
Branching (linguistics)
Encyclopedia
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. Linguistics can be broadly broken into three categories or subfields of study: language form, language meaning, and language in context....
, branching is the general tendency towards a given order of word
Word
In language, a word is the smallest free form that may be uttered in isolation with semantic or pragmatic content . This contrasts with a morpheme, which is the smallest unit of meaning but will not necessarily stand on its own...
s within sentence
Sentence (linguistics)
In the field of linguistics, a sentence is an expression in natural language, and often defined to indicate a grammatical unit consisting of one or more words that generally bear minimal syntactic relation to the words that precede or follow it...
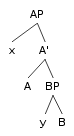
s and smaller grammatical units within sentences (such as subordinate propositions, prepositional phrases, etc.). Such ordering and nesting of phrases can be represented as a tree where branches can be divided into other minor branches, which may also branch in turn.
Language typically construct phrases with a head word
Head (linguistics)
In linguistics, the head is the word that determines the syntactic type of the phrase of which it is a member, or analogously the stem that determines the semantic category of a compound of which it is a component. The other elements modify the head....
(or nucleus) and zero or more dependents (modifiers). For example, in English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
a noun phrase
Noun phrase
In grammar, a noun phrase, nominal phrase, or nominal group is a phrase based on a noun, pronoun, or other noun-like word optionally accompanied by modifiers such as adjectives....
can be constructed as follows:
- noun (e.g. "people")
- article + noun (e.g., "the man")
- numeral + noun (e.g., "ten geographers")
- article + adjective + noun (e.g., "the beautiful trees")
- noun phrase + 's + noun (e.g., "the woman's eyes")
- article + noun + relative clause (e.g., "the house that the crane demolished")
- etc.
In a dependent clause, the head word is the verb, and the dependents are the arguments of the verb. In a noun phrase, the head word is the main noun
Noun
In linguistics, a noun is a member of a large, open lexical category whose members can occur as the main word in the subject of a clause, the object of a verb, or the object of a preposition .Lexical categories are defined in terms of how their members combine with other kinds of...
, and the dependents are the adjective
Adjective
In grammar, an adjective is a 'describing' word; the main syntactic role of which is to qualify a noun or noun phrase, giving more information about the object signified....
, the numeral
Number names
In linguistics, number names are specific words in a natural language that represent numbers.In writing, numerals are symbols also representing numbers...
, the genitive (-'s) of noun, and the relative clause
Relative clause
A relative clause is a subordinate clause that modifies a noun phrase, most commonly a noun. For example, the phrase "the man who wasn't there" contains the noun man, which is modified by the relative clause who wasn't there...
.
There are also verb phrases, prepositional phrases, and the like. In every case, the constituents are placed in a given order, which is more or less fixed according to the language in question. Also in some cases, the dependents can in turn be the head words of inner phrases (as in "the black cat's paws", "an awfully messy room", etc.).
Branching is typically ordered. In English, an article can be added to a bare noun only by placing it before the noun. An adjective can usually be added to an article-noun phrase only in between the article and the noun, whereas a dependent clause can be added only following the noun. This is also true of prepositional phrases. The subject comes before the main verb in the vast majority of sentences in the indicative mood, and the direct object in a sentence is nearly always found following its main verb.
The rules exemplified above constitute the branching tendency of the language, which can be predominantly left-branching or right-branching.
Left-branching languages, such as Turkish
Turkish language
Turkish is a language spoken as a native language by over 83 million people worldwide, making it the most commonly spoken of the Turkic languages. Its speakers are located predominantly in Turkey and Northern Cyprus with smaller groups in Iraq, Greece, Bulgaria, the Republic of Macedonia, Kosovo,...
, Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
, Tamil
Tamil language
Tamil is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by Tamil people of the Indian subcontinent. It has official status in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and in the Indian union territory of Pondicherry. Tamil is also an official language of Sri Lanka and Singapore...
, and Basque
Basque language
Basque is the ancestral language of the Basque people, who inhabit the Basque Country, a region spanning an area in northeastern Spain and southwestern France. It is spoken by 25.7% of Basques in all territories...
tend to place dependents before the head words. Adjectives precede nouns, direct objects come before verbs, and there are postpositions. In less formal terminology, this ordering is called head-last or head-final.
An example from Basque:
- [1]Hillary Clinton [2]izan da, [3]inkestek [4]aurreikusten zutenaren [5]kontra, [6]New Hampshireko (AEB) [7]primarioetan [8]boto-emaile [9]demokrata [10]gehien [11]bereganatu duen [12]hautagaia.
- [1]Hillary Clinton [2]was [12]the candidate who [11]got [10]the most [9]Democratic [8]voters [7]in the primaries [6]of New Hampshire (USA), [5]contrary [4]to what was forecast in the [3]polls.
Right-branching languages, such as Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
, Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
, and Khmer
Khmer language
Khmer , or Cambodian, is the language of the Khmer people and the official language of Cambodia. It is the second most widely spoken Austroasiatic language , with speakers in the tens of millions. Khmer has been considerably influenced by Sanskrit and Pali, especially in the royal and religious...
tend to place dependents after the head words. Adjectives follow nouns, direct objects follow verbs, and adposition
Adposition
Prepositions are a grammatically distinct class of words whose most central members characteristically express spatial relations or serve to mark various syntactic functions and semantic roles...
s are prepositional. This is also known as head-first order.
An example from the Spanish:
- [1]Hillary Clinton [2]fue [12]la candidata que [11]logró [10]la mayoría de los [8]votos [9]Demócratas [7]en las primarias [6]de New Hampshire (USA), [5]contrario a [4]lo que pronosticaban [3]las encuestas.
Reenumerating the sentence to compare against the English word order:
- [A]Hillary Clinton [B]was [C]the candidate who [D]got [E]the most [F]Democratic [G]voters [H]in the primaries [I]of New Hampshire (USA), [J]contrary [K]to what was forecast in the [L]polls.
we can see the similarity between these two right-branching languages:
- [A]Hillary Clinton [B]fue [C]la candidata que [D]logró [E]la mayoría de los [G]votos [F]Demócratas [H]en las primarias [I]de New Hampshire (USA), [J]contrario a [K]lo que pronosticaban [L]las encuestas.
with the only distinction being adjective placement.
Though article
Article (grammar)
An article is a word that combines with a noun to indicate the type of reference being made by the noun. Articles specify the grammatical definiteness of the noun, in some languages extending to volume or numerical scope. The articles in the English language are the and a/an, and some...
s (words like a and the in English) have been thought of as the dependents of nouns, it is now thought that articles and nouns form a dependent phrase, in which the article is the head. Consistent with this new view, languages that place the verb before the object in clauses also tend to place the article before the noun, and languages that place the verb after the object also tend to place the article after the noun.
For most languages, the main branching tendency is just a tendency and it often shows exceptions. Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
, for example, while overwhelmingly right-branching, puts numeral modifiers before nouns and, in certain cases, objects before verbs. Languages like English and German - though regarded as being right-branching because the main verbs precede direct objects - place adjectives and numerals before their nouns. Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
and most other languages of northeastern Asia and the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
, on the other hand, are practically a model for rigidly left-branching languages. The Mon–Khmer and Austronesian languages
Austronesian languages
The Austronesian languages are a language family widely dispersed throughout the islands of Southeast Asia and the Pacific, with a few members spoken on continental Asia that are spoken by about 386 million people. It is on par with Indo-European, Niger-Congo, Afroasiatic and Uralic as one of the...
of southeast Asia and many African languages
African languages
There are over 2100 and by some counts over 3000 languages spoken natively in Africa in several major language families:*Afro-Asiatic spread throughout the Middle East, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahel...
come close to rigidly right-branching, with numerals as well as adjectives following their nouns and degree words like "very", "too", "extremely", "quite" following the adjectives they modify.
See also
- Adjunct (grammar)Adjunct (grammar)In linguistics, an adjunct is an optional, or structurally dispensable, part of a sentence that, when removed, will not affect the remainder of the sentence except to discard from it some auxiliary information...
- SpecifierSpecifierIn X-bar theory in linguistics, specifiers, head words, and complements together form phrases. Specifiers differ from complements because they are not sisters of the head, but rather sisters of the phrase formed by the head and the complement...
- Complement (linguistics)Complement (linguistics)In grammar the term complement is used with different meanings. The primary meaning is a word, phrase or clause that is necessary in a sentence to complete its meaning. We find complements that function as an argument and complements that exist within arguments.Both complements and modifiers add...
- X-bar theoryX-bar theoryX-bar theory is a component of linguistic theory which attempts to identify syntactic features presumably common to all those human languages that fit in a presupposed framework...
- Word orderWord orderIn linguistics, word order typology refers to the study of the order of the syntactic constituents of a language, and how different languages can employ different orders. Correlations between orders found in different syntactic subdomains are also of interest...
- Right-branching sentenceRight-branching sentenceIn English grammar, a right-branching sentence is a sentence in which the main subject of the sentence is described first, and is followed by a sequence of modifiers that provide additional information about the subject. For example, the following sentence is right-branching.Note that the sentence...

