
Quantitative precipitation forecast
Encyclopedia
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
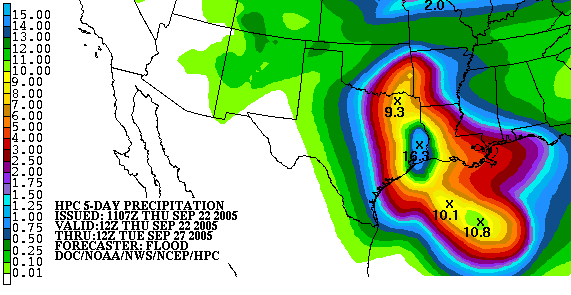
accumulated over a specified time period over a specified area. A QPF will be created when precipitation amounts reaching a minimum threshold are expected during the forecast's valid period. Valid periods of precipitation forecasts are normally synoptic hours such as 0000, 0600, 1200 and 1800 GMT. Terrain is considered in QPFs by use of topography or based upon climatological precipitation patterns from observations with fine detail. Starting in the mid-to-late 1990s, QPFs were used within hydrologic forecast models to simulate impact to rivers throughout the United States. Forecast models
Numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic...
show significant sensitivity to humidity levels within the planetary boundary layer
Planetary boundary layer
The planetary boundary layer , also known as the atmospheric boundary layer , is the lowest part of the atmosphere and its behavior is directly influenced by its contact with a planetary surface. On Earth it usually responds to changes in surface forcing in an hour or less...
, or in the lowest levels of the atmosphere, which decreases with height. QPF can be generated on a quantitative, forecasting amounts, or a qualitative, forecasting the probability of a specific amount, basis. Radar imagery forecasting techniques show higher skill than model forecasts within 6 to 7 hours of the time of the radar image. The forecasts can be verified through use of rain gauge
Rain gauge
A rain gauge is a type of instrument used by meteorologists and hydrologists to gather and measure the amount of liquid precipitation over a set period of time....
measurements, weather radar
Weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, estimate its type . Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the...
estimates, or a combination of both. Various skill scores can be determined to measure the value of the rainfall forecast.
Use of radar
Algorithms exist to forecast rainfall based on short term radar trends, within a matter of hours. Radar imagery forecasting techniques show higher skill than model forecasts within 6 to 7 hours of the time of the radar image.Use of forecast models
In the past, the forecaster was responsible for generating the entire weather forecast based upon available observations. Today, meteorologists' input is generally confined to choosing a model based on various parameters, such as model biases and performance. Using a consensus of forecast models, as well as ensemble members of the various models, can help reduce forecast error. However, regardless how small the average error becomes with any individual system, large errors within any particularly piece of guidance are still possible on any given model run. Professionals are required to interpret the model data into weather forecasts that are understandable to the lay person. Professionals can use knowledge of local effects which may be too small in size to be resolved by the model to add information to the forecast. As an example, terrain is considered in the QPF process by using topography or climatological precipitation patterns from observations with fine detail. Using model guidance and comparing the various forecast fields to climatology, extreme events such as excessive precipitation associated with later floodFlood
A flood is an overflow of an expanse of water that submerges land. The EU Floods directive defines a flood as a temporary covering by water of land not normally covered by water...
events lead to better forecasts. While increasing accuracy of forecast models implies that humans may no longer be needed in the forecast process at some point in the future, there is currently still a need for human intervention.
Ensemble forecasting
The detail that can be given into a forecast decreases with time as these errors increase. There becomes a point when the errors are so large that the forecast has no correlationCorrelation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
with the actual state of the atmosphere. Looking at a single forecast model gives no indication of how likely that forecast is to be correct. Ensemble forecasting
Ensemble forecasting
Ensemble forecasting is a numerical prediction method that is used to attempt to generate a representative sample of the possible future states of a dynamical system...
entails the production of many forecasts in order to reflect the uncertainty in the initial state of the atmosphere (due to errors in the observations and insufficient sampling). The uncertainty in the forecast can then be assessed by the range of different forecasts produced. Ensemble forecasts are increasingly being used for operational weather forecasting (for example at European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts
European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts
The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts is an independent intergovernmental organisation supported by 19 European Member States and 15 Co-operating States...
(ECMWF), National Centers for Environmental Prediction
National Centers for Environmental Prediction
The United States National Centers for Environmental Prediction delivers national and global weather, water, climate and space weather guidance, forecasts, warnings and analyses to its Partners and External User Communities...
(NCEP), and the Canadian forecasting center). Ensemble mean forecasts for precipitation have the same problems associated with their use in other fields, as they average out more extreme values, and therefore have limited usefulness for extreme events. In the case of the SREF ensemble mean, used within the United States, this decreasing usefulness starts with values as low as 0.5 inches (12.7 mm).
Probability approach
National Weather Service
The National Weather Service , once known as the Weather Bureau, is one of the six scientific agencies that make up the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration of the United States government...
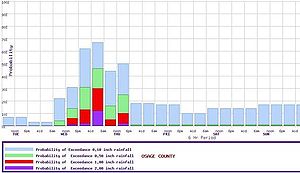
forecasts, as a period's chance of rain equals the chance that 0.01 inch (0.254 mm) will fall in any particular spot. In this case, it is known as probability of precipitation
Probability of Precipitation
A probability of precipitation is a formal measure of the likelihood of precipitation that is often published from weather forecasting models. Its definition varies.-U.S. usage:...
. These probabilities can be derived from a deterministic forecast using computer post-processing.
Australia
The Bureau of MeteorologyBureau of Meteorology
The Bureau of Meteorology is an Executive Agency of the Australian Government responsible for providing weather services to Australia and surrounding areas. It was established in 1906 under the Meteorology Act, and brought together the state meteorological services that existed before then...
began a method of forecasting rainfall using a combination, or ensemble, of different forecast models in 2006. It is termed The Poor Man's Ensemble (PME). Its forecasts are more accurate over time than any of the individual models composing the ensemble. The PME is quick to produce, and is available through their Water and the Land page on their website.
Hong Kong
The Hong Kong Observatory generates short term rainstorm warnings for systems which are expected to accumulate a certain amount of rainfall per hour over the next few hours. They use three levels of warning. The amber warning indicates that a rainfall intensity of 30 millimetres (1.2 in) per hour is expected. The red warning indicates rainfall amounts of 50 millimetres (2 in) per hour are anticipated. The black warning indicates that rainfall rates of 70 millimetres (2.8 in) are possible.United States
Within the United States, the Hydrometeorological Prediction CenterHydrometeorological Prediction Center
The Hydrometeorological Prediction Center is one of nine service centers under the umbrella of the National Centers for Environmental Prediction , a part of the National Weather Service, which in turn is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration of the U.S. government...
, River Forecast Centers, and local forecast offices within the National Weather Service create precipitation forecasts for up to five days in the future, forecasting amounts equal to or greater than 0.01 inch (0.254 mm). Starting in the mid-to-late 1990s, QPFs were used within hydrologic forecast models to simulate impact of rainfall on river stages.
Verification

Rain gauge
A rain gauge is a type of instrument used by meteorologists and hydrologists to gather and measure the amount of liquid precipitation over a set period of time....
observations can be gridded into areal averages, which are then compared to the grids for the forecast models. Weather radar
Weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, estimate its type . Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the...
estimates can be used outright, or corrected for rain gauge observations.
Several statistical scores can be based on the observed and forecast fields. One, known as a bias, compares the size of the forecast field to the observed field, with the goal of a score of 1. The threat score involves the intersection
Intersection (set theory)
In mathematics, the intersection of two sets A and B is the set that contains all elements of A that also belong to B , but no other elements....
of the forecast and observed sets, with a maximum possible verification score of 1. The probability of detection
Statistical power
The power of a statistical test is the probability that the test will reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is actually false . The power is in general a function of the possible distributions, often determined by a parameter, under the alternative hypothesis...
, or POD, is found by dividing the overlap between the forecast and observed fields by the size of the observed field: the goal here is a score of 1. The critical success index, or CSI, divides the overlap between the forecast and observed fields by the combined size of the forecast and observed fields: the goal here is a score of 1. The false alarm rate
Type I and type II errors
In statistical test theory the notion of statistical error is an integral part of hypothesis testing. The test requires an unambiguous statement of a null hypothesis, which usually corresponds to a default "state of nature", for example "this person is healthy", "this accused is not guilty" or...
, or FAR, divides the area of the forecast which does not overlap the observed field by the size of the forecasted area. The goal value in this measure is zero.
With tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
s which impact the United States, the GFS
Global Forecast System
The Global Forecast System is a global numerical weather prediction computer model run by NOAA. This mathematical model is run four times a day and produces forecasts up to 16 days in advance, but with decreasing spatial and temporal resolution over time...
global forecast model performed best in regards to its rainfall forecasts over the last few years, outperforming the NAM
North American Mesoscale Model
The North American Mesoscale Model , refers to a numerical weather prediction model run by National Centers for Environmental Prediction for short-term weather forecasting. Currently, the Weather Research and Forecasting Non-hydrostatic Mesoscale Model model is run as the NAM, thus, three names ...
and ECMWF forecast models.
See also
- Tropical cyclone rainfall forecastingTropical cyclone rainfall forecastingTropical cyclone rainfall forecasting involves using scientific models and other tools to predict the precipitation expected in tropical cyclones such as hurricanes and typhoons. Knowledge of tropical cyclone rainfall climatology is helpful in the determination of a tropical cyclone rainfall...
- European Flood Alert SystemEuropean Flood Alert SystemThe European Flood Alert System project is a European Commission initiative to increase preparedness for riverine floods across Europe.- History :Over the last decades severe fluvial floods of trans-national dimensions have taken place in Europe...
: using QPF and EPS for flood forecasting - Hydrological Ensemble Prediction Experiment

