
Diffusion damping
Encyclopedia

Cosmology
Cosmology is the discipline that deals with the nature of the Universe as a whole. Cosmologists seek to understand the origin, evolution, structure, and ultimate fate of the Universe at large, as well as the natural laws that keep it in order...
theory, diffusion damping, also called photon diffusion damping, is a physical process which reduced density inequalities (anisotropies) in the early universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
, making the universe itself and the cosmic microwave background radiation
Cosmic microwave background radiation
In cosmology, cosmic microwave background radiation is thermal radiation filling the observable universe almost uniformly....
(CMB) more uniform. Around 300,000 years after the Big Bang
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
, during the epoch of recombination
Recombination (cosmology)
In cosmology, recombination refers to the epoch at which charged electrons and protons first became bound to form electrically neutral hydrogen atoms.Note that the term recombination is a misnomer, considering that it represents the first time that electrically neutral hydrogen formed. After the...
, diffusing photons
Photon diffusion
Photon diffusion is a situation where photons travel through a material without being absorbed, but rather undergoing repeated scattering events which change the direction of their path. The path of any given photon is then effectively a random walk...
travelled from hot regions of space to cold ones, equalising the temperatures of these regions. This effect is responsible, along with baryon acoustic oscillations
Baryon acoustic oscillations
In cosmology, baryon acoustic oscillations refers to an overdensity or clustering of baryonic matter at certain length scales due to acoustic waves which propagated in the early universe. In the same way that supernova experiments provide a "standard candle" for astronomical observations, BAO...
, the Doppler effect
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
, and the effects of gravity on electromagnetic radiation
Gravitational redshift
In astrophysics, gravitational redshift or Einstein shift describes light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation of certain wavelengths that originate from a source that is in a region of a stronger gravitational field that appear to be of longer wavelength, or redshifted, when seen or...
, for the eventual formation of galaxies and galaxy clusters, these being the dominant large scale structures which are observed in the universe. It is a damping
Damping
In physics, damping is any effect that tends to reduce the amplitude of oscillations in an oscillatory system, particularly the harmonic oscillator.In mechanics, friction is one such damping effect...
by diffusion, not of diffusion.
The strength of diffusion damping is calculated by a mathematical expression for the damping factor, which figures into the Boltzmann equation
Boltzmann equation
The Boltzmann equation, also often known as the Boltzmann transport equation, devised by Ludwig Boltzmann, describes the statistical distribution of one particle in rarefied gas...
, an equation which describes the amplitude of perturbations in the CMB. The strength of the diffusion damping is chiefly governed by the distance photons travel before being scattered (diffusion length). What affect the diffusion length are primarily the properties of the plasma in question: different sorts of plasma may experience different sorts of diffusion damping. The evolution of a plasma may also affect the damping process. The scale on which diffusion damping works is called the Silk scale and its value corresponds to the size of galaxies of the present day. The mass contained within the Silk scale is called the Silk mass and it corresponds to the mass of the galaxies.
Introduction
Diffusion damping took place about 13.7 billion years ago, during the stage of the early universe called recombinationRecombination (cosmology)
In cosmology, recombination refers to the epoch at which charged electrons and protons first became bound to form electrically neutral hydrogen atoms.Note that the term recombination is a misnomer, considering that it represents the first time that electrically neutral hydrogen formed. After the...
or matter-radiation decoupling. This period occurred between 240,000 and 310,000 years after the Big Bang
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
.This is equivalent to a redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
of z = 1000. Recombination was the stage during which simple atoms, e.g. hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
, began to form in the cooling, but still very hot, soup of proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s, electrons and photons that composed the universe. Prior to the recombination epoch, this soup, a plasma
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
, was largely opaque
Opacity (optics)
Opacity is the measure of impenetrability to electromagnetic or other kinds of radiation, especially visible light. In radiative transfer, it describes the absorption and scattering of radiation in a medium, such as a plasma, dielectric, shielding material, glass, etc...
to the electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
of photons. This meant that the permanently excited photons were scattered by the protons and electrons too often to travel very far in straight lines. During the recombination epoch, the universe cooled rapidly as free electrons were captured by atomic nuclei; atoms formed from their constituent parts and the universe became transparent: the amount of photon scattering decreased dramatically. Scattering less, photons could diffuse (travel) much greater distances. There is no significant diffusion damping for electrons, which cannot diffuse nearly as far as photons can in similar circumstances. Thus all damping by electron diffusion is negligible when compared to photon diffusion damping.
Acoustic perturbations of initial density fluctuations in the universe made some regions of space hotter and denser than others. These differences in temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
and density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
are called anisotropies. Photons diffused from the hot, overdense regions of plasma to the cold, underdense ones: they dragged along the protons and electrons: the photons pushed electrons along, and these, in turn, pulled on protons by the Coulomb force. This caused the temperatures and densities of the hot and cold regions to be averaged and the universe became less anisotropic (characteristically various) and more isotropic (characteristically uniform). This reduction in anisotropy is the damping of diffusion damping. Diffusion damping thus damps temperature and density anisotropies in the early universe. With baryonic matter (protons and electrons) escaping the dense areas along with the photons; the temperature and density inequalities were adiabatically damped. That is to say the ratios of photons to baryons remained constant during the damping process.
Photon diffusion was first described in Joseph Silk's 1968 paper entitled "Cosmic Black-Body Radiation and Galaxy Formation", which was published in The Astrophysical Journal
Astrophysical Journal
The Astrophysical Journal is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering astronomy and astrophysics. It was founded in 1895 by the American astronomers George Ellery Hale and James Edward Keeler. It publishes three 500-page issues per month....
. As such, diffusion damping is sometimes also called Silk damping, though this term may apply only to one possible damping scenario. Silk damping was thus named after its discoverer.
Magnitude
The magnitude of diffusion damping is calculated as a damping factor or suppression factor, represented by the symbol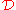 , which figures into the Boltzmann equation
, which figures into the Boltzmann equationBoltzmann equation
The Boltzmann equation, also often known as the Boltzmann transport equation, devised by Ludwig Boltzmann, describes the statistical distribution of one particle in rarefied gas...
, an equation which describes the amplitude of perturbations in the CMB. The strength of the diffusion damping is chiefly governed by the distance photons travel before being scattered (diffusion length). What affect the diffusion length are primarily the properties of the plasma in question: different sorts of plasma may experience different sorts of diffusion damping. The evolution of a plasma may also affect the damping process.
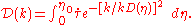
Where:
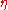 is the conformal time.
is the conformal time.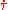 is the "differential optical depth for Thomson scattering". Thomson scatteringThomson scatteringThomson scattering is the elastic scattering of electromagnetic radiation by a free charged particle, as described by classical electromagnetism. It is just the low-energy limit of Compton scattering: the particle kinetic energy and photon frequency are the same before and after the scattering...
is the "differential optical depth for Thomson scattering". Thomson scatteringThomson scatteringThomson scattering is the elastic scattering of electromagnetic radiation by a free charged particle, as described by classical electromagnetism. It is just the low-energy limit of Compton scattering: the particle kinetic energy and photon frequency are the same before and after the scattering...
is the scattering of electromagnetic radiation (light) by charged particles such as electrons.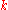 is the wave number of the wave being suppressed.
is the wave number of the wave being suppressed.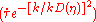 is the visibility function.
is the visibility function.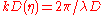
The damping factor
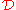 , when factored into the Boltzmann equation
, when factored into the Boltzmann equationBoltzmann equation
The Boltzmann equation, also often known as the Boltzmann transport equation, devised by Ludwig Boltzmann, describes the statistical distribution of one particle in rarefied gas...
for the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB), reduces the amplitude of perturbations:

Where:
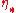 is the conformal time at decoupling.
is the conformal time at decoupling. is the "monopole [perturbation] of the photon distribution function"
is the "monopole [perturbation] of the photon distribution function"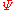 is a "gravitational-potential [perturbation] in the Newtonian gauge". The Newtonian gauge is a quantity with importance in the General Theory of Relativity.
is a "gravitational-potential [perturbation] in the Newtonian gauge". The Newtonian gauge is a quantity with importance in the General Theory of Relativity. is the effective temperature.
is the effective temperature.
 , or the effective diffusion scale, which in turn depends on a crucial value, the diffusion length,
, or the effective diffusion scale, which in turn depends on a crucial value, the diffusion length, 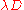 . The diffusion length relates how far photons travel during diffusion, and comprises a finite number of short steps in random directions. The average of these steps is the Compton mean free path
. The diffusion length relates how far photons travel during diffusion, and comprises a finite number of short steps in random directions. The average of these steps is the Compton mean free pathMean free path
In physics, the mean free path is the average distance covered by a moving particle between successive impacts which modify its direction or energy or other particle properties.-Derivation:...
, and is denoted by
 . As the direction of these steps are randomly taken,
. As the direction of these steps are randomly taken, 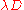 is approximately equal to
is approximately equal to  , where
, where  is the number of steps the photon takes before the conformal time at decoupling (
is the number of steps the photon takes before the conformal time at decoupling (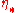 ).
).The diffusion length increases at recombination because the mean free path does, with less photon scattering occurring; this increases the amount of diffusion and damping. The mean free path increases because the electron ionisation fraction,
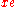 , decreases as ionised hydrogen
, decreases as ionised hydrogenHydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
bind with the free, charged electrons. As this occurs, the mean free path increases proportionally:
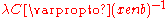 . That is, the mean free path of the photons is inversely proportional
. That is, the mean free path of the photons is inversely proportionalProportionality
Proportionality may refer to:*Proportionality , the relationship of two variables whose ratio is constant*Proportionality , A legal principle under municipal law in which the punishment of a certain crime should be in proportion to the severity of the crime itself, and under international law an...
to the electron ionisation fraction and the baryon number density (
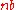 ). That means that the more baryons there were, and the more they were ionised, the shorter the average photon could travel before encountering one and being scattered. Small changes to these values before or during recombination can augment the damping effect considerably. This dependence on the baryon density by photon diffusion allows scientists to use analysis of the latter to investigate the former, in addition to the history of ionisation.
). That means that the more baryons there were, and the more they were ionised, the shorter the average photon could travel before encountering one and being scattered. Small changes to these values before or during recombination can augment the damping effect considerably. This dependence on the baryon density by photon diffusion allows scientists to use analysis of the latter to investigate the former, in addition to the history of ionisation.The effect of diffusion damping is greatly augmented by the finite width of the surface of last scattering (SLS). The finite width of the SLS means the CMB photons we see were not all emitted at the same time, and the fluctuations we see are not all in phase. It also means that during recombination, the diffusion length changed dramatically, as the ionisation fraction shifted.
Model dependence
In general, diffusion damping produces its effects independent of the cosmological model being studied, thereby masking the effects of other, model-dependent phenomena. This means that without an accurate model of diffusion damping, scientists cannot judge the relative merits of cosmological models, whose theoretical predictions cannot be compared with observational data, this data being obscured by damping effects. For example, the peaks in the power spectrum due to acoustic oscillations are decreased in amplitude by diffusion damping. This deamplification of the power spectrum hides features of the curve, features that would otherwise be more visible.Though general diffusion damping can damp perturbations in collisionless dark matter simply due to photon dispersion, the term Silk damping applies only to damping of adiabatic models of baryonic matter, which is coupled to the diffusing photons, not dark matter
Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
, and diffuses with them. Silk damping is not as significant in models of cosmological development which posit early isocurvature fluctuations (i.e. fluctuations which do not require a constant ratio of baryons and photons). In this case, increases in baryon density do not require a corresponding increases in photon density, and the lower the photon density, the less diffusion there would be: the less diffusion, the less damping. Photon diffusion is not dependent on the causes of the initial fluctuations in the density of the universe.
Speed
Damping occurs at two different scales, with the process working more quickly over short ranges than over longer distances. Here, a short length is one that is lower than the mean free path of the photons. A long distance is one that is greater than the mean free path, if still less than the diffusion length. On the smaller scale, perturbations are damped almost instantaneously. On the larger scale, anisotropies are decreased more slowly, with significant degradation happening within one unit of Hubble time.The Silk scale and the Silk mass
Diffusion damping exponentially decreases anisotropies in the CMB on a scale (the Silk scale) much smaller than a degreeDegree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
, or smaller than approximately 3 megaparsecs
Parsec
The parsec is a unit of length used in astronomy. It is about 3.26 light-years, or just under 31 trillion kilometres ....
. This angular scale corresponds to a multipole moment
 . The mass contained within the Silk scale is the silk mass. Numerical evaluations of the Silk mass yield results on the order of
. The mass contained within the Silk scale is the silk mass. Numerical evaluations of the Silk mass yield results on the order of 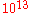 solar masses at recombination and on the order of the mass of a present-day galaxy
solar masses at recombination and on the order of the mass of a present-day galaxyGalaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
or galaxy cluster
Galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster is a compact cluster of galaxies. Basic difference between a galaxy group and a galaxy cluster is that there are many more galaxies in a cluster than in a group. Also, galaxies in a cluster are more compact and have higher velocity dispersion. One of the key features of cluster is...
in the current era.
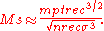
As diffusion damping works at this level, scientists say it affects small angles and corresponding anisotropies. This is to be contrasted with other effects which operate on a scale called intermediate
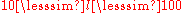 or large
or large 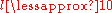 . Searches for anisotropies on a small scale are not as difficult as those on larger scales, partly because they may employ ground-based telescopes and their results can be more easily predicted by current theoretical models.
. Searches for anisotropies on a small scale are not as difficult as those on larger scales, partly because they may employ ground-based telescopes and their results can be more easily predicted by current theoretical models.Galaxy formation
Scientists study photon diffusion damping (and CMB anisotropies in general) because of the insight the subject provides into the question, "How did the universe come to be?". Specifically, primordial anisotropies in the temperature and density of the universe are supposed to be the causes of later large-scale structure formation. Thus it was the amplification of small perturbations in the pre-recombination universe that grew into the galaxies and galaxy clusters of the present era. Diffusion damping made the universe isotropic within distances on the order of the Silk Scale. That this scale corresponds to the size of observed galaxies (when the passage of time is taken into account) implies that diffusion damping is responsible for limiting the size of these galaxies. The theory is that clumps of matter in the early universe became the galaxies that we see today, and the size of these galaxies is related to the temperature and density of the clumps.Diffusion may also have had a significant effect on the evolution of primordial cosmic magnetic fields, fields which may have been amplified over time to become galactic magnetic fields. However, these cosmic magnetic fields may have been damped by radiative diffusion: just as acoustic oscillations in the plasma were damped by the diffusion of photons, so were magnetosonic wave
Magnetosonic wave
A magnetosonic wave is a longitudinal wave of ions in a magnetized plasma propagating perpendicular to the stationary magnetic field...
s (waves of ions travelling through a magnetised plasma). This process began before the era of neutrino decoupling
Neutrino decoupling
In Big Bang cosmology, neutrino decoupling refers to the epoch at which neutrinos ceased interacting with baryonic matter, and thereby ceased influencing the dynamics of the universe at early times. Prior to decoupling, neutrinos were in thermal equilibrium with protons, neutrons, and electrons,...
and ended at the time of recombination.
See also
- Timeline of the Big BangTimeline of the Big BangThis timeline of the Big Bang describes the history of the universe according to the prevailing scientific theory of how the universe came into being, using the cosmological time parameter of comoving coordinates...
- Timeline of cosmologyTimeline of cosmologyThis timeline of cosmological theories and discoveries is a chronological record of the development of humanity's understanding of the cosmos over the last two-plus millennia. Modern cosmological ideas follow the development of the scientific discipline of physical cosmology.-Pre-1900:* ca...
- Joseph Silk
- Photon diffusionPhoton diffusionPhoton diffusion is a situation where photons travel through a material without being absorbed, but rather undergoing repeated scattering events which change the direction of their path. The path of any given photon is then effectively a random walk...

