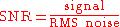.gif)
Signal to noise ratio (image processing)
Encyclopedia
The Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) is used in imaging as a physical measure of the sensitivity
of a (digital or film) imaging system
. Industry standards measure SNR in decibels (dB) of power
and therefore apply the 20 log rule to the "pure" SNR ratio (a ratio of 1:1 yields 0 decibels, for instance). In turn, yielding the "sensitivity." Industry standards measure and define sensitivity in terms of the ISO film speed
equivalent; SNR:32.04 dB = excellent image quality and SNR:20 dB = acceptable image quality.
 Traditionally, SNR has been defined as the ratio of the average signal value
Traditionally, SNR has been defined as the ratio of the average signal value 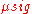 to the standard deviation
to the standard deviation
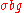 of the background:
of the background:
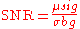
However, when presented with a high-contrast scene, many imaging systems clamp
the background to uniform black, forcing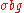 to zero, artificially making the SNR infinite.
to zero, artificially making the SNR infinite.
In this case a better definition of SNR is the ratio of the average signal value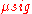 to the standard deviation of the signal
to the standard deviation of the signal 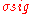 :
:
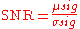
which gives a meaningful result in the presence of clamping.
is fitted
to the array of line data and subtracted from the original array line data. This is done to remove any trends
. Finding the mean of this data yields the average signal and background values. The net signal is calculated from the difference of the average signal and background values. The RMS or root mean square
noise is defined from the signal region. Finally, SNR is determined as the ratio of the net signal to the RMS noise.
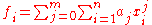
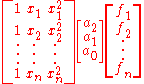
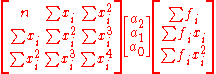
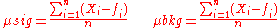
where
Hence, the net signal value is determined by :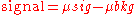 .
.
The SNR is thus given by
Using the industry standard 20 log rule...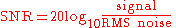
Sensitometry
Sensitometry is the scientific study of light-sensitive materials, especially photographic film. The study has its origins in the work by Ferdinand Hurter and Vero Charles Driffield with early black-and-white emulsions...
of a (digital or film) imaging system
Photography
Photography is the art, science and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film...
. Industry standards measure SNR in decibels (dB) of power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
and therefore apply the 20 log rule to the "pure" SNR ratio (a ratio of 1:1 yields 0 decibels, for instance). In turn, yielding the "sensitivity." Industry standards measure and define sensitivity in terms of the ISO film speed
Film speed
Film speed is the measure of a photographic film's sensitivity to light, determined by sensitometry and measured on various numerical scales, the most recent being the ISO system....
equivalent; SNR:32.04 dB = excellent image quality and SNR:20 dB = acceptable image quality.
Definition of SNR

 to the standard deviation
to the standard deviationStandard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
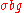 of the background:
of the background: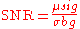
However, when presented with a high-contrast scene, many imaging systems clamp
Clamping (graphics)
In computer graphics, clamping is the process of limiting a position to an area. Unlike wrapping, clamping merely moves the point to the nearest available value.To put clamping into perspective, pseudocode for clamping is:...
the background to uniform black, forcing
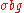 to zero, artificially making the SNR infinite.
to zero, artificially making the SNR infinite.In this case a better definition of SNR is the ratio of the average signal value
 to the standard deviation of the signal
to the standard deviation of the signal  :
: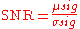
which gives a meaningful result in the presence of clamping.
Explanation
The line data is gathered from the arbitrarily defined signal and background regions and input into an array (refer to image to the right). To calculate the average signal and background values, a second order polynomialPolynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
is fitted
Curve fitting
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function...
to the array of line data and subtracted from the original array line data. This is done to remove any trends
Trend estimation
Trend estimation is a statistical technique to aid interpretation of data. When a series of measurements of a process are treated as a time series, trend estimation can be used to make and justify statements about tendencies in the data...
. Finding the mean of this data yields the average signal and background values. The net signal is calculated from the difference of the average signal and background values. The RMS or root mean square
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
noise is defined from the signal region. Finally, SNR is determined as the ratio of the net signal to the RMS noise.
Polynomial and coefficients
- The second order polynomial is calculated by the following double summation.
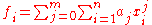
-
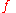 = output sequenceFunction (mathematics)In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
= output sequenceFunction (mathematics)In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...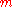 = the polynomial order
= the polynomial order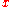 = the input sequenceFunction (mathematics)In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
= the input sequenceFunction (mathematics)In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
(array/line values) from the signal region or background region, respectively.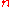 = the number of lines
= the number of lines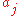 = the polynomial fit coefficients
= the polynomial fit coefficients
- The polynomial fit coefficients can thus be calculated by a system of equations.
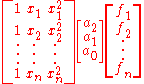
- Which can be written...
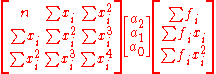
- Computer software or rigorous row operations will solve for the coefficients.
Net signal, signal, and background
The second-order polynomial is subtracted from the original data to remove any trends and then averaged. This yields the signal and background values: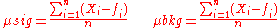
where
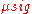 = average signal value
= average signal value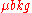 = average background value
= average background value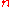 = number of lines in background or signal region
= number of lines in background or signal region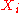 = value of the ith line in the signal region or background region, respectively.
= value of the ith line in the signal region or background region, respectively.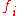 = value of the ith output of the second order polynomial.
= value of the ith output of the second order polynomial.
Hence, the net signal value is determined by :
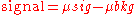 .
.RMS noise and SNR
- The RMS Noise is defined as the square rootSquare rootIn mathematics, a square root of a number x is a number r such that r2 = x, or, in other words, a number r whose square is x...
of the absolute valueAbsolute valueIn mathematics, the absolute value |a| of a real number a is the numerical value of a without regard to its sign. So, for example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of -3 is also 3...
of the sum of variancesVarianceIn probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
from the signal region.
The SNR is thus given by
Using the industry standard 20 log rule...
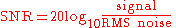
See also
- Coefficient of variationCoefficient of variationIn probability theory and statistics, the coefficient of variation is a normalized measure of dispersion of a probability distribution. It is also known as unitized risk or the variation coefficient. The absolute value of the CV is sometimes known as relative standard deviation , which is...
- Minimum resolvable contrastMinimum Resolvable ContrastMinimum resolvable contrast is a subjective measure of a visible spectrum sensor’s or camera's sensitivity and ability to resolve data. A snapshot image of a series of three bar targets of selected spatial frequencies and various contrast coatings captured by the UUT are used to determine the...
- Minimum resolvable temperature differenceMinimum resolvable temperature differenceMinimum resolvable temperature difference is a measure for assessing the performance of infrared cameras, and is inversely proportional to the modulation transfer function....
- Optical transfer functionOptical transfer functionThe optical transfer function of an imaging system is the true measure of resolution that the system is capable of...
- Signal transfer functionSignal transfer functionThe signal transfer function is a measure of the signal output versus the signal input of a system such as an infrared system or sensor. There are many general applications of the SiTF...
Further reading
- ISO 15739:2003, Photography -- Electronic still-picture imaging -- Noise measurements: specifies methods for measuring and reporting the noise versus signal level and dynamic range of electronic still-picture cameras. It applies to both monochrome and colour electronic still-picture cameras.
- ISO 12232:2006, Photography -- Digital still cameras -- Determination of exposure index, ISO speed ratings, standard output sensitivity, and recommended exposure index: specifies the method for assigning and reporting ISO speed ratings, ISO speed latitude ratings, standard output sensitivity values, and recommended exposure index values, for digital still cameras. ISO 12232:2006 is applicable to both monochrome and colour digital still cameras. It revises ISO 12232:1998.