
Sample and hold
Encyclopedia

Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
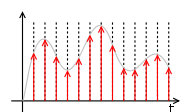
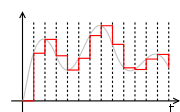
, a sample and hold (S/H, also "follow-and-hold") circuit is an analog device that samples (captures, grabs) the voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
of a continuously varying analog signal
Analog signal
An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are...
and holds (locks, freezes) its value at a constant level for a specified minimal period of time. Sample and hold circuits and related peak detectors are the elementary analog memory
Memory
In psychology, memory is an organism's ability to store, retain, and recall information and experiences. Traditional studies of memory began in the fields of philosophy, including techniques of artificially enhancing memory....
devices. They are typically used in analog-to-digital converter
Analog-to-digital converter
An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
s to eliminate variations in input signal that can corrupt the conversion process.
A typical sample and hold circuit stores electric charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
in a capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
and contains at least one fast FET switch
Field-effect transistor
The field-effect transistor is a transistor that relies on an electric field to control the shape and hence the conductivity of a channel of one type of charge carrier in a semiconductor material. FETs are sometimes called unipolar transistors to contrast their single-carrier-type operation with...
and at least one operational amplifier
Operational amplifier
An operational amplifier is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output...
. To sample the input signal the switch connects the capacitor to the output of a buffer amplifier
Buffer amplifier
A buffer amplifier is one that provides electrical impedance transformation from one circuit to another...
. The buffer amplifier charges or discharges the capacitor so that the voltage across the capacitor is practically equal, or proportional to, input voltage. In hold mode the switch disconnects the capacitor from the buffer. The capacitor is invariably discharged by its own leakage currents
Leakage (electronics)
In electronics, leakage may refer to a gradual loss of energy from a charged capacitor. It is primarily caused by electronic devices attached to the capacitors, such as transistors or diodes, which conduct a small amount of current even when they are turned off...
and useful load currents, which makes the circuit inherently volatile
Volatile memory
Volatile memory, also known as volatile storage, is computer memory that requires power to maintain the stored information, unlike non-volatile memory which does not require a maintained power supply...
, but the loss of voltage (voltage drop) within a specified hold time
Hold time
In digital electronics, hold time is the minimum amount of time that a data signal should be held steady after a clock event so that the data are reliably sampled in synchronous circuits such as flip-flops.Hold time may also refer to:...
remains within an acceptable error margin.
Purpose
The sample and hold circuits are essentially used in linear systems. In some kinds of analog-to-digital converters, the input is often compared to a voltage generated internally from a digital-to-analog converterDigital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
(D-A-C). The circuit tries a series of values and stops converting once the voltages are "the same" within some defined error margin. If the input value was permitted to change during this comparison process, the resulting conversion would be inaccurate and possibly completely unrelated to the true input value. Such successive approximation converters will often incorporate internal sample and hold circuitry. In addition, sample and hold circuits are often used when multiple samples need to be measured at the same time. Each value is sampled and held, using a common sample clock.
Implementation
In order that the input voltage is held constant for all practical purposes, it is essential that the capacitor have very low leakageLeakage
Leakage may refer to:*Leakage *Memory leak, in computer science*Leakage *Leakage *Leakage *Leakage...
, and that it not be loaded to any significant degree which calls for a very high input impedance
Input impedance
The input impedance of an electrical network is the equivalent impedance "seen" by a power source connected to that network. If the source provides known voltage and current, such impedance can be calculated using Ohm's Law...
.
A true sample and hold circuit is connected to the buffer for a short period of time; a track and hold circuit is designed to track input continuously.
The current carrying capacity of devices (like amplifiers) that provide signals to the analog switch must be very high, so that it can sufficiently drive capacitive loads. Hence the input amplifiers used in the circuit are operational amplifiers with good slew rates and capable of driving capacitive loads stably.
The analog switches used in the circuit must have low on and off leakage currents, for which an efficient bipolar transistor arrangement with low leakage currents in the off condition is employed. The output amplifier must have good slew rate and low bias currents. A MOSFET unity gain follower may be used for the purpose.

