Total cost
Encyclopedia
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, and cost accounting
Cost accounting
Cost accounting information is designed for managers. Since managers are taking decisions only for their own organization, there is no need for the information to be comparable to similar information from other organizations...
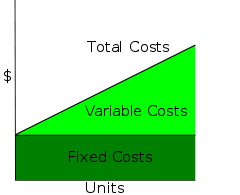
, total cost (TC) describes the total economic cost
Economic cost
The economic cost of a decision depends on both the cost of the alternative chosen and the benefit that the best alternative would have provided if chosen. Economic cost differs from accounting cost because it includes opportunity cost....
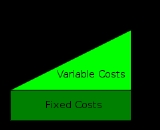
of production and is made up of variable cost
Variable cost
Variable costs are expenses that change in proportion to the activity of a business. Variable cost is the sum of marginal costs over all units produced. It can also be considered normal costs. Fixed costs and variable costs make up the two components of total cost. Direct Costs, however,...
s, which vary according to the quantity of a good produced and include inputs such as labor and raw materials, plus fixed cost
Fixed cost
In economics, fixed costs are business expenses that are not dependent on the level of goods or services produced by the business. They tend to be time-related, such as salaries or rents being paid per month, and are often referred to as overhead costs...
s, which are independent of the quantity of a good produced and include inputs (capital
Capital (economics)
In economics, capital, capital goods, or real capital refers to already-produced durable goods used in production of goods or services. The capital goods are not significantly consumed, though they may depreciate in the production process...
) that cannot be varied in the short term, such as buildings and machinery.
Total cost in economics includes the total opportunity cost
Opportunity cost
Opportunity cost is the cost of any activity measured in terms of the value of the best alternative that is not chosen . It is the sacrifice related to the second best choice available to someone, or group, who has picked among several mutually exclusive choices. The opportunity cost is also the...
of each factor of production as part of its fixed or variable costs.
The rate at which total cost changes as the amount produced changes is called marginal cost
Marginal cost
In economics and finance, marginal cost is the change in total cost that arises when the quantity produced changes by one unit. That is, it is the cost of producing one more unit of a good...
. This is also known as the marginal unit variable cost.
If one assumes that the unit variable cost is constant, as in cost-volume-profit analysis
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Coon-Volume-profit , in managerial economics is a form of cost accounting. It is a simplified model, useful for elementary instruction and for short-run decisions....
developed and used in cost accounting
Cost accounting
Cost accounting information is designed for managers. Since managers are taking decisions only for their own organization, there is no need for the information to be comparable to similar information from other organizations...
by the accountants, then total cost is linear in volume, and given by: total cost = fixed costs + unit variable cost * amount.
The total cost of producing a specific level of output is the cost of all the factors of input used. Conventionally economist use models with two inputs capital, K. and labor, L. Capital is assumed to be the fixed input meaning that the amount of capital used does not vary with the level of production. The rental price per unit of capital is denoted r. Thus the total fixed costs equal Kr. Labor is the variable input meaning that the amount of labor used varies with the level of output. In fact in the short run the only way to vary output is by varying the amount of the variable input. Labor is denoted L and the per unit cost or wage rate is denoted w so the total variable costs is Lw. Consequently total cost is fixed costs (FC) plus variable cost (VC) or TC = FC + VC = Kr +wL.
Other economic models have the total variable cost curve
Cost curve
In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. In a free market economy, productively efficient firms use these curves to find the optimal point of production , and profit maximizing firms can use them to decide output quantities to...
(and therefore total cost curve) illustrate the concepts of increasing, and later diminishing, marginal return
Marginal return
Marginal return refers to the additional output resulting from a one unit increase in the use of variable inputs, while other inputs are held constant....
s.
In marketing
Marketing
Marketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments...
, it is necessary to know how total costs divide between variable and fixed. This distinction is crucial in forecasting the earnings generated by various changes in unit sales and thus the financial impact of proposed marketing campaigns. In a survey of nearly 200 senior marketing managers, 60 percent responded that they found the "variable and fixed costs" metric very useful.
See also
- Semi variable costSemi variable costSemi-variable cost is an expense which contains both a fixed-cost component and a variable-cost component. The fixed cost element shall be a part of the cost that needs to be paid irrespective of the level of activity achieved by the entity. On the other hand the variable component of the cost is...
- Cost curveCost curveIn economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. In a free market economy, productively efficient firms use these curves to find the optimal point of production , and profit maximizing firms can use them to decide output quantities to...
- Total cost of acquisitionTotal cost of acquisitionThe Total Cost of Acquisition is a managerial accounting concept that includes all the costs associated with buying goods, services, or assets. Generally, it is the net price plus other costs needed to purchase the item and get it to the point of use...
- Total cost of ownershipTotal cost of ownershipTotal cost of ownership is a financial estimate whose purpose is to help consumers and enterprise managers determine direct and indirect costs of a product or system...

