due to the atomic structure) of the material is infinite. When the finite size of a crystal is taken into account, the wavefunctions of electrons are altered and states that are forbidden within the bulk semiconductor gap are allowed at the surface. Similarly, when a metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
is deposited onto a semiconductor (by thermal evaporation (deposition)
Evaporation (deposition)
Evaporation is a common method of thin film deposition. The source material is evaporated in a vacuum. The vacuum allows vapor particles to travel directly to the target object , where they condense back to a solid state...
, for example), the wavefunction of an electron in the semiconductor must match that of an electron in the metal at the interface. Since the Fermi level
Fermi level
The Fermi level is a hypothetical level of potential energy for an electron inside a crystalline solid. Occupying such a level would give an electron a potential energy \epsilon equal to its chemical potential \mu as they both appear in the Fermi-Dirac distribution function,which...
s of the two materials must match at the interface, there exists gap states that decay deeper into the semiconductor.
Band-Bending at the metal-semiconductor interface
As mentioned above, when a metalMetal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
is deposited onto a semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
, even when the metal film is smaller than a single atomic layer, the Fermi levels of the metal and semiconductor must match. This pins the Fermi level
Fermi level
The Fermi level is a hypothetical level of potential energy for an electron inside a crystalline solid. Occupying such a level would give an electron a potential energy \epsilon equal to its chemical potential \mu as they both appear in the Fermi-Dirac distribution function,which...
in the semiconductor to a position in the bulk gap. Shown to the right is a diagram of band-bending interfaces between two different metals (high and low work function
Work function
In solid-state physics, the work function is the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point immediately outside the solid surface...
s) and two different semiconductors (n-type and p-type).
Volker Heine
Volker Heine
Volker Heine FRS is a New Zealand-British physicist.He was educated at Wanganui Collegiate School and the University of Otago, then Clare College, Cambridge where he became a fellow and professor. He obtained his PhD in physics in Cambridge as student of Sir Nevill Mott.He was elected Fellow of...
was one of the first to respect the length of the tail end of metal electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
states extending into the semiconductor's energy gap. He calculated the variation in surface state energy by matching wavefunctions of a free-electron metal to gapped states in an undoped semiconductor, showing that in most cases the position of the surface state energy is quite stable regardless of the metal used.
Branching point
It is somewhat crude to suggest that the MIGS are tail ends of metalMetal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
states that leak into the semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
. Since the mid-gap states do exist within some depth of the semiconductor, they must be a mixture (a Fourier series
Fourier series
In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a set of simple oscillating functions, namely sines and cosines...
) of valence
Valence (chemistry)
In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can be defined as the number of valence bonds...
and conduction band states from the bulk. The resulting positions of these states, as calculated by J. Tersoff , must be closer to either the valence- or conduction- band thus acting as acceptor or donor dopants, respectively. The point that divides these two types of MIGS is called the branching point, E_B. Tersoff argued
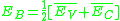
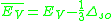 , where
, where 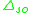 is the spin orbit splitting of
is the spin orbit splitting of 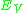 at the
at the 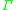 point.
point.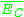 is the indirect conduction band minimum.
is the indirect conduction band minimum.Metal/Semiconductor contact point barrier height
In order for the Fermi levels to match at the interface, there must be charge transfer between the metalMetal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
and semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
. The amount of charge transfer was formulated by Linus Pauling and later revised to be:

where
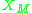 and
and 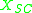 are the electronegativities of the metal and semiconductor, respectively. The charge transfer produces a dipole
are the electronegativities of the metal and semiconductor, respectively. The charge transfer produces a dipoleDipole
In physics, there are several kinds of dipoles:*An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.*A...
at the interface and thus a potential barrier called the Schottky barrier
Schottky barrier
A Schottky barrier, named after Walter H. Schottky, is a potential barrier formed at a metal–semiconductor junction which has rectifying characteristics, suitable for use as a diode...
height. In the same derivation of the branching point mentioned above, Tersoff derives the barrier height to be:
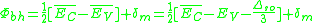
where
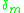 is a parameter adjustable for the specific metal, dependent mostly on its electronegativity,
is a parameter adjustable for the specific metal, dependent mostly on its electronegativity, 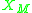 . Tersoff showed that the experimentally measured phi_bp fits his theoretical model for Au
. Tersoff showed that the experimentally measured phi_bp fits his theoretical model for AuGold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
in contact with 10 common semiconductors, including Si
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
, Ge
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, hard, grayish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to its group neighbors tin and silicon. The isolated element is a semiconductor, with an appearance most similar to elemental silicon....
, GaP
Gap
-General:* Gap , a spacing between large trees in a forest* Gap , a mountain pass, often carved by a river* Gap year, a prolonged period between a life stage-Places:* Gap, Hautes-Alpes, France* Gap, Pennsylvania, United States...
, and GaAs
Gaas
Gaas is a commune in the Landes department in Aquitaine in south-western France....
.
Another derivation of the contact barrier height in terms of experimentally measurable parameters was worked out by Federico Garcia-Moliner who considered the density of states
Density of states
In solid-state and condensed matter physics, the density of states of a system describes the number of states per interval of energy at each energy level that are available to be occupied by electrons. Unlike isolated systems, like atoms or molecules in gas phase, the density distributions are not...
and dipole
Dipole
In physics, there are several kinds of dipoles:*An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.*A...
contributions more rigorously .
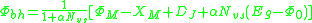
 is dependent on the charge densities of the both materials
is dependent on the charge densities of the both materials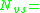 density of surface states
density of surface states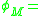 work function of metal
work function of metal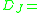 sum of dipole contributions considering dipole corrections to the jellium model
sum of dipole contributions considering dipole corrections to the jellium model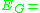 semiconductor gap
semiconductor gap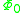 Ef – Ev in semiconductor
Ef – Ev in semiconductorThus
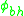 can be calculated by theoretically deriving or experimentally measuring each parameter. Garcia-Moliner also discusses two limits
can be calculated by theoretically deriving or experimentally measuring each parameter. Garcia-Moliner also discusses two limits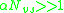 (The Bardeen Limit), where the high density of interface states pins the Fermi level at that of the semiconductor regardless of
(The Bardeen Limit), where the high density of interface states pins the Fermi level at that of the semiconductor regardless of 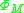 .
.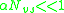 (The Schottky
(The SchottkySchottky barrier
A Schottky barrier, named after Walter H. Schottky, is a potential barrier formed at a metal–semiconductor junction which has rectifying characteristics, suitable for use as a diode...
Limit)where
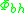 varies with strongly with the characteristics of the metal, including the particular lattice structure as accounted for in
varies with strongly with the characteristics of the metal, including the particular lattice structure as accounted for in 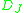 .
.Applications
When a bias voltage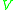 is applied across the interface of an n-type semiconductor and a metal, the Fermi level in the semiconductor is shifted with respect to the metal's and the band bending decreases. In effect, the capacitance across the depletion layer in the semiconductor is bias voltage dependent and goes as
is applied across the interface of an n-type semiconductor and a metal, the Fermi level in the semiconductor is shifted with respect to the metal's and the band bending decreases. In effect, the capacitance across the depletion layer in the semiconductor is bias voltage dependent and goes as 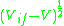 . This makes the metal/semiconductor junction useful in varactor devices used frequently in electronics.
. This makes the metal/semiconductor junction useful in varactor devices used frequently in electronics.

