
Neutrino decoupling
Encyclopedia
In Big Bang
cosmology
, neutrino decoupling refers to the epoch at which neutrinos ceased interacting with baryonic matter, and thereby ceased influencing the dynamics of the universe at early times. Prior to decoupling, neutrino
s were in thermal equilibrium
with proton
s, neutron
s, and electron
s, which was maintained through the weak interaction
. Decoupling occurred approximately at the time when the rate of those weak interactions was slower than the rate of expansion of the universe. Alternatively, it was the time when the time scale for weak interactions became greater than the age of the universe
at that time. Neutrino decoupling took place approximately one second after the Big Bang, when the temperature
of the universe was approximately 10 billion
kelvin
s, or 1 MeV
.
by their interactions with electron
s and positron
s, such as the reaction
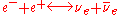 .
.
The approximate rate of these interactions is set by the number density
of electrons and positrons, the averaged product of the cross section
for interaction and the velocity
of the particles. The number density of the relativistic
of the relativistic
electrons and positrons depends on the cube of the temperature , so that
, so that  . The product of the cross section and velocity for weak interactions for temperatures (energies) below W/Z boson masses (~100 GeV) is given approximately by
. The product of the cross section and velocity for weak interactions for temperatures (energies) below W/Z boson masses (~100 GeV) is given approximately by 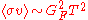 , where
, where 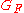 is Fermi's constant (as is standard in particle physics
is Fermi's constant (as is standard in particle physics
calculations, factors of the speed of light
 are set equal to 1). Putting it all together, the rate of weak interactions
are set equal to 1). Putting it all together, the rate of weak interactions 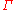 is
is
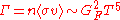 .
.
This can be compared to the expansion rate which is given by the Hubble parameter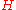 , with
, with
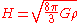 ,
,
where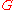 is the gravitational constant
is the gravitational constant
and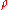 is the energy density
is the energy density
of the universe. At this point in cosmic history, the energy density is dominated by radiation, so that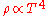 . As the rate of weak interaction depends more strongly on temperature, it will fall more quickly as the universe cools. Thus when the two rates are approximately equal (dropping terms of order unity, including an effective degeneracy
. As the rate of weak interaction depends more strongly on temperature, it will fall more quickly as the universe cools. Thus when the two rates are approximately equal (dropping terms of order unity, including an effective degeneracy
term which counts the number of states of particles which are interacting) gives the approximate temperature at which neutrinos decouple:
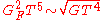 .
.
Solving for temperature gives
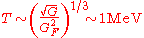 .
.
While this is a very rough derivation, it illustrates the important physical phenomena which determined when neutrinos decoupled.
, analogous to the cosmic microwave background radiation
of visible light which was emitted at a much later epoch. "The detection of the neutrino background is far beyond the capabilities of the present generation of neutrino detectors." There is data, however, which indirectly indicates the presence of a neutrino background. One piece of evidence is damping of the angular
power spectrum of the CMB, which results from anisotropies in the neutrino background.
Another indirect measurement of neutrino decoupling is allowed by the role that neutrino decoupling plays in setting the ratio of neutron
s to proton
s. Before decoupling, the number of neutrons and protons are maintained in their equilibrium abundances by weak interactions, specifically beta decay
and electron capture
(or inverse beta decay) according to
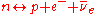
and
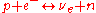 .
.
Once the rate of weak interactions is slower than the characteristic rate of the expansion of the universe, this equilibrium cannot be maintained, and the abundance of neutrons to protons "freezes in," at a value
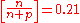 .
.
This value is simply found by evaluating the Boltzmann factor
for neutrons and protons at decoupling time, according to
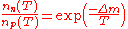 ,
,
where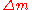 is the mass difference between neutrons and protons and
is the mass difference between neutrons and protons and  is the temperature at decoupling. This ratio is critical to the synthesis of atom
is the temperature at decoupling. This ratio is critical to the synthesis of atom
s during Big Bang nucleosynthesis
, the process which formed the majority of helium
atoms in the universe, as it "is the dominant factor in determining the amount of helium produced." As helium atoms are stable, the neutrons are locked in, and beta decay
of neutrons into protons, electrons, and neutrinos can no longer occur. Thus the abundance of neutrons remained essentially fixed to the present day. This abundance can be measured by astronomer
s, and, as it was determined by the ratio of neutrons to protons at neutrino decoupling, the helium abundance indirectly measures the temperature at which neutrino decoupling took place, and is in agreement with the figure derived above.
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
cosmology
Cosmology
Cosmology is the discipline that deals with the nature of the Universe as a whole. Cosmologists seek to understand the origin, evolution, structure, and ultimate fate of the Universe at large, as well as the natural laws that keep it in order...
, neutrino decoupling refers to the epoch at which neutrinos ceased interacting with baryonic matter, and thereby ceased influencing the dynamics of the universe at early times. Prior to decoupling, neutrino
Neutrino
A neutrino is an electrically neutral, weakly interacting elementary subatomic particle with a half-integer spin, chirality and a disputed but small non-zero mass. It is able to pass through ordinary matter almost unaffected...
s were in thermal equilibrium
Thermal equilibrium
Thermal equilibrium is a theoretical physical concept, used especially in theoretical texts, that means that all temperatures of interest are unchanging in time and uniform in space...
with proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s, neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s, and electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s, which was maintained through the weak interaction
Weak interaction
Weak interaction , is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, alongside the strong nuclear force, electromagnetism, and gravity. It is responsible for the radioactive decay of subatomic particles and initiates the process known as hydrogen fusion in stars...
. Decoupling occurred approximately at the time when the rate of those weak interactions was slower than the rate of expansion of the universe. Alternatively, it was the time when the time scale for weak interactions became greater than the age of the universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
at that time. Neutrino decoupling took place approximately one second after the Big Bang, when the temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
of the universe was approximately 10 billion
1000000000 (number)
1,000,000,000 is the natural number following 999,999,999 and preceding 1,000,000,001.In scientific notation, it is written as 109....
kelvin
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s, or 1 MeV
MEV
MeV and meV are multiples and submultiples of the electron volt unit referring to 1,000,000 eV and 0.001 eV, respectively.Mev or MEV may refer to:In entertainment:* Musica Elettronica Viva, an Italian musical group...
.
Derivation of decoupling time
Neutrinos are kept from free streamingFree streaming
In astronomy, free streaming is a term used to describe a particle, most often a photon, which propagates through a medium without scattering.-Use in defining surfaces:...
by their interactions with electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s and positron
Positron
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. The positron has an electric charge of +1e, a spin of ½, and has the same mass as an electron...
s, such as the reaction
 .
.The approximate rate of these interactions is set by the number density
Number density
In physics, astronomy, and chemistry, number density is an intensive quantity used to describe the degree of concentration of countable objects in the three-dimensional physical space...
of electrons and positrons, the averaged product of the cross section
Cross section (physics)
A cross section is the effective area which governs the probability of some scattering or absorption event. Together with particle density and path length, it can be used to predict the total scattering probability via the Beer-Lambert law....
for interaction and the velocity
Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
of the particles. The number density
 of the relativistic
of the relativisticTheory of relativity
The theory of relativity, or simply relativity, encompasses two theories of Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity. However, the word relativity is sometimes used in reference to Galilean invariance....
electrons and positrons depends on the cube of the temperature
 , so that
, so that  . The product of the cross section and velocity for weak interactions for temperatures (energies) below W/Z boson masses (~100 GeV) is given approximately by
. The product of the cross section and velocity for weak interactions for temperatures (energies) below W/Z boson masses (~100 GeV) is given approximately by 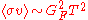 , where
, where 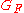 is Fermi's constant (as is standard in particle physics
is Fermi's constant (as is standard in particle physicsParticle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
calculations, factors of the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
 are set equal to 1). Putting it all together, the rate of weak interactions
are set equal to 1). Putting it all together, the rate of weak interactions  is
is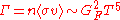 .
.This can be compared to the expansion rate which is given by the Hubble parameter
 , with
, with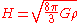 ,
,where
 is the gravitational constant
is the gravitational constantGravitational constant
The gravitational constant, denoted G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of the gravitational attraction between objects with mass. It appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is also known as the universal...
and
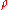 is the energy density
is the energy densityEnergy density
Energy density is a term used for the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Often only the useful or extractable energy is quantified, which is to say that chemically inaccessible energy such as rest mass energy is ignored...
of the universe. At this point in cosmic history, the energy density is dominated by radiation, so that
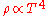 . As the rate of weak interaction depends more strongly on temperature, it will fall more quickly as the universe cools. Thus when the two rates are approximately equal (dropping terms of order unity, including an effective degeneracy
. As the rate of weak interaction depends more strongly on temperature, it will fall more quickly as the universe cools. Thus when the two rates are approximately equal (dropping terms of order unity, including an effective degeneracyDegenerate energy level
In physics, two or more different quantum states are said to be degenerate if they are all at the same energy level. Statistically this means that they are all equally probable of being filled, and in Quantum Mechanics it is represented mathematically by the Hamiltonian for the system having more...
term which counts the number of states of particles which are interacting) gives the approximate temperature at which neutrinos decouple:
 .
.Solving for temperature gives
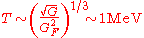 .
.While this is a very rough derivation, it illustrates the important physical phenomena which determined when neutrinos decoupled.
Observational evidence
While neutrino decoupling can not be observed directly, it is expected to have left behind a cosmic neutrino backgroundCosmic neutrino background
The cosmic neutrino background is the universe's background particle radiation composed of neutrinos.Like the cosmic microwave background radiation , the CνB is a relic of the big bang, and while the CMB dates from when the universe was 379,000 years old, the CνB decoupled from matter when the...
, analogous to the cosmic microwave background radiation
Cosmic microwave background radiation
In cosmology, cosmic microwave background radiation is thermal radiation filling the observable universe almost uniformly....
of visible light which was emitted at a much later epoch. "The detection of the neutrino background is far beyond the capabilities of the present generation of neutrino detectors." There is data, however, which indirectly indicates the presence of a neutrino background. One piece of evidence is damping of the angular
Angular
The angular is a large bone in the lower jaw of amphibians and reptiles , which is connected to all other lower jaw bones: the dentary , the splenial, the suprangular, and the articular...
power spectrum of the CMB, which results from anisotropies in the neutrino background.
Another indirect measurement of neutrino decoupling is allowed by the role that neutrino decoupling plays in setting the ratio of neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s to proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s. Before decoupling, the number of neutrons and protons are maintained in their equilibrium abundances by weak interactions, specifically beta decay
Beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle is emitted from an atom. There are two types of beta decay: beta minus and beta plus. In the case of beta decay that produces an electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus , while in the case of a...
and electron capture
Electron capture
Electron capture is a process in which a proton-rich nuclide absorbs an inner atomic electron and simultaneously emits a neutrino...
(or inverse beta decay) according to

and
 .
.Once the rate of weak interactions is slower than the characteristic rate of the expansion of the universe, this equilibrium cannot be maintained, and the abundance of neutrons to protons "freezes in," at a value
 .
.This value is simply found by evaluating the Boltzmann factor
Boltzmann factor
In physics, the Boltzmann factor is a weighting factor that determines the relative probability of a particle to be in a state i in a multi-state system in thermodynamic equilibrium at temperature T...
for neutrons and protons at decoupling time, according to
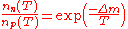 ,
,where
 is the mass difference between neutrons and protons and
is the mass difference between neutrons and protons and  is the temperature at decoupling. This ratio is critical to the synthesis of atom
is the temperature at decoupling. This ratio is critical to the synthesis of atomAtom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s during Big Bang nucleosynthesis
Big Bang nucleosynthesis
In physical cosmology, Big Bang nucleosynthesis refers to the production of nuclei other than those of H-1 during the early phases of the universe...
, the process which formed the majority of helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
atoms in the universe, as it "is the dominant factor in determining the amount of helium produced." As helium atoms are stable, the neutrons are locked in, and beta decay
Beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle is emitted from an atom. There are two types of beta decay: beta minus and beta plus. In the case of beta decay that produces an electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus , while in the case of a...
of neutrons into protons, electrons, and neutrinos can no longer occur. Thus the abundance of neutrons remained essentially fixed to the present day. This abundance can be measured by astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
s, and, as it was determined by the ratio of neutrons to protons at neutrino decoupling, the helium abundance indirectly measures the temperature at which neutrino decoupling took place, and is in agreement with the figure derived above.

