Time to digital converter
Encyclopedia
In electronic
instrumentation
and signal processing
, a time to digital converter (abbreviated TDC) is a device for converting a signal of sporadic pulse
s into a digital representation of their time
indices. In other words, a TDC outputs the time of arrival for each incoming pulse. Because the magnitude
s of the pulses are not usually measured, a TDC is used when the important information is to be found in the timing of events. In practice, a TDC usually follows a discriminator. TDCs are most often used in applications where measurement events happen infrequently, such as high energy physics experiment
s, where the sheer number of data channels
in most detectors ensures that each channel will be excited only infrequently by particles such as electrons, photons, and ions.
In its simplest implementation, a TDC is simply a high-frequency
counter
with a buffered output.
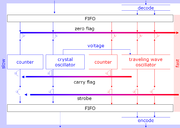 Typically a TDC has a crystal oscillator
Typically a TDC has a crystal oscillator
, which has good long term stability, but oscillates too slowly (80 MHz in 2007). A faster overtone crystal oscillator or a SAW oscillator
could be used for the reference, but the TDC also has a VCO
for the ultimate frequency needed. To be fast this is a loop of transistors (series of logic gates, namely inverters). This also acts as a Johnson counter
, which divides this frequency down to a slow frequency.
A phase-locked loop
is used to lock this low frequency to the frequency of the crystal oscillator. A slow synchronous counter
, counts the slow oscillations.
For every stop pulse a copy of the timer is stored. Some TDCs start the counter after a start pulse and stop after a stop pulse. But this is incompatible with the TDC and allows only one stop pulse.
The speed of counters fabricated in CMOS
-technology is limited by the capacity between the gate and the channel and by the resistance of the channel and the signal traces. The product of both is the cut-off-frequency. Modern chip technology allows multiple metal layers and therefore coil
s with a large number of windings to be inserted into the chip.
This allows to peak the device for a specific frequency
, which may lie well above the cut-off-frequency of the original transistor. The counter is then called a prescaler
.
The frequency of the voltage-controlled oscillator
, for which the use of a coil is more common, has to be matched to the prescaler. A peaked variant of the Johnson counter is the traveling-wave
counter which also achieves sub-cycle resolution. Other methods to achieve sub-cycle resolution include analog-to-digital converter
s and vernier
Johnson counters
.
s down and outputs a stop pulse. For low jitter
the synchronous counter
has to feed a zero flag
from the most significant bit
down to the least significant bit
and then combine it with the output from the Johnson counter.
A digital-to-analog converter
(DAC) could be used to achieve sub-cycle resolution, but it is easier to either use vernier Johnson counters or traveling-wave Johnson counters.
The delay generator can be used for pulse width modulation, e.g. to drive a MOSFET
to load a Pockels cell within 8 ns with a specific charge.
The output of a delay generator can gate a digital-to-analog converter and so pulses of a variable height can be generated. This allows matching to low levels needed by analog electronics, higher levels for ECL
and even higher levels for TTL
. If a series of DACs is gated in sequence, variable pulse shapes can be generated to account for any transfer function.
which can be implemented as a cascade of differential amplifier
s, where the latter stages are driven into saturation, that means either into the low or the high state (1-bit ADC). At every leading edge of the time-discrete and voltage-discrete signal the time is fed into the FIFO.
differentiates
a copy of the input signal. A look at Fourier transformation shows, that this can be accomplished by a 90° phase shift for all frequency components. Omitting the 1/f has some benefits. This signal is fed into a second comparator to get the maximum. At the end the signals of both comparators is send into an AND gate. A constant fraction discriminator reduces jitter when the single particles produce short pulses of different height and the measurement device blurs them into long pulses with a constant shape.
can be used to convert pulses into edges and vice versa.
A gate
has an analog and a logic input. When the logic input is low, the output is zero. A typical sampling pulse of 1 ns width and a 1Msamples ADC and a signal-to-noise ratio
of 100 means that the analog signal has to be suppressed by a factor of 100000 (low leakage
). If the gate is used in conjunction with an integrator
, the transmission should be constant over the integration interval within 0.001.
In a sampling oscilloscope
an edge of a signal is sharpened by a diode
pair, then fed through a delay generator, then converted into a pulse, and then gates the signal. The output of the gate is held in a capacitor and converted by an ADC. A multi-channel analyzer derives the gate pulse from a const-fraction discriminator and uses a fixed delay for a third copy of the original signal to account for the delay in the discriminator. If a series of gates is opened in a short sequence, the pulse shape can be sampled. No const-fraction discriminator is needed then and the system is very flexible concerning the pulse shape.
Often the sampled charge could be stored in the capacitor formed by the gate and channel of a MOSFET. The any current drawn by the ADC will not reduce the charge. Furthermore by drawing the current a long time a large charge amplification is possible. This is called a sample and hold
circuit or also a track and hold circuit. The binary variant is called a buffer.
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
instrumentation
Instrumentation
Instrumentation is defined as the art and science of measurement and control of process variables within a production, or manufacturing area....
and signal processing
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, a time to digital converter (abbreviated TDC) is a device for converting a signal of sporadic pulse
Pulse
In medicine, one's pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the heartbeat by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed against a bone, such as at the neck , at the wrist , behind the knee , on the inside of the elbow , and near the...
s into a digital representation of their time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
indices. In other words, a TDC outputs the time of arrival for each incoming pulse. Because the magnitude
Magnitude (mathematics)
The magnitude of an object in mathematics is its size: a property by which it can be compared as larger or smaller than other objects of the same kind; in technical terms, an ordering of the class of objects to which it belongs....
s of the pulses are not usually measured, a TDC is used when the important information is to be found in the timing of events. In practice, a TDC usually follows a discriminator. TDCs are most often used in applications where measurement events happen infrequently, such as high energy physics experiment
Experiment
An experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. Experiments vary greatly in their goal and scale, but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results...
s, where the sheer number of data channels
Channel (communications)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
in most detectors ensures that each channel will be excited only infrequently by particles such as electrons, photons, and ions.
In its simplest implementation, a TDC is simply a high-frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
counter
Counter
In digital logic and computing, a counter is a device which stores the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock signal.- Electronic counters :...
with a buffered output.
Implementation


Crystal oscillator
A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal of piezoelectric material to create an electrical signal with a very precise frequency...
, which has good long term stability, but oscillates too slowly (80 MHz in 2007). A faster overtone crystal oscillator or a SAW oscillator
Surface acoustic wave
]A surface acoustic wave is an acoustic wave traveling along the surface of a material exhibiting elasticity, with an amplitude that typically decays exponentially with depth into the substrate.-Discovery:...
could be used for the reference, but the TDC also has a VCO
Voltage-controlled oscillator
A voltage-controlled oscillator or VCO is an electronic oscillator designed to be controlled in oscillation frequency by a voltage input. The frequency of oscillation is varied by the applied DC voltage, while modulating signals may also be fed into the VCO to cause frequency modulation or phase...
for the ultimate frequency needed. To be fast this is a loop of transistors (series of logic gates, namely inverters). This also acts as a Johnson counter
Counter
In digital logic and computing, a counter is a device which stores the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock signal.- Electronic counters :...
, which divides this frequency down to a slow frequency.
A phase-locked loop
Phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input "reference" signal. It is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector...
is used to lock this low frequency to the frequency of the crystal oscillator. A slow synchronous counter
Counter
In digital logic and computing, a counter is a device which stores the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock signal.- Electronic counters :...
, counts the slow oscillations.
For every stop pulse a copy of the timer is stored. Some TDCs start the counter after a start pulse and stop after a stop pulse. But this is incompatible with the TDC and allows only one stop pulse.
The speed of counters fabricated in CMOS
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits...
-technology is limited by the capacity between the gate and the channel and by the resistance of the channel and the signal traces. The product of both is the cut-off-frequency. Modern chip technology allows multiple metal layers and therefore coil
Coil
A coil is a series of loops. A coiled coil is a structure in which the coil itself is in turn also looping.-Electromagnetic coils:An electromagnetic coil is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet...
s with a large number of windings to be inserted into the chip.
This allows to peak the device for a specific frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, which may lie well above the cut-off-frequency of the original transistor. The counter is then called a prescaler
Prescaler
A prescaler is an electronic counting circuit used to reduce a high frequency electrical signal to a lower frequency by integer division.-Example of use:...
.
The frequency of the voltage-controlled oscillator
Voltage-controlled oscillator
A voltage-controlled oscillator or VCO is an electronic oscillator designed to be controlled in oscillation frequency by a voltage input. The frequency of oscillation is varied by the applied DC voltage, while modulating signals may also be fed into the VCO to cause frequency modulation or phase...
, for which the use of a coil is more common, has to be matched to the prescaler. A peaked variant of the Johnson counter is the traveling-wave
Distributed Amplifier
Distributed amplifiers are circuit designs that incorporate transmission line theory into traditional amplifier design to obtain a larger gain-bandwidth product than is realizable by conventional circuits.-History:...
counter which also achieves sub-cycle resolution. Other methods to achieve sub-cycle resolution include analog-to-digital converter
Analog-to-digital converter
An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
s and vernier
Vernier scale
A vernier scale is an additional scale which allows a distance or angle measurement to be read more precisely than directly reading a uniformly-divided straight or circular measurement scale...
Johnson counters
Counter
In digital logic and computing, a counter is a device which stores the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock signal.- Electronic counters :...
.
Delay generator
This is a digital to time converter. Whereas the TDC measures the time between a start and a stop pulse, the delay generator gets a start pulse at its inputs, then countCounter
In digital logic and computing, a counter is a device which stores the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock signal.- Electronic counters :...
s down and outputs a stop pulse. For low jitter
Jitter
Jitter is the undesired deviation from true periodicity of an assumed periodic signal in electronics and telecommunications, often in relation to a reference clock source. Jitter may be observed in characteristics such as the frequency of successive pulses, the signal amplitude, or phase of...
the synchronous counter
Counter
In digital logic and computing, a counter is a device which stores the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock signal.- Electronic counters :...
has to feed a zero flag
Status register
A status register or flag register is a collection of flag bits for a processor. An example is the FLAGS register of the x86 architecture....
from the most significant bit
Most significant bit
In computing, the most significant bit is the bit position in a binary number having the greatest value...
down to the least significant bit
Least significant bit
In computing, the least significant bit is the bit position in a binary integer giving the units value, that is, determining whether the number is even or odd. The lsb is sometimes referred to as the right-most bit, due to the convention in positional notation of writing less significant digits...
and then combine it with the output from the Johnson counter.
A digital-to-analog converter
Digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
(DAC) could be used to achieve sub-cycle resolution, but it is easier to either use vernier Johnson counters or traveling-wave Johnson counters.
The delay generator can be used for pulse width modulation, e.g. to drive a MOSFET
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The basic principle of this kind of transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925...
to load a Pockels cell within 8 ns with a specific charge.
The output of a delay generator can gate a digital-to-analog converter and so pulses of a variable height can be generated. This allows matching to low levels needed by analog electronics, higher levels for ECL
ECL
ECL may stand for:*ECL programming language, an extensible programming language developed at Harvard*ECL, data-centric programming language for Big Data, a declarative, data centric programming language used for data intensive supercomputing...
and even higher levels for TTL
TTL
TTL may refer to:* Taiwan Tobacco and Liquor, a state-owned manufacturer of cigarettes and alcohol in Taiwan* Through-the-lens metering, a feature of cameras capable of measuring light levels in a scene through their lens...
. If a series of DACs is gated in sequence, variable pulse shapes can be generated to account for any transfer function.
Discriminator
Even if the input is binary, after sampling with the oscillator signal the signal is analog (due to the finite edge width). Therefore an analog-to-digital converter is always employed after the sampler, the same is true for a simple comparatorComparator
In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and switches its output to indicate which is larger. They are commonly used in devices such as Analog-to-digital converters .- Input voltage range :...
which can be implemented as a cascade of differential amplifier
Differential amplifier
A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two voltages but does not amplify the particular voltages.- Theory :Many electronic devices use differential amplifiers internally....
s, where the latter stages are driven into saturation, that means either into the low or the high state (1-bit ADC). At every leading edge of the time-discrete and voltage-discrete signal the time is fed into the FIFO.
Constant fraction discriminator
As a TDC is mainly a logic device and has problems with voltages between low and high state. A constant fraction discriminatorConstant fraction discriminator
A constant fraction discriminator is an electronic signal processing device, designed to mimic the mathematical operation of finding a maximum of a pulse by finding the zero of its slope....
differentiates
Derivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
a copy of the input signal. A look at Fourier transformation shows, that this can be accomplished by a 90° phase shift for all frequency components. Omitting the 1/f has some benefits. This signal is fed into a second comparator to get the maximum. At the end the signals of both comparators is send into an AND gate. A constant fraction discriminator reduces jitter when the single particles produce short pulses of different height and the measurement device blurs them into long pulses with a constant shape.
Utilities
A flip flopFlip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic...
can be used to convert pulses into edges and vice versa.
A gate
Gate
A gate is a point of entry to a space enclosed by walls, or a moderately sized opening in a fence. Gates may prevent or control entry or exit, or they may be merely decorative. Other terms for gate include yett and port...
has an analog and a logic input. When the logic input is low, the output is zero. A typical sampling pulse of 1 ns width and a 1Msamples ADC and a signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
of 100 means that the analog signal has to be suppressed by a factor of 100000 (low leakage
Leakage
Leakage may refer to:*Leakage *Memory leak, in computer science*Leakage *Leakage *Leakage *Leakage...
). If the gate is used in conjunction with an integrator
Integrator
An integrator is a device to perform the mathematical operation known as integration, a fundamental operation in calculus.The integration function is often part of engineering, physics, mechanical, chemical and scientific calculations....
, the transmission should be constant over the integration interval within 0.001.
In a sampling oscilloscope
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a type of electronic test instrument that allows observation of constantly varying signal voltages, usually as a two-dimensional graph of one or more electrical potential differences using the vertical or 'Y' axis, plotted as a function of time,...
an edge of a signal is sharpened by a diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
pair, then fed through a delay generator, then converted into a pulse, and then gates the signal. The output of the gate is held in a capacitor and converted by an ADC. A multi-channel analyzer derives the gate pulse from a const-fraction discriminator and uses a fixed delay for a third copy of the original signal to account for the delay in the discriminator. If a series of gates is opened in a short sequence, the pulse shape can be sampled. No const-fraction discriminator is needed then and the system is very flexible concerning the pulse shape.
Often the sampled charge could be stored in the capacitor formed by the gate and channel of a MOSFET. The any current drawn by the ADC will not reduce the charge. Furthermore by drawing the current a long time a large charge amplification is possible. This is called a sample and hold
Sample and hold
In electronics, a sample and hold circuit is an analog device that samples the voltage of a continuously varying analog signal and holds its value at a constant level for a specified minimal period of time. Sample and hold circuits and related peak detectors are the elementary analog memory...
circuit or also a track and hold circuit. The binary variant is called a buffer.

