Beta-catenin
Encyclopedia

Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
that in humans is encoded by the CTNNB1 gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
. In Drosophila
Drosophila
Drosophila is a genus of small flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "fruit flies" or more appropriately pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit...
, the homologous protein is called armadillo. β-catenin is a subunit of the cadherin
Cadherin
Cadherins are a class of type-1 transmembrane proteins. They play important roles in cell adhesion, ensuring that cells within tissues are bound together. They are dependent on calcium ions to function, hence their name.The cadherin superfamily includes cadherins, protocadherins, desmogleins, and...
protein complex and has been implicated as an integral component in the Wnt signaling pathway
Wnt signaling pathway
The Wnt signaling pathway is a network of proteins best known for their roles in embryogenesis and cancer, but also involved in normal physiological processes in adult animals.-Discovery:...
.
Structure
When β-catenin was sequenced, it was found to be a member of the armadillo family of proteins. These proteins have multiple copies of the so-called armadillo repeat domain, which is specialized for protein-protein binding. When β-catenin is not associated with cadherins and alpha-catenin, it can interact with other proteins such as ICATCTNNBIP1
Beta-catenin-interacting protein 1 is a protein that is encoded in humans by the CTNNBIP1 gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene binds CTNNB1 and prevents interaction between CTNNB1 and TCF family members. The encoded protein is a negative regulator of the Wnt signaling pathway....
and APC
APC (gene)
Adenomatous polyposis coli also known as deleted in polyposis 2.5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APC gene. Mutations in the APC gene may result in colorectal cancer....
.
Function
β-Catenin is part of a complex of proteins that constitute adherens junctionAdherens junction
Adherens junctions are protein complexes that occur at cell–cell junctions in epithelial tissues, usually more basal than tight junctions...
s (AJs). AJs are necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial
Epithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
cell layers by regulating cell growth and adhesion
Cell adhesion
Cellular adhesion is the binding of a cell to a surface, extracellular matrix or another cell using cell adhesion molecules such as selectins, integrins, and cadherins. Correct cellular adhesion is essential in maintaining multicellular structure...
between cells. β-Catenin also anchors the actin
Actin
Actin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a cellular "scaffolding" or "skeleton" contained within a cell's cytoplasm and is made out of protein. The cytoskeleton is present in all cells; it was once thought to be unique to eukaryotes, but recent research has identified the prokaryotic cytoskeleton...
and may be responsible for transmitting the contact inhibition signal that causes cells to stop dividing once the epithelial sheet is complete.
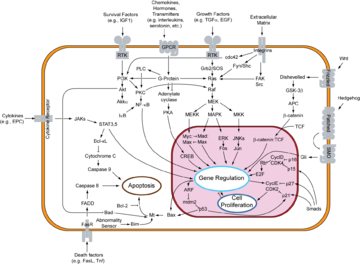
Recent evidence suggests that β-catenin plays an important role in various aspects of liver biology including liver development (both embryonic and postnatal), liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy, HGF-induced hepatomegaly, liver zonation, and pathogenesis of liver cancer.
Role in the Wnt signaling pathway
When Wnt is not present, GSK-3GSK-3
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 is a serine/threonine protein kinase that mediates the addition of phosphate molecules on certain serine and threonine amino acids in particular cellular substrates...
(a kinase) constitutively phosphorylates the β-catenin protein. β-catenin is associated with axin
AXIN1
Axin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AXIN1 gene.-Interactions:AXIN1 has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin, GSK3B, TSC2, APC, LRP5, DVL1, MAP3K1, CSNK1E, Casein kinase 1, alpha 1 and PPP2R5A.-Further reading:...
(scaffolding protein) complexed with GSK3 and APC
APC (gene)
Adenomatous polyposis coli also known as deleted in polyposis 2.5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APC gene. Mutations in the APC gene may result in colorectal cancer....
(adenomatosis polyposis coli). The creation of said complex acts to substantially increase the phosphorylation of β-catenin by facilitating the action of GSK3. When β-catenin is phosphorylated, it is degraded and, thus, will not build up in the cell to a significant level. When Wnt binds to frizzled
Frizzled
Frizzled is a family of G protein-coupled receptor proteins that serve as receptors in the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. When activated, Frizzled leads to activation of Dishevelled in the cytosol.-Species distribution:...
(Fz), its receptor, dishevelled
Dishevelled
Dishevelled is a family of proteins involved in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways. Dsh is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that acts directly downstream of frizzled receptors...
(Dsh), is recruited to the membrane. GSK3 is inhibited by the activation of Dsh by Fz. Because of this, β-catenin is permitted to build up in the cytosol
Cytosol
The cytosol or intracellular fluid is the liquid found inside cells, that is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into compartments....
and can be subsequently translocated into the nucleus
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
to perform a variety of functions. It can act in conjunction with TCF and LEF
TCF/LEF family
The TCF/LEF family is a group of transcription factors which bind to DNA through a high mobility group domain. They are involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, where they recruit the coactivator beta-catenin to enhancer elements of genes they target. They can also recruit members of the Groucho...
to activate specific target genes involved in different processes.
Clinical significance
The gene that codes for β-catenin can function as an oncogeneOncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, they are often mutated or expressed at high levels.An oncogene is a gene found in the chromosomes of tumor cells whose activation is associated with the initial and continuing conversion of normal cells into cancer...
. An increase in β-catenin production has been noted in those people with basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal-cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer. It rarely metastasizes or kills. However, because it can cause significant destruction and disfigurement by invading surrounding tissues, it is still considered malignant. Statistically, approximately 3 out of 10 Caucasians may develop a...
and leads to the increase in proliferation of related tumors. Mutations in this gene are a cause of colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer, commonly known as bowel cancer, is a cancer caused by uncontrolled cell growth , in the colon, rectum, or vermiform appendix. Colorectal cancer is clinically distinct from anal cancer, which affects the anus....
(CRC), pilomatrixoma (PTR), medulloblastoma
Medulloblastoma
Medulloblastoma is a highly malignant primary brain tumor that originates in the cerebellum or posterior fossa.Previously, medulloblastomas were thought to represent a subset of primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the posterior fossa...
(MDB), and ovarian cancer. Also, β-catenin binds to the product of the APC gene, which is mutated in adenomatous polyposis of the colon.
Interactions with other proteins
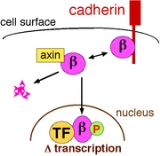
β-catenin contains armadillo repeats and is able to bind to other proteins. Inside cells, β-catenin can be found in complexes with cadherins, transcription factorTranscription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
s (TF in Figure 2), and other proteins such as axin, a component of the Wnt signalling pathway and galectin-3, beta-galactoside-binding protein. The ability of β-catenin to bind to other proteins is regulated by tyrosine kinase
Tyrosine kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to a protein in a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions....
s and serine kinases such as GSK-3
GSK-3
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 is a serine/threonine protein kinase that mediates the addition of phosphate molecules on certain serine and threonine amino acids in particular cellular substrates...
.
When β-catenin is not assembled in complexes with cadherins, it can form a complex with axin. While bound to axin, β-catenin can be phosphorylated
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation activates or deactivates many protein enzymes....
by GSK-3, which creates a signal for the rapid ubiquitin
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotic organisms. Among other functions, it directs protein recycling.Ubiquitin can be attached to proteins and label them for destruction...
-dependent degradation of β-catenin by proteosomes
Proteasome
Proteasomes are very large protein complexes inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some bacteria. In eukaryotes, they are located in the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The main function of the proteasome is to degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks...
. Various signals such as the Wnt signalling pathway can inhibit GSK-3-mediated phosphorylation of β-catenin, allowing β-catenin to go to the cell nucleus, interact with transcription factors, and regulate gene transcription
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
.
β-Catenin can be phosphorylated by other kinases such as protein kinase A
CAMP-dependent protein kinase
In cell biology, Protein kinase A refers to a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP . PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase...
(PKA). Phosphorylation of β-catenin by PKA has been associated with reduced degradation of β-catenin, increased levels of β-catenin in the nucleus and interaction of β-catenin with TCF family transcription factors to regulate gene expression.
In addition, β-catenin has been shown to interact
Protein-protein interaction
Protein–protein interactions occur when two or more proteins bind together, often to carry out their biological function. Many of the most important molecular processes in the cell such as DNA replication are carried out by large molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein...
with:
- Androgen receptorAndrogen receptorThe androgen receptor , also known as NR3C4 , is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding of either of the androgenic hormones testosterone or dihydrotestosterone in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus...
- APCAPC (gene)Adenomatous polyposis coli also known as deleted in polyposis 2.5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APC gene. Mutations in the APC gene may result in colorectal cancer....
- AXIN1AXIN1Axin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AXIN1 gene.-Interactions:AXIN1 has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin, GSK3B, TSC2, APC, LRP5, DVL1, MAP3K1, CSNK1E, Casein kinase 1, alpha 1 and PPP2R5A.-Further reading:...
- CBY1CBY1Protein chibby homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CBY1 gene.-Interactions:CBY1 has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin.-Further reading:...
- CDH1CDH1 (gene)Cadherin-1 also known as CAM 120/80 or epithelial cadherin or uvomorulin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH1 gene. CDH1 has also been designated as CD324 . It is a tumor suppressor gene.- Function :Cadherin-1 is a classical member of the cadherin superfamily...
, - CDH2CDH2Cadherin-2 , also known as neural cadherin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH2 gene. CDH2 has also been designated as CD325 .- Function :...
, - CDH3CDH3 (gene)Cadherin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH3 gene.-Interactions:CDH3 has been shown to interact with CDH1, Beta-catenin, Plakoglobin, Nephrin and Catenin , alpha 1.-Further reading:...
- CDK5R1CDK5R1Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK5R1 gene.-Interactions:CDK5R1 has been shown to interact with CDK5RAP2, Beta-catenin, Cyclin-dependent kinase 5, Amphiphysin, Protein SET, CAMK2A, Actinin, alpha 1 and PCTK1.-Further reading:...
- CHUKCHUKInhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha also known as IKK1 or conserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase is a protein kinase that in humans is encoded by the CHUK gene. IKK-α is part of the IκB kinase complex that plays an important role in regulating the NF-κB transcription...
, - CTNNA1,
- CTNND1CTNND1Catenin delta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTNND1 gene.-Interactions:CTNND1 has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin, FYN, Collagen, type XVII, alpha 1, PTPN6, YES1, PTPRJ, VE-cadherin, MUC1, CDH1, CDH2, PTPRM, Cortactin, Nephrin, ZBTB33 and PSEN1.-Further reading:...
- EGFREpidermal growth factor receptorThe epidermal growth factor receptor is the cell-surface receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family of extracellular protein ligands...
- FHL2FHL2Four and a half LIM domains protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FHL2 gene.-Interactions:FHL2 has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin, Titin, Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16, Integrin, beta 6, Androgen receptor, ITGA7, CREB1, MAPK1, CD49c, ZNF638, BRCA1,...
- GSK3BGSK3BGlycogen synthase kinase 3 beta, also known as GSK3B, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSK3B gene.- Function :Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is a proline-directed serine-threonine kinase that was initially identified as a phosphorylating and inactivating glycogen synthase. Two isoforms,...
- HER2/neuHER2/neuHER-2 also known as proto-oncogene Neu, receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2, CD340 or p185 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ERBB2 gene. Over expression of this gene is correlated with higher aggressiveness in breast cancers...
- HNF4AHepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alphaHepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha also known as NR2A1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the HNF4A gene.- Function :...
- IKK2IKK2IKK-β also known as inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IKBKB gene.- Function :...
- LEF1Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LEF1 gene.- Function :Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor-1 is a 48-kD nuclear protein that is expressed in pre-B and T cells. It binds to a functionally important site in the T-cell receptor-alpha enhancer and confers...
- MAGI1MAGI1Membrane-associated guanylate kinase, WW and PDZ domain-containing protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAGI1 gene.-Interactions:...
- MUC1MUC1Mucin 1, cell surface associated or polymorphic epithelial mucin is a mucin encoded by the MUC1 gene in humans. MUC1 is a proteoglycan with extensive O-linked glycosylation of its extracellular domain. Mucins line the apical surface of epithelial cells in the lungs, stomach, intestines, eyes and...
- NR5A1Steroidogenic factor 1The steroidogenic factor 1 protein controls sexual development in the embryo and at puberty.SF1 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors and is encoded by the NR5A1 gene .- Function :SF-1 is a critical regulator of reproduction, regulating the transcription...
- PCAFPCAFP300/CBP-associated factor , also known as K acetyltransferase 2B , is a human gene and trancriptional coactivator associated with p53.-Structure:...
, - PHF17PHF17Protein Jade-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PHF17 gene.-Interactions:PHF17 has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin and Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor....
- PlakoglobinPlakoglobinJunction plakoglobin, also known as gamma-catenin or JUP, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JUP gene.- Function :...
- PTPN14PTPN14Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 14 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN14 gene.-Interactions:PTPN14 has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin.-Further reading:...
- PTPRFPTPRFReceptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase F is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPRF gene.The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell...
- PTPRKPTPRKReceptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase kappa is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPRK gene.-Interactions:PTPRK has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin and Plakoglobin.-Further reading:...
- PSEN1PSEN1Presenilin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSEN1 gene.- Function :Alzheimer's disease patients with an inherited form of the disease carry mutations in the presenilin proteins or the amyloid precursor protein...
- RuvB-like 1RuvB-like 1RuvB-like 1 , also known as RUVBL1 and TIP49, is a human gene. RUVBL1 can form a hexamer. The hexamer can form a dodecamer with RUVBL2 protein.-Interactions:...
- SMAD7Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 or SMAD7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD7 gene.SMAD7 is a protein that, as its name describes, is a homolog of the Drosophila gene: "Mothers against decapentaplegic". It belongs to the SMAD family of proteins, which belong to the TGFβ...
- SLC9A3R1Sodium-hydrogen antiporter 3 regulator 1Sodium-hydrogen antiporter 3 regulator 1 is a regulator of Sodium-hydrogen antiporter 3. It is encoded by the gene SLC9A3R1. It is also known as ERM Binding Protein 50 or Na+/H+ Exchanger Regulatory Factor...
, - SMARCA4SMARCA4Transcription activator BRG1 also known as ATP-dependent helicase SMARCA4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCA4 gene.- Function :...
- USP9XUSP9XProbable ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase FAF-X is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the USP9X gene.-Interactions:USP9X has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin, MARK4, NUAK1 and MLLT4.-Further reading:...
- VE-cadherinVE-cadherinCadherin 5, type 2 or VE-cadherin also known as CD144 , is a type of cadherin...
- PTK7PTK7Tyrosine-protein kinase-like 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTK7 gene.-Further reading:...

