
Well-field system
Encyclopedia
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
land distribution method existing between the ninth century BCE (late Western Zhou Dynasty
Zhou Dynasty
The Zhou Dynasty was a Chinese dynasty that followed the Shang Dynasty and preceded the Qin Dynasty. Although the Zhou Dynasty lasted longer than any other dynasty in Chinese history, the actual political and military control of China by the Ji family lasted only until 771 BC, a period known as...
) to around the end of the Warring States Period
Warring States Period
The Warring States Period , also known as the Era of Warring States, or the Warring Kingdoms period, covers the Iron Age period from about 475 BC to the reunification of China under the Qin Dynasty in 221 BC...
. Its name comes from Chinese character
Chinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
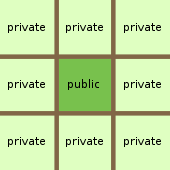
井 (jǐng), which means 'well' and looks like the # symbol
Number sign
Number sign is a name for the symbol #, which is used for a variety of purposes including, in some countries, the designation of a number...
; this character represents the theoretical appearance of land division: a square area of land was divided into nine identically-sized sections; the eight outer sections (私田; sītián) were privately cultivated by serf
SERF
A spin exchange relaxation-free magnetometer is a type of magnetometer developed at Princeton University in the early 2000s. SERF magnetometers measure magnetic fields by using lasers to detect the interaction between alkali metal atoms in a vapor and the magnetic field.The name for the technique...
s and the center section (公田; gōngtián) was communally cultivated on behalf of the landowning aristocrat.
While all fields were aristocrat-owned,, the private fields were managed exclusively by serfs and the produce was entirely the farmers'. It was only produce from the communal fields, worked on by all eight families, that went to the aristocrats, and which, in turn, could go to the king as tribute
Tribute
A tribute is wealth, often in kind, that one party gives to another as a sign of respect or, as was often the case in historical contexts, of submission or allegiance. Various ancient states, which could be called suzerains, exacted tribute from areas they had conquered or threatened to conquer...
.
As part of a larger feudal fēngjiàn
Fengjian
Fēngjiàn is the political ideology of the Zhou Dynasty of ancient China. Fengjian is a "decentralized system of government," comparable to European feudalism, though recent scholarship has suggested that fengjian lacks some of the fundamental aspects of feudalism.-Ranks:The sizes of troops and...
system, the well-field system became strained in the Spring and Autumn Period as kinship ties between aristocrats became meaningless. When the system became economically untenable in the Warring States Period
Warring States Period
The Warring States Period , also known as the Era of Warring States, or the Warring Kingdoms period, covers the Iron Age period from about 475 BC to the reunification of China under the Qin Dynasty in 221 BC...
, it was replaced by a system of private land ownership. It was first suspended in the state of Qin
Qin (state)
The State of Qin was a Chinese feudal state that existed during the Spring and Autumn and Warring States Periods of Chinese history...
by Shang Yang
Shang Yang
Shang Yang was an important statesman of the State of Qin during the Warring States Period of Chinese history. Born Wei Yang in the State of Wei, with the support of Duke Xiao of Qin Yang enacted numerous reforms in Qin...
and other states soon followed suit.
As part of the "turning the clock back" reformations by Wang Mang
Wang Mang
Wang Mang , courtesy name Jujun , was a Han Dynasty official who seized the throne from the Liu family and founded the Xin Dynasty , ruling AD 9–23. The Han dynasty was restored after his overthrow and his rule marks the separation between the Western Han Dynasty and Eastern Han Dynasty...
during the short-lived Xin Dynasty
Xin Dynasty
The Xin Dynasty was a Chinese dynasty which lasted from AD 9 to 23. It followed the Western Han Dynasty and preceded the Eastern Han Dynasty....
, the system was restored temporarily and renamed to the King's Fields (王田; wángtián). The practice was more-or-less ended by the Song Dynasty
Song Dynasty
The Song Dynasty was a ruling dynasty in China between 960 and 1279; it succeeded the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, and was followed by the Yuan Dynasty. It was the first government in world history to issue banknotes or paper money, and the first Chinese government to establish a...
, but scholars like Zhang Zai and Su Xun were enthusiastic about its restoration and spoke of it in a perhaps oversimplifying admiration, invoking Mencius
Mencius
Mencius was a Chinese philosopher who was arguably the most famous Confucian after Confucius himself.-Life:Mencius, also known by his birth name Meng Ke or Ko, was born in the State of Zou, now forming the territory of the county-level city of Zoucheng , Shandong province, only thirty kilometres ...
's frequent praise of the system.
See also
- Agriculture in ChinaAgriculture in ChinaAgriculture is an important economic sector of China, employing over 300 million farmers. China ranks first in worldwide farm output, primarily producing rice, wheat, potatoes, sorghum, peanuts, tea, millet, barley, cotton, oilseed, pork, and fish.-History:...
- Economic history of ChinaEconomic history of ChinaChina's economic system before the late-1990s, with state ownership of certain industries and central control over planning and the financial system, has enabled the government to mobilize whatever surplus was available and greatly increase the proportion of the national economic output devoted to...
- EjidoEjidoThe ejido system is a process whereby the government promotes the use of communal land shared by the people of the community. This use of community land was a common practice during the time of Aztec rule in Mexico...
- Equal-field systemEqual-field systemThe Equal-field system land system was a historical system of land ownership and distribution in China used from the Six Dynasties to Mid-Tang dynasty....
- Sharecropper
- Tenancy

