Tau Scorpii
Encyclopedia
Tau Scorpii is a star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Scorpius
Scorpius
Scorpius, sometimes known as Scorpio, is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for scorpion, and its symbol is . It lies between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east...
. Tau Scorpii also has the traditional name Alniyat or Al Niyat, which it shares with σ Scorpii
Sigma Scorpii
Sigma Scorpii is a star system in the constellation Scorpius. It has the traditional name Al Niyat, although this name is sometimes also applied to Tau Scorpii, or to the asterism formed by both Sigma and Tau. Sigma Scorpii is 735 light years from the Sun.The primary component of the system,...
. The name derives from the Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
النياط an-niyāţ meaning "the arteries".
Tau Scorpii is a blue-white B-type
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is a classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. The spectral class of a star is a designated class of a star describing the ionization of its chromosphere, what atomic excitations are most prominent in the light, giving an objective measure...
dwarf
Main sequence
The main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell...
with an apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
of +2.82. It is approximately 430 light years
Light Years
Light Years is the seventh studio album by Australian recording artist Kylie Minogue. It was released on 25 September 2000 by Parlophone and Mushroom Records. The album's style was indicative of her return to "mainstream pop dance tunes"....
from Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
.
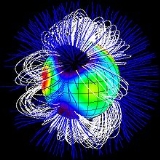
Magnetic field
It is a magnetic star whose surface magnetic field was mapped by means of Zeeman–Doppler imaging.X-ray source
Auger electron
The Auger effect is a physical phenomenon in which the transition of an electron in an atom filling in an inner-shell vacancy causes the emission of another electron. When a core electron is removed, leaving a vacancy, an electron from a higher energy level may fall into the vacancy, resulting in...
ionization effect. ROSAT
ROSAT
ROSAT was a German Aerospace Center-led satellite X-ray telescope, with instruments built by Germany, the UK and the US...
observed that τ Sco was a star with a harder X-ray spectrum than usual for B0V stars. Over the energy range 0.8-1.2 keV, its X-ray luminosity is Lx = 1.8 x 1031 erg s−1 with a large Lx to Lbol of log Lx/Lbol = -6.53 from ASCA
Advanced Satellite for Cosmology and Astrophysics
ASCA is the fourth cosmic X-ray astronomy mission by Japan's , and the second for which the United States is providing part of the scientific payload. The satellite was successfully launched on February 20, 1993. The first eight months of the ASCA mission were devoted to performance verification...
measurements. ROSAT
ROSAT
ROSAT was a German Aerospace Center-led satellite X-ray telescope, with instruments built by Germany, the UK and the US...
arrived at a log Lx/Lbol ≃ -5.93 for the range 0.1-2.4 keV.
The hard component of the X-ray spectrum from τ Sco as studied with XMM-Newton
XMM-Newton
The XMM-Newton is an orbiting X-ray observatory launched by ESA in December 1999 on a Ariane 5 rocket...
supports the presence of in-falling clumps of plasma in τ Sco.
See also
- Lists of stars in the constellation Scorpius
- Class B Stars
- Index table for X-ray and gamma-ray sources
External links
- Jim Kaler's Stars, University of Illinois: Al NIYAT (Tau Scorpii)

