
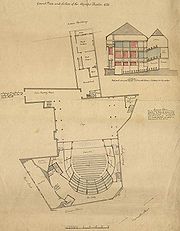
Olympic Theatre
Encyclopedia
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
theatre
Theater (structure)
A theater or theatre is a structure where theatrical works or plays are performed or other performances such as musical concerts may be produced. While a theater is not required for performance , a theater serves to define the performance and audience spaces...
, opened in 1806 and located at the junction of Drury Lane
Drury Lane
Drury Lane is a street on the eastern boundary of the Covent Garden area of London, running between Aldwych and High Holborn. The northern part is in the borough of Camden and the southern part in the City of Westminster....
, Wych Street
Wych Street
Wych Street was a street in London, roughly where Australia House now stands on Aldwych. It ran west from the church of St Clement Danes on the Strand to a point towards the southern end of Drury Lane...
, and Newcastle Street. The theatre specialised in comedies
Comedy
Comedy , as a popular meaning, is any humorous discourse or work generally intended to amuse by creating laughter, especially in television, film, and stand-up comedy. This must be carefully distinguished from its academic definition, namely the comic theatre, whose Western origins are found in...
throughout much of its existence. Along with three other Victorian
Victorian era
The Victorian era of British history was the period of Queen Victoria's reign from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. It was a long period of peace, prosperity, refined sensibilities and national self-confidence...
theatres (Opera Comique
Opera Comique
The Opera Comique was a 19th-century theatre constructed in Westminster, London, between Wych Street and Holywell Street with entrances on the East Strand. It opened in 1870 and was demolished in 1902, to make way for the construction of the Aldwych and Kingsway...
, Globe
Globe Theatre (Newcastle Street)
The Globe was a Victorian theatre built in 1868 and demolished in 1902. It was the third of five London theatres to bear the name. It was also known at various times as the Royal Globe Theatre or Globe Theatre Royal. Its repertoire consisted mainly of comedies and musical shows...
and Gaiety
Gaiety Theatre, London
The Gaiety Theatre, London was a West End theatre in London, located on Aldwych at the eastern end of the Strand. The theatre was established as the Strand Musick Hall , in 1864 on the former site of the Lyceum Theatre. It was rebuilt several times, but closed from the beginning of World War II...
), the Olympic was eventually demolished in 1904 to make way for the development of the Aldwych
Aldwych
Aldwych is a place and road in the City of Westminster in London, England.-Description:Aldwych, the road, is a crescent, connected to the Strand at both ends. At its centre, it meets the Kingsway...
. Newcastle and Wych streets also vanished.
1806-1849: Early days and Madame Vestris
The first Olympic theatre was built in 1806 on the site of Drury House (later Craven House), for the impresario Philip AstleyPhilip Astley
Philip Astley was an English equestrian, circus owner, and inventor, regarded as being the "father of the modern circus"...
, a retired cavalry officer. The original name of the house was the Olympic Pavilion. It was said to be built from the timbers of the French warship Ville de Paris
French ship Ville de Paris (1764)
The Ville de Paris was a large three-decker French ship of the line that became famous as the flagship of the Comte de Grasse during the American Revolutionary War....
. It opened on 1 December 1806 as 'a house of public exhibition of horsemanship and droll.' In 1813, Astley sold the theatre to Robert William Elliston
Robert William Elliston
Robert William Elliston was an English actor and theatre manager.He was born in London, the son of a watchmaker. He was educated at St Paul's School, but ran away from home and made his first appearance on the stage as Tressel in Richard III at Bath in 1791...
, who refurbished the interior and renamed it the Little Drury Lane, reflecting its proximity to the large Drury Lane Theatre
Theatre Royal, Drury Lane
The Theatre Royal, Drury Lane is a West End theatre in Covent Garden, in the City of Westminster, a borough of London. The building faces Catherine Street and backs onto Drury Lane. The building standing today is the most recent in a line of four theatres at the same location dating back to 1663,...
nearby. Elliston had the theatre substantially rebuilt and reopened it with William Thomas Moncrieff
William Thomas Moncrieff
William Thomas Moncrieff was an English dramatist.-Biography:He was born in London, the son of a Strand tradesman named Thomas. The name Moncrieff he assumed for theatrical purposes...
's comedy Rochester – or, King Charles the Second's Merry Days. John Scott purchased the playhouse at Ellison's bankruptcy
Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal status of an insolvent person or an organisation, that is, one that cannot repay the debts owed to creditors. In most jurisdictions bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor....
auction in 1826 and gave the building gas lighting
Gas lighting
Gas lighting is production of artificial light from combustion of a gaseous fuel, including hydrogen, methane, carbon monoxide, propane, butane, acetylene, ethylene, or natural gas. Before electricity became sufficiently widespread and economical to allow for general public use, gas was the most...
.

Lucia Elizabeth Vestris
Lucia Elizabeth Vestris was an English actress and a contralto opera singer, appearing in Mozart and Rossini works. While popular in her time, she was more notable as a theatre producer and manager...
(1787–1856) took over the house, becoming the first female actor-manager in the history of London theatre. She had already made her fortune as a singer, a dancer (of some repute) and an actor. Together with her business partner, Maria Foote
Maria Foote
Maria Foote, Countess of Harrington was an English actress of the nineteenth century.-Early life:Foote was born 24 July 1797 at Plymouth. Her father, Samuel T. Foote , who claimed to be a descendant of Samuel Foote, sold out of the army, became manager of the Plymouth theatre, and married a Miss...
, and her husband, the actor Charles James Mathews
Charles James Mathews
Charles James Mathews was a British actor. He was one of the few British actors to be successful in French-speaking roles in France. A son of the actor Charles Mathews, he achieved a greater reputation than his father in the same profession and also excelled at light comedy...
, Madame Vestris initiated several theatrical innovations, such as the use of historically correct costumes and more elaborate scenery
Theatrical scenery
Theatrical scenery is that which is used as a setting for a theatrical production. Scenery may be just about anything, from a single chair to an elaborately re-created street, no matter how large or how small, whether or not the item was custom-made or is, in fact, the genuine item, appropriated...
, including a box set with ceiling, which she is said to have introduced for the first time in Britain. Her stewardship began with a programme of four pieces including Olympic Revels, and under her management the theatre continued to feature comedies. Many were written by J. R. Planché
James Planche
James Robinson Planché was a British dramatist, antiquary and officer of arms. Over a period of approximately 60 years he wrote, adapted, or collaborated on 176 plays in a wide range of genres including extravaganza, farce, comedy, burletta, melodrama and opera...
and Charles Dance, featuring Vestris in breeches role
Breeches role
A breeches role is a role in which an actress appears in male clothing .In opera it also refers to any male character that is sung and acted by a female singer...
s, and the popular comedian of the day, John Liston
John Liston
John Liston , English comedian, was born in London.He made his public debut on the stage at Weymouth as Lord Duberley in The Heir-at-law...
. The plays often burlesqued classical themes: My Great Aunt – or, Relations and Friends; The Loan of a Lover; The Court Beauties; The Garrick Fever; Faint Heart Never Won Fair Lady; Olympic Revels – or Prometheus and Pandora; Olympic Devils – or Orpheus and Eurydice; The Paphian Bower – or Venus and Adonis; Telemachus – or The Island of Calypso. While Vestris' licence only allowed the performance of extravaganza
Extravaganza
An extravaganza is a literary or musical work characterized by freedom of style and structure and usually containing elements of burlesque, pantomime, music hall and parody. It sometimes also has elements of cabaret, circus, revue, variety, vaudeville and mime...
s and burlesques, the quality of the performance was paramount, with much time spent on rehearsal and selection of the company.
The 1840s were a period of decline for the theatre. Madame Ventris gave her last performance in 1839 and left to join the Theatre Royal, Covent Garden
Royal Opera House
The Royal Opera House is an opera house and major performing arts venue in Covent Garden, central London. The large building is often referred to as simply "Covent Garden", after a previous use of the site of the opera house's original construction in 1732. It is the home of The Royal Opera, The...
, and the house writers, E. L. Blanchard, John Courtney, Thomas Egerton Wilks, and I. P. Wooler, have not met with posthumous fame. A fire in 1849 is characterised by the Victorian Web as 'suspicious.'
1850-1889: Comedy, melodrama and operetta

Dion Boucicault
Dionysius Lardner Boursiquot , commonly known as Dion Boucicault, was an Irish actor and playwright famed for his melodramas. By the later part of the 19th century, Boucicault had become known on both sides of the Atlantic as one of the most successful actor-playwright-managers then in the...
's Broken Vow was staged in 1851, Planché began writing for the Olympic again, and John Maddison Morton
John Maddison Morton
John Maddison Morton was an English playwright who specialized in one-act farces. His most famous farce was Box and Cox . He also wrote comic dramas, pantomimes and other theatrical pieces.-Biography:...
also wrote many plays for the house. Other playwrights featured at the Olympic in the 1850s were Robert B. Brough
Robert Barnabas Brough
Robert Barnabas Brough was an English writer. He wrote poetry, novels and plays and was a contributor to many periodicals.-Life and work:...
, Francis Burnand
Francis Burnand
Sir Francis Cowley Burnand , often credited as F. C. Burnand, was an English comic writer and dramatist....
, John Stirling Coyne, John Oxenford
John Oxenford
John Oxenford , English dramatist, was born at Camberwell, London, England.-Life:He began his literary career by writing on finance...
, Mrs Alfred Phillips, John Palgrave Simpson
John Palgrave Simpson
John Palgrave Simpson was a Victorian playwright. He wrote more than fifty pieces in a variety of genres, including dramas, comedies, operas, and spectacles, between 1850 and 1885. Simpson also published novels, travel books and journalistic commentaries...
, Tom Taylor
Tom Taylor
Tom Taylor was an English dramatist, critic, biographer, public servant, and editor of Punch magazine...
, and Montagu Williams
Montagu Williams
Montagu Stephen Williams Q.C. was an English teacher, army officer, actor, playwright, barrister and magistrate....
. The theatre was managed by the actor-manager
Actor-manager
An actor-manager is a leading actor who sets up their own permanent theatrical company and manages the company's business and financial arrangements, sometimes taking over the management of a theatre, to perform plays of their own choice and in which they will usually star...
Alfred Wigan
Alfred Wigan
Alfred Sydney Wigan was an actor-manager who took part in the first Royal Command Performance before Queen Victoria on 28 December 1848....
from 1853 to 1857. The staples of the repertoire in the 1850s and 1860s continued to be comedies. A notable exception was Tom Taylor's celebrated 1863 social melodrama
Melodrama
The term melodrama refers to a dramatic work that exaggerates plot and characters in order to appeal to the emotions. It may also refer to the genre which includes such works, or to language, behavior, or events which resemble them...
The Ticket-of-Leave Man, based on a French dramatic tale, Le Retour de Melun. It starred Henry Neville
Henry Gartside Neville
Thomas Henry Gartside Neville was an English actor, dramatist, teacher and theatre manager. He began his career playing dashing juvenile leads, later specialising in Shakespearean roles, modern comedy and melodrama. His most famous role was as Bob Brierley in Tom Taylor's The Ticket-of-Leave Man...
, who went on to play in over 2000 performances of the work. Nellie Farren
Nellie Farren
Nellie Farren was an English actress and singer best known for her roles as the "principal boy" in musical burlesques at the Gaiety Theatre.Born into a theatrical family, Farren began acting as a child...
spent two productive years at the theatre early in her career.

Savoy Theatre
The Savoy Theatre is a West End theatre located in the Strand in the City of Westminster, London, England. The theatre opened on 10 October 1881 and was built by Richard D'Oyly Carte on the site of the old Savoy Palace as a showcase for the popular series of comic operas of Gilbert and Sullivan,...
(1881), the Lyric Theatre
Lyric Theatre (London)
The Lyric Theatre is a West End theatre on Shaftesbury Avenue in the City of Westminster.Designed by architect C. J. Phipps, it was built by producer Henry Leslie with profits from the Alfred Cellier and B. C. Stephenson hit, Dorothy, which he transferred from the Prince of Wales Theatre to open...
, Shaftesbury Avenue (1888), Her Majesty's Theatre
Her Majesty's Theatre
Her Majesty's Theatre is a West End theatre, in Haymarket, City of Westminster, London. The present building was designed by Charles J. Phipps and was constructed in 1897 for actor-manager Herbert Beerbohm Tree, who established the Royal Academy of Dramatic Art at the theatre...
(1897) and many others. The capacity of the theatre was at this time 889. The Olympic reopened with performances of The Girl I Left Behind Me and The Hidden Hand and My Wife's Bonnet in November 1864. Burnand's contributions in the 1860s included Fair Rosamond – The Maze, The Maid, and The Monarch; Deerfoot; Robin Hood – or, The Forrester's Fate!; Cupid and Psyche – or, Beautiful as a Butterfly; Acis and Galatæa – or, The Nimble Nymph and the Terrible Troglodyte! and King of the Merrows – or, The Prince and the Piper. Morton's plays included Ticklish Times; A Husband to Order; A Regular Fix!; and Gotobed Tom!. In 1870, W. S. Gilbert
W. S. Gilbert
Sir William Schwenck Gilbert was an English dramatist, librettist, poet and illustrator best known for his fourteen comic operas produced in collaboration with the composer Sir Arthur Sullivan, of which the most famous include H.M.S...
became another of the theatre's notable authors, producing The Princess
The Princess (play)
The Princess is a blank verse farcical play, in five scenes with music, by W. S. Gilbert which adapts and parodies Alfred Lord Tennyson's humorous 1847 narrative poem, The Princess: A Medley. It was first produced at the Olympic Theatre in London on 8 January 1870.Gilbert called the piece "a...
. Later Gilbert plays at the Olympic were The Ne'er-do-Weel
The Ne'er-do-Weel
The Ne'er-do-Weel is a three-act drama written by the English dramatist W. S. Gilbert. It is the second of three plays that he wrote at the request of the actor Edward Sothern. The story concerns Jeffery Rollestone, a gentleman who becomes a vagabond after Maud, the girl he loves, leaves him. He...
(1878) and Gretchen
Gretchen (play)
Gretchen is a tragic four-act play, in blank verse, written by W. S. Gilbert in 1878–79 based on Goethe's version of part of the Faust legend....
(1879).
Henry Neville managed the theatre from 1873 to 1879. The 1870s saw the staging of Wilkie Collins
Wilkie Collins
William Wilkie Collins was an English novelist, playwright, and author of short stories. He was very popular during the Victorian era and wrote 30 novels, more than 60 short stories, 14 plays, and over 100 non-fiction pieces...
's dramatisations of his own novels, The Woman in White
The Woman in White (novel)
The Woman in White is an epistolary novel written by Wilkie Collins in 1859, serialized in 1859–1860, and first published in book form in 1860...
and The Moonstone
The Moonstone
The Moonstone by Wilkie Collins is a 19th-century British epistolary novel, generally considered the first detective novel in the English language. The story was originally serialized in Charles Dickens' magazine All the Year Round. The Moonstone and The Woman in White are considered Wilkie...
; and Charles Collette
Charles Collette
Charles Henry Collette was an English stage actor, composer and writer noted for his work in comedy in a long career onstage. He appeared, beginning in the late 1860s, in many Bancroft productions and was engaged by other managers, including J. L...
in his own one-act musical farce with the striking title, Cryptoconchoidsyphonostomata
Cryptoconchoidsyphonostomata
Cryptoconchoidsyphonostomata, or While it's to be Had was a one-act play styled a "successful romantic Extravaganza", written by R. H. Edgar and Charles Collette, an actor who also starred in the leading role of Plantagenet Smith and wrote the words and music of the play's hit song...
, or While it's to be Had! (1875), which had opened with Trial by Jury
Trial by Jury
Trial by Jury is a comic opera in one act, with music by Arthur Sullivan and libretto by W. S. Gilbert. It was first produced on 25 March 1875, at London's Royalty Theatre, where it initially ran for 131 performances and was considered a hit, receiving critical praise and outrunning its...
earlier that year at the Royalty Theatre
Royalty Theatre
The Royalty Theatre was a small London theatre situated at 73 Dean Street, Soho and opened on 25 May 1840 as Miss Kelly's Theatre and Dramatic School and finally closed to the public in 1938. The architect was Samuel Beazley, a resident in Soho Square, who also designed St James's Theatre, among...
. The Olympic of this period was described by Edward Walford, in his book Old and New London (1897), as having shown 'principally melodramas of the superior kind.' From time to time, operas and operettas were also presented, including Quite an Adventure, and Claude Duval or Love and Larceny by Edward Solomon
Edward Solomon
Edward Solomon was a prolific English composer, as well as a conductor, orchestrator and pianist. Though he died before his fortieth birthday, he wrote dozens of works produced for the stage, including several for the D'Oyly Carte Opera Company, such as The Nautch Girl, among others.-Early...
and Henry Pottinger Stephens
Henry Pottinger Stephens
Henry Pottinger Stephens, also known as Henry Beauchamp , was an English dramatist and journalist. With a variety of partners, he wrote burlesques, comic operas and musical comedies that briefly rivalled the Savoy Operas in popular esteem.-Life and career:"Pot" Stephens was born in Barrow-on-Soar,...
, and the rival production of H.M.S. Pinafore
H.M.S. Pinafore
H.M.S. Pinafore; or, The Lass That Loved a Sailor is a comic opera in two acts, with music by Arthur Sullivan and a libretto by W. S. Gilbert. It opened at the Opera Comique in London, England, on 25 May 1878 and ran for 571 performances, which was the second-longest run of any musical...
mounted in 1879 by Richard D'Oyly Carte
Richard D'Oyly Carte
Richard D'Oyly Carte was an English talent agent, theatrical impresario, composer and hotelier during the latter half of the Victorian era...
's erstwhile partners.
1889-1899: New building and final closure
The building was demolished in 1889 and a new, much enlarged theatre was constructed in 1890 by W. G. R. SpragueW. G. R. Sprague
W. G. R. Sprague was a theatre architect in the grand age.Born in Australia, the son of actress Dolores Drummond who returned with acclaim to London in 1874. Sprague was articled to Frank Matcham for four years, then in 1880 to Walter Emden for three years; and then in partnershp with Bertie Crewe...
and Bertie Crewe
Bertie Crewe
Bertie Crewe was one of the leading English theatre architects in the boom of 1885 to 1915-Biography:Born in Essex and partly trained by Frank Matcham, Crewe and his contemporaries W.G.R...
, whose surviving theatres in London include the Gielgud
Gielgud Theatre
The Gielgud Theatre is a West End theatre, located on Shaftesbury Avenue in the City of Westminster, London, at the corner of Rupert Street. The house currently has 889 seats on three levels.-History:...
, Wyndham's Theatre
Wyndham's Theatre
Wyndham's Theatre is a West End theatre, one of two opened by the actor/manager Charles Wyndham . Located on Charing Cross Road, in the City of Westminster, it was designed by W.G.R. Sprague about 1898, the architect of six other London theatres between then and 1916...
, the Noel Coward Theatre
Noël Coward Theatre
The Noël Coward Theatre, formerly known as the Albery Theatre, is a West End theatre on St. Martin's Lane in the City of Westminster. It opened on 12 March 1903 as the New Theatre and was built by Sir Charles Wyndham behind Wyndham's Theatre which was completed in 1899. The building was designed by...
, the Aldwych Theatre
Aldwych Theatre
The Aldwych Theatre is a West End theatre, located on Aldwych in the City of Westminster. The theatre was listed Grade II on 20 July 1971. Its seating capacity is 1,200.-Origins:...
, the Novello Theatre
Novello Theatre
The Novello Theatre is a West End theatre on Aldwych, in the City of Westminster.-History:The theatre was built as one of a pair with the Aldwych Theatre on either side of the Waldorf Hotel, both being designed by W. G. R. Sprague. The theatre opened as the Waldorf Theatre on 22 May 1905, and was...
and the Shaftesbury Theatre
Shaftesbury Theatre
The Shaftesbury Theatre is a West End Theatre, located on Shaftesbury Avenue, in the London Borough of Camden.-History:The theatre was designed for the brothers Walter and Frederick Melville by Bertie Crewe and opened on 26 December 1911 with a production of The Three Musketeers, as the New...
. The new theatre, with a capacity of 2,150, was large enough to accommodate full-scale opera, including the British première of Tchaikovsky
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky (Russian: Пётр Ильи́ч Чайко́вский ; often "Peter Ilich Tchaikovsky" in English. His names are also transliterated "Piotr" or "Petr"; "Ilitsch", "Il'ich" or "Illyich"; and "Tschaikowski", "Tschaikowsky", "Chajkovskij"...
's Eugene Onegin
Eugene Onegin (opera)
Eugene Onegin, Op. 24, is an opera in 3 acts , by Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky. The libretto was written by Konstantin Shilovsky and the composer and his brother Modest, and is based on the novel in verse by Alexander Pushkin....
, conducted by Henry Wood
Henry Wood (conductor)
Sir Henry Joseph Wood, CH was an English conductor best known for his association with London's annual series of promenade concerts, known as the Proms. He conducted them for nearly half a century, introducing hundreds of new works to British audiences...
with a cast that included Charles Manners, in 1892.
The last manager of the Olympic was Sir Ben Greet
Ben Greet
Sir Philip Barling "Ben" Greet was a Shakespearean actor, director, and impresario.-Early life:The younger son of Captain William Greet RN and his wife, Sarah Barling, Greet was born on board HMS Crocodile, a Royal Navy recruiting ship tied up at the Tower of London. He was educated at the Royal...
, later manager of the Old Vic
Old Vic
The Old Vic is a theatre located just south-east of Waterloo Station in London on the corner of The Cut and Waterloo Road. Established in 1818 as the Royal Coburg Theatre, it was taken over by Emma Cons in 1880 when it was known formally as the Royal Victoria Hall. In 1898, a niece of Cons, Lilian...
. Among his presentations were Hamlet
Hamlet
The Tragical History of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark, or more simply Hamlet, is a tragedy by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written between 1599 and 1601...
and Macbeth
Macbeth
The Tragedy of Macbeth is a play by William Shakespeare about a regicide and its aftermath. It is Shakespeare's shortest tragedy and is believed to have been written sometime between 1603 and 1607...
. The theatre closed permanently in 1899 and was demolished in 1904.
External links
- Picture of the first theatre
- Pictures of the Olympic Theatre after rebuilding
- Statistics and list of managers
- Architectural drawings of the theatre
- Playbills (text) from the Olympic Theatre, at the University of KentUniversity of KentThe University of Kent, previously the University of Kent at Canterbury, is a public research university based in Kent, United Kingdom...

