
Step detection
Encyclopedia
In statistics
and signal processing
, step detection (also known as step smoothing, step filtering, shift detection, jump detection or edge detection
) is the process of finding abrupt changes (steps, jumps, shifts) in the mean level of a time series
or signal. It is usually considered as a special kind of statistical method known as change point detection
. Often, the step is small and the time series is corrupted by some kind of noise, and this makes the problem challenging because the step may be hidden by the noise. Therefore, statistical and/or signal processing algorithms are often required.
The step detection problem occurs in multiple scientific and engineering contexts, for example in statistical process control
(the control chart
being the most directly related method), in exploration geophysics (where the problem is to segment a well-log recording into stratigraphic zones), in genetics (the problem of separating microarray data into similar copy-number regimes), and in biophysics (detecting state transitions in a molecular machine as recorded in time-position traces). For 2D signals, the related problem of edge detection
has been studied intensively for image processing
.
Such algorithms include the classical CUSUM
method applied to changes in mean. By contrast, offline algorithms are applied to the data potentially long after it has been received. Most offline algorithms for step detection in digital data can be categorised as top-down, bottom-up, sliding window, or global methods.
. Alternatively, a nonlinear filter such as the median filter
is applied to the signal. Filters such as these attempt to remove the noise whilst preserving the abrupt steps.
methods, and total variation denoising
which uses methods from convex optimization. Where the steps can be modelled as a Markov chain
, then Hidden Markov Models are also often used (a popular approach in the biophysics community). When there are only a few unique values of the mean, then k-means clustering can also be used.
, signal processing
approaches to step detection generally do not use classical smoothing techniques such as the low pass filter. Instead, most algorithms are explicitly nonlinear or time-varying.
with a few knots, or as level set
s with a few unique levels. Many algorithms for step detection are therefore best understood as either 0-degree spline fitting, or level set recovery, methods.
are appropriate. These techniques are best understood as methods for finding a level set description of the underlying piecewise constant signal.
.
Here, xi for i = 1, ...., N is the input discrete-time input signal of length N, and mi is a the signal output from the algorithm. The goal is to minimize H[m] with respect to the output signal m. The form of the function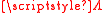 determines the particular algorithm. For example, choosing:
determines the particular algorithm. For example, choosing:
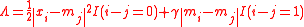
where I(S) = 0 if the condition S is false, and one otherwise, obtains the total variation denoising
algorithm with regularization parameter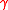 . Similarly:
. Similarly:
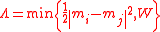
leads to the mean shift algorithm, when using an adaptive step size Euler integrator initialized with the input signal x. Here W > 0 is a parameter that determines the support of the mean shift kernel. Another example is:
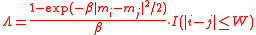
leading to the bilateral filter
, where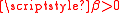 is the tonal kernel parameter, and W is the spatial kernel support. Yet another special case is:
is the tonal kernel parameter, and W is the spatial kernel support. Yet another special case is:
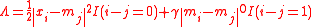
specifying a group of algorithms that attempt to greedily fit 0-degree splines to the signal. Here,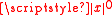 is defined as zero if x = 0, and one otherwise.
is defined as zero if x = 0, and one otherwise.
Many of the functionals in equation defined by the particular choice of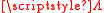 are convex
are convex
: they can be minimized using methods from convex optimization. Still others are non-convex but a range of algorithms for minimizing these functionals have been devised.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
and signal processing
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, step detection (also known as step smoothing, step filtering, shift detection, jump detection or edge detection
Edge detection
Edge detection is a fundamental tool in image processing and computer vision, particularly in the areas of feature detection and feature extraction, which aim at identifying points in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or, more formally, has discontinuities...
) is the process of finding abrupt changes (steps, jumps, shifts) in the mean level of a time series
Time series
In statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
or signal. It is usually considered as a special kind of statistical method known as change point detection
Change detection
In statistical analysis, change detection tries to identify changes in the probability distribution of a stochastic process or time series. In general the problem concerns both detecting whether or not a change has occurred, or whether several changes might have occurred, and identifying the times...
. Often, the step is small and the time series is corrupted by some kind of noise, and this makes the problem challenging because the step may be hidden by the noise. Therefore, statistical and/or signal processing algorithms are often required.
The step detection problem occurs in multiple scientific and engineering contexts, for example in statistical process control
Statistical process control
Statistical process control is the application of statistical methods to the monitoring and control of a process to ensure that it operates at its full potential to produce conforming product. Under SPC, a process behaves predictably to produce as much conforming product as possible with the least...
(the control chart
Control chart
Control charts, also known as Shewhart charts or process-behaviour charts, in statistical process control are tools used to determine whether or not a manufacturing or business process is in a state of statistical control.- Overview :...
being the most directly related method), in exploration geophysics (where the problem is to segment a well-log recording into stratigraphic zones), in genetics (the problem of separating microarray data into similar copy-number regimes), and in biophysics (detecting state transitions in a molecular machine as recorded in time-position traces). For 2D signals, the related problem of edge detection
Edge detection
Edge detection is a fundamental tool in image processing and computer vision, particularly in the areas of feature detection and feature extraction, which aim at identifying points in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or, more formally, has discontinuities...
has been studied intensively for image processing
Image processing
In electrical engineering and computer science, image processing is any form of signal processing for which the input is an image, such as a photograph or video frame; the output of image processing may be either an image or, a set of characteristics or parameters related to the image...
.
Algorithms
When the step detection must be performed as and when the data arrives, then online algorithms are usually used.Such algorithms include the classical CUSUM
CUSUM
In statistical quality control, the CUSUM is a sequential analysis technique due to E. S. Page of the University of Cambridge. It is typically used for monitoring change detection...
method applied to changes in mean. By contrast, offline algorithms are applied to the data potentially long after it has been received. Most offline algorithms for step detection in digital data can be categorised as top-down, bottom-up, sliding window, or global methods.
Top-down
These algorithms start with the assumption that there are no steps and introduce possible candidate steps one at a time, testing each candidate to find the one that minimizes some criteria (such as the least-squares fit of the estimated, underlying piecewise constant signal). An example is the stepwise jump placement algorithm, first studied in geophysical problems, that has found recent uses in modern biophysics.Bottom-up
Bottom-up algorithms take the "opposite" approach to top-down methods, first assuming that there is a step in between every sample in the digital signal, and then successively merging steps based on some criteria tested for every candidate merge.Sliding window
By considering a small "window" of the signal, these algorithms look for evidence of a step occurring within the window. The window "slides" across the time series, one time step at a time. The evidence for a step is tested by statistical procedures, for example, by use of the two-sample Student's t-testStudent's t-test
A t-test is any statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's t distribution if the null hypothesis is supported. It is most commonly applied when the test statistic would follow a normal distribution if the value of a scaling term in the test statistic were known...
. Alternatively, a nonlinear filter such as the median filter
Median filter
In signal processing, it is often desirable to be able to perform some kind of noise reduction on an image or signal. The median filter is a nonlinear digital filtering technique, often used to remove noise. Such noise reduction is a typical pre-processing step to improve the results of later...
is applied to the signal. Filters such as these attempt to remove the noise whilst preserving the abrupt steps.
Global
Global algorithms consider the entire signal in one go, and attempt to find the steps in the signal by some kind of optimization procedure. Algorithms include waveletWavelet
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that starts out at zero, increases, and then decreases back to zero. It can typically be visualized as a "brief oscillation" like one might see recorded by a seismograph or heart monitor. Generally, wavelets are purposefully crafted to have...
methods, and total variation denoising
Total variation denoising
In signal processing, Total variation denoising, also known as total variation regularization is a process, most often used in digital image processing that has applications in noise removal. It is based on the principle that signals with excessive and possibly spurious detail have high total...
which uses methods from convex optimization. Where the steps can be modelled as a Markov chain
Markov chain
A Markov chain, named after Andrey Markov, is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another, between a finite or countable number of possible states. It is a random process characterized as memoryless: the next state depends only on the current state and not on the...
, then Hidden Markov Models are also often used (a popular approach in the biophysics community). When there are only a few unique values of the mean, then k-means clustering can also be used.
Linear versus nonlinear signal processing methods for step detection
Because steps and (independent) noise have theoretically infinite bandwidth and so overlap in the Fourier basisFourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
, signal processing
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
approaches to step detection generally do not use classical smoothing techniques such as the low pass filter. Instead, most algorithms are explicitly nonlinear or time-varying.
Step detection and piecewise constant signals
Because the aim of step detection is a find a series of instantaneous jumps in the mean of a signal, the wanted, underlying, mean signal is piecewise constant. For this reason, step detection can be profitably viewed as the problem of recovering a piecewise constant signal corrupted by noise. There are two complementary models for piecewise constant signals: as 0-degree splinesSpline (mathematics)
In mathematics, a spline is a sufficiently smooth piecewise-polynomial function. In interpolating problems, spline interpolation is often preferred to polynomial interpolation because it yields similar results, even when using low-degree polynomials, while avoiding Runge's phenomenon for higher...
with a few knots, or as level set
Level set
In mathematics, a level set of a real-valued function f of n variables is a set of the formthat is, a set where the function takes on a given constant value c....
s with a few unique levels. Many algorithms for step detection are therefore best understood as either 0-degree spline fitting, or level set recovery, methods.
Step detection as level set recovery
When there are only a few unique values of the mean, clustering techniques such as k-means clustering or mean-shiftMean-shift
Mean shift is a non-parametric feature-space analysis technique, a so-called mode seeking algorithm. Application domains include clustering in computer vision and image processing.- Overview :...
are appropriate. These techniques are best understood as methods for finding a level set description of the underlying piecewise constant signal.
Step detection as 0-degree spline fitting
Many algorithms explicitly fit 0-degree splines to the noisy signal in order to detect steps (including stepwise jump placement methods), but there are other popular algorithms that can also be seen to be spline fitting methods after some transformation, for example total variation denoisingTotal variation denoising
In signal processing, Total variation denoising, also known as total variation regularization is a process, most often used in digital image processing that has applications in noise removal. It is based on the principle that signals with excessive and possibly spurious detail have high total...
.
Generalized step detection by piecewise constant denoising
All the algorithms mentioned above have certain advantages and disadvantages in particular circumstances, yet, a surprisingly large number of these step detection algorithms are special cases of a more general algorithm. This algorithm involves the minimization of a global functional:Here, xi for i = 1, ...., N is the input discrete-time input signal of length N, and mi is a the signal output from the algorithm. The goal is to minimize H[m] with respect to the output signal m. The form of the function
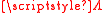 determines the particular algorithm. For example, choosing:
determines the particular algorithm. For example, choosing: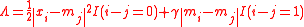
where I(S) = 0 if the condition S is false, and one otherwise, obtains the total variation denoising
Total variation denoising
In signal processing, Total variation denoising, also known as total variation regularization is a process, most often used in digital image processing that has applications in noise removal. It is based on the principle that signals with excessive and possibly spurious detail have high total...
algorithm with regularization parameter
 . Similarly:
. Similarly: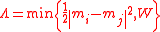
leads to the mean shift algorithm, when using an adaptive step size Euler integrator initialized with the input signal x. Here W > 0 is a parameter that determines the support of the mean shift kernel. Another example is:
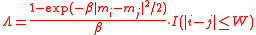
leading to the bilateral filter
Bilateral filter
A bilateral filter is an edge-preserving and noise reducing smoothing filter. The intensity value at each pixel in an image is replaced by a weighted average of intensity values from nearby pixels. This weight is based on a Gaussian distribution. Crucially the weights depend not only on Euclidean...
, where
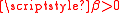 is the tonal kernel parameter, and W is the spatial kernel support. Yet another special case is:
is the tonal kernel parameter, and W is the spatial kernel support. Yet another special case is: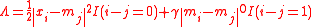
specifying a group of algorithms that attempt to greedily fit 0-degree splines to the signal. Here,
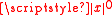 is defined as zero if x = 0, and one otherwise.
is defined as zero if x = 0, and one otherwise.Many of the functionals in equation defined by the particular choice of
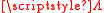 are convex
are convexConvex function
In mathematics, a real-valued function f defined on an interval is called convex if the graph of the function lies below the line segment joining any two points of the graph. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph is a convex set...
: they can be minimized using methods from convex optimization. Still others are non-convex but a range of algorithms for minimizing these functionals have been devised.

