
Elastic instability
Encyclopedia
Elastic instability is a form of instability occurring in elastic systems, such as buckling
Buckling
In science, buckling is a mathematical instability, leading to a failure mode.Theoretically, buckling is caused by a bifurcation in the solution to the equations of static equilibrium...
of beams and plates subject to large compressive loads.
Single degree of freedom-systems
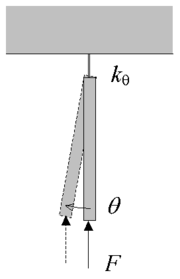
Consider as a simple example a rigid beam of length L, hinged in one end and free in the other, and having an angular springSpring (device)
A spring is an elastic object used to store mechanical energy. Springs are usually made out of spring steel. Small springs can be wound from pre-hardened stock, while larger ones are made from annealed steel and hardened after fabrication...
attached to the hinged end. The beam is loaded in the free end by a force F acting in the compressive axial direction of the beam, see the figure to the right.
Moment equilibrium condition
Assuming a clockwise angular deflection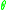 , the clockwise moment
, the clockwise momentMoment (physics)
In physics, the term moment can refer to many different concepts:*Moment of force is the tendency of a force to twist or rotate an object; see the article torque for details. This is an important, basic concept in engineering and physics. A moment is valued mathematically as the product of the...
exerted by the force becomes
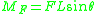 . The moment equilibrium
. The moment equilibriumMechanical equilibrium
A standard definition of static equilibrium is:This is a strict definition, and often the term "static equilibrium" is used in a more relaxed manner interchangeably with "mechanical equilibrium", as defined next....
equation is given by
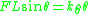
where
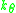 is the spring constant of the angular spring (Nm/radian). Assuming
is the spring constant of the angular spring (Nm/radian). Assuming 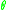 is small enough, implementing the taylor expansion of the sine
is small enough, implementing the taylor expansion of the sineSine
In mathematics, the sine function is a function of an angle. In a right triangle, sine gives the ratio of the length of the side opposite to an angle to the length of the hypotenuse.Sine is usually listed first amongst the trigonometric functions....
function and keeping the two first terms yields
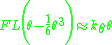
which has three solutions, the trivial
 , and
, and
which is imaginary
Complex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
(i.e. not physical) for
 and real
and realComplex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
otherwise. This implies that for small compressive forces, the only equilibrium state is given by
 , while if the force exceeds the value
, while if the force exceeds the value 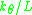 there is suddenly another mode of deformation possible.
there is suddenly another mode of deformation possible.Energy method
The same result can be obtained by considering energyEnergy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
relations. The energy stored in the angular spring is

and the work done by the force is simply the force multiplied by the vertical displacement of the beam end, which is
 . Thus,
. Thus,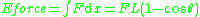
The energy equilibrium condition
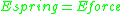 now yields
now yields 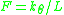 as before (besides from the trivial
as before (besides from the trivial  ).
).Stability of the solutions
Any solution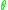 is stable
is stableStability theory
In mathematics, stability theory addresses the stability of solutions of differential equations and of trajectories of dynamical systems under small perturbations of initial conditions...
iff
IFF
IFF, Iff or iff may refer to:Technology/Science:* Identification friend or foe, an electronic radio-based identification system using transponders...
a small change in the deformation angle
 results in a reaction moment trying to restore the original angle of deformation. The net clockwise moment acting on the beam is
results in a reaction moment trying to restore the original angle of deformation. The net clockwise moment acting on the beam is
An infinitesimal
Infinitesimal
Infinitesimals have been used to express the idea of objects so small that there is no way to see them or to measure them. The word infinitesimal comes from a 17th century Modern Latin coinage infinitesimus, which originally referred to the "infinite-th" item in a series.In common speech, an...
clockwise change of the deformation angle
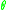 results in a moment
results in a moment
which can be rewritten as

since
 due to the moment equilibrium condition. Now, a solution
due to the moment equilibrium condition. Now, a solution 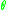 is stable iff a clockwise change
is stable iff a clockwise change  results in a negative change of moment
results in a negative change of moment 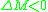 and vice versa. Thus, the condition for stability becomes
and vice versa. Thus, the condition for stability becomes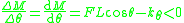
The solution
 is stable only for
is stable only for 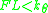 , which is expected. By expanding the cosine term in the equation, the approximate stability condition is obtained:
, which is expected. By expanding the cosine term in the equation, the approximate stability condition is obtained:
for
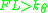 , which the two other solutions satisfy. Hence, these solutions are stable.
, which the two other solutions satisfy. Hence, these solutions are stable.Multiple degrees of freedom-systems


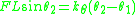
where
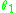 and
and 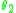 are the angles of the two beams. Linearizing by assuming these angles are small yields
are the angles of the two beams. Linearizing by assuming these angles are small yields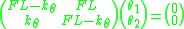
The non-trivial solutions to the system is obtained by finding the roots of the determinant
Determinant
In linear algebra, the determinant is a value associated with a square matrix. It can be computed from the entries of the matrix by a specific arithmetic expression, while other ways to determine its value exist as well...
of the system matrix
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
, i.e. for
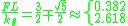
Thus, for the two degrees of freedom-system there are two critical values for the applied force F. These correspond to two different modes of deformation which can be computed from the nullspace of the system matrix. Dividing the equations by
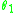 yields
yields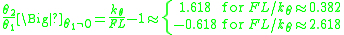
For the lower critical force the ratio is positive and the two beams deflect in the same direction while for the higher force they form a "banana" shape. These two states of deformation represent the buckling
Buckling
In science, buckling is a mathematical instability, leading to a failure mode.Theoretically, buckling is caused by a bifurcation in the solution to the equations of static equilibrium...
mode shapes of the system.
Further reading
- Theory of elastic stability, S. TimoshenkoStephen TimoshenkoStanford University:* Bergman, E. O., * Kurzweil, A. C., * , * Huang, Y. S., * Wang, T. K., * Weber, H. S., * , * , * , -Publications:...
and J. Gere

