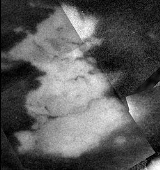
Shikoku Facula
Encyclopedia
Shikoku Facula is a region of bright material on Saturn
's moon Titan
.
Shikoku was first seen in Cassini images taken in October 2004 and has been observed several times since. Prior to provisionally receiving an official name in August 2005, this feature was nicknamed "Great Britain", due to its shape's resemblance to that island on Earth. This feature, 200×160 kilometers across, is located within Titan's Shangri-la
dark region and is centered at 10.4° South Latitude
, 164.1° West Longitude
.
Images of Shikoku reveal a complex boundary between the feature's margin and the dark terrain that surrounds it, as well as several dark channels terminating along the bright-dark boundary.
This feature was observed by the Cassini RADAR
instrument's SAR imaging
mode on April 30, 2006. This new view reveals variations in roughness across Shikoku, including a circular patch of smooth terrain 35 kilometers across in northeastern Shikoku that may be an impact crater.http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA08426 This circular feature, along with another region of relatively smooth terrain in southcentral Shikoku, do not appear to have a counterpart in the near-infrared images taken by the Imaging Science Subsystem cameras.
Shikoku Facula is named after Shikoku
, the smallest of the four main Japan
ese islands.
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest planet in the Solar System, after Jupiter. Saturn is named after the Roman god Saturn, equated to the Greek Cronus , the Babylonian Ninurta and the Hindu Shani. Saturn's astronomical symbol represents the Roman god's sickle.Saturn,...
's moon Titan
Titan (moon)
Titan , or Saturn VI, is the largest moon of Saturn, the only natural satellite known to have a dense atmosphere, and the only object other than Earth for which clear evidence of stable bodies of surface liquid has been found....
.
Shikoku was first seen in Cassini images taken in October 2004 and has been observed several times since. Prior to provisionally receiving an official name in August 2005, this feature was nicknamed "Great Britain", due to its shape's resemblance to that island on Earth. This feature, 200×160 kilometers across, is located within Titan's Shangri-la
Shangri-la (Titan)
Shangri-la is a large, dark region of Saturn's moon Titan at . It is named after Shangri-La, the mythical paradise in Tibet. It is thought to be an immense plain of dark material. It is thought that these regions of Titan were seas, but that they are now dry....
dark region and is centered at 10.4° South Latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
, 164.1° West Longitude
Longitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
.
Images of Shikoku reveal a complex boundary between the feature's margin and the dark terrain that surrounds it, as well as several dark channels terminating along the bright-dark boundary.
This feature was observed by the Cassini RADAR
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
instrument's SAR imaging
Synthetic aperture radar
Synthetic-aperture radar is a form of radar whose defining characteristic is its use of relative motion between an antenna and its target region to provide distinctive long-term coherent-signal variations that are exploited to obtain finer spatial resolution than is possible with conventional...
mode on April 30, 2006. This new view reveals variations in roughness across Shikoku, including a circular patch of smooth terrain 35 kilometers across in northeastern Shikoku that may be an impact crater.http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA08426 This circular feature, along with another region of relatively smooth terrain in southcentral Shikoku, do not appear to have a counterpart in the near-infrared images taken by the Imaging Science Subsystem cameras.
Shikoku Facula is named after Shikoku
Shikoku
is the smallest and least populous of the four main islands of Japan, located south of Honshū and east of the island of Kyūshū. Its ancient names include Iyo-no-futana-shima , Iyo-shima , and Futana-shima...
, the smallest of the four main Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
ese islands.

