
Myelomalacia
Encyclopedia
Bleeding
Bleeding, technically known as hemorrhaging or haemorrhaging is the loss of blood or blood escape from the circulatory system...
(bleeding) of the spinal cord can occur as a sequel to acute
Acute (medicine)
In medicine, an acute disease is a disease with either or both of:# a rapid onset, as in acute infection# a short course ....
injury, such as that caused by intervertebral disc
Intervertebral disc
Intervertebral discs lie between adjacent vertebrae in the spine. Each disc forms a cartilaginous joint to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, and acts as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together.-Structure:...
extrusion (being forced or pressed out).
The disorder causes flaccid paraplegia
Paraplegia
Paraplegia is an impairment in motor or sensory function of the lower extremities. The word comes from Ionic Greek: παραπληγίη "half-striking". It is usually the result of spinal cord injury or a congenital condition such as spina bifida that affects the neural elements of the spinal canal...
(impairment of motor function in lower extremities), total areflexia
Hyporeflexia
Hyporeflexia is the condition of below normal or absent reflexes. It can be tested for by using a reflex hammer. It is the opposite of hyperreflexia....
(below normal or absence of reflexes) of the pelvic limbs and anus, loss of deep pain perception caudal
Coccyx
The coccyx , commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column. Comprising three to five separate or fused vertebrae below the sacrum, it is attached to the sacrum by a fibrocartilaginous joint, the sacrococcygeal symphysis, which permits limited movement between...
(in a direction toward the coccyx [tail]) to the site of spinal cord injury, muscular atrophy
Atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations , poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target organ, disuse or lack of exercise or disease intrinsic to the tissue itself...
(wasting away of muscle tissue), depressed mental state, and respiratory difficulty due to intercostal
Intercostal muscle
Intercostal muscles are several groups of muscles that run between the ribs, and help form and move the chest wall. The intercostal muscles are mainly involved in the mechanical aspect of breathing...
(muscles that run between the ribs) and diaphragmatic paralysis
Paralysis
Paralysis is loss of muscle function for one or more muscles. Paralysis can be accompanied by a loss of feeling in the affected area if there is sensory damage as well as motor. A study conducted by the Christopher & Dana Reeve Foundation, suggests that about 1 in 50 people have been diagnosed...
. Gradual cranial
Human skull
The human skull is a bony structure, skeleton, that is in the human head and which supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.In humans, the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones...
migration of the neurological deficits
Functional Neurological Deficit
The diagnosis of Functional Neurological Deficit provides an umbrella term for a variety of symptoms of apparent neurological origin but which current models struggle to explain psychologically or organically. Presentation may be similar to a wide range of other neurological conditions from...
(problems relating to the nervous system), is known as ascending syndrome and is said to be a typical feature of diffuse myelomalacia. Although clinical signs of myelomalacia are observed within the onset (start) of paraplegia, sometimes they may become evident only in the post-operative period, or even days after the onset of paraplegia. Death from myelomalacia may occur as a result of respiratory paralysis when the ascending lesion
Lesion
A lesion is any abnormality in the tissue of an organism , usually caused by disease or trauma. Lesion is derived from the Latin word laesio which means injury.- Types :...
(abnormal damaged tissue) reaches the motor nuclei
Facial motor nucleus
The facial motor nucleus is a collection of neurons in the brainstem that belong to the facial nerve . These lower motor neurons innervate the muscles of facial expression and the stapedius.-Anatomy:...
of the phrenic nerve
Phrenic nerve
The phrenic nerve originates mainly from the 4th cervical nerve, but also receives contributions from the 5th and 3rd cervical nerves in humans....
s (nerves between the C3-C5 region of the spine) in the cervical (neck
Neck
The neck is the part of the body, on many terrestrial or secondarily aquatic vertebrates, that distinguishes the head from the torso or trunk. The adjective signifying "of the neck" is cervical .-Boner anatomy: The cervical spine:The cervical portion of the human spine comprises seven boney...
) region.
Classification
Myelomalacia effects the neurological functions in the spinal cord. Once breached, the ramification of the damage directly affects the motor functions of the body. Because the central nervous system is affected, the condition is classified under the neurologicalNeurology
Neurology is a medical specialty dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Specifically, it deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of disease involving the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems, including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue,...
field of study.
Spinal Cord Injury
When myelomalacia occurs, the damage done to the spinal cord may range from minimal to extensive. The spinal cord and the brain work together, making them the key components of the central nervous system. Damage to this system affects specific functions of the body, primarily relating to the function of muscles. The areas most commonly injured include the cervical vertebraeCervical vertebrae
In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also...
(C1-C7), and the lumbar spine
Lumbar vertebrae
The lumbar vertebrae are the largest segments of the movable part of the vertebral column, and are characterized by the absence of the foramen transversarium within the transverse process, and by the absence of facets on the sides of the body...
(L1-L5).
Symptoms
The onset of myelomalacia may be so subtle that it is overlooked. Depending on the extent of the spinal cord injury, the symptomSymptom
A symptom is a departure from normal function or feeling which is noticed by a patient, indicating the presence of disease or abnormality...
s may vary. In some cases, the symptom may be as common as hypertension
Hypertension
Hypertension or high blood pressure is a cardiac chronic medical condition in which the systemic arterial blood pressure is elevated. What that means is that the heart is having to work harder than it should to pump the blood around the body. Blood pressure involves two measurements, systolic and...
. Though every case is different, several cases reported loss of motor functions in the extremities
Limb (anatomy)
A limb is a jointed, or prehensile , appendage of the human or other animal body....
, areflexia or sudden jerks of the limbs, loss of pain perception, or even paralysis; all of which are possible indicators of a damaged and softened spinal cord. In the most severe cases, paralysis of the respiratory system manifests in death.
Cause
The most common way the disorder occurs is from a result of hemorrhagingBleeding
Bleeding, technically known as hemorrhaging or haemorrhaging is the loss of blood or blood escape from the circulatory system...
(bleeding within) or inadequate blood supply to the spinal cord, making it weak and susceptible to damage.
Because myelomalacia involves a damaged spinal cord, it may occur in any individual. Those most at risk are the geriatric population due to weaker bone density. Once the spinal injury has occurred, one of two things may happen. Firstly, hemorrhaging within the spinal cord may cause compression, which damages the spinal cord even further. Another consequence of myelomalacia is improper circulation
Circulatory system
The circulatory system is an organ system that passes nutrients , gases, hormones, blood cells, etc...
of blood to the area damaged, resulting in further damage to the spinal cord.

Sport Athletes
Due to extensive physical contact and activity, many athletes become victim to myelomalacia. Any accidents or injuries attained during athletic competition to the spinal cord may result in myelomalacia. Accounts of awkward landing on the ground or being hit intensively have attested to spinal cord injury.Geriatric
With the growth in the elderly population of humans, there has been a rise to myelomalacia. Because the human body begins to deteriorate with age, and because human population is living many years longer, there has been a growth in cases of myelomalacia. As the bones in the body begin to weaken in a process known as osteopeniaOsteopenia
Osteopenia is a condition where bone mineral density is lower than normal. It is considered by many doctors to be a precursor to osteoporosis. However, not every person diagnosed with osteopenia will develop osteoporosis...
, the body is more vulnerable to damage. A simple fall may trigger damage to the myelomalacia and spinal cord damage may soon ensue.
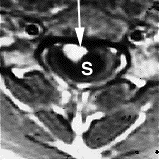
Diagnosing
There are two tests that can provide a definite diagnosis of myelomalacia; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
, or myelography
Myelography
Myelography is a type of radiographic examination that uses a contrast medium to detect pathology of the spinal cord, including the location of a spinal cord injury, cysts, and tumors...
. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology
Radiology
Radiology is a medical specialty that employs the use of imaging to both diagnose and treat disease visualized within the human body. Radiologists use an array of imaging technologies to diagnose or treat diseases...
to visualize the internal structure of the body used in the diagnosing of myelomalacia. Certain MRI findings can detect where bone density and matter has been lost in people with spinal cord injuries. Another common test performed in spinal cord injuries is the myelography. A myelography is a specific type of radiographic
examination that uses contrast medium to detect pathology
Pathology
Pathology is the precise study and diagnosis of disease. The word pathology is from Ancient Greek , pathos, "feeling, suffering"; and , -logia, "the study of". Pathologization, to pathologize, refers to the process of defining a condition or behavior as pathological, e.g. pathological gambling....
of the spinal cord, including the location of spinal cord injury, cyst
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct membrane and division on the nearby tissue. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst could go away on its own or may have to be removed through surgery.- Locations :* Acne...
s, and tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
s. This examination is used to find the cause of pain not found in an MRI test.
Treatment
There is no known cure for nerve damageNerve injury
Nerve injury is injury to nervous tissue. There is no single classification system that can describe all the many variations of nerve injury. Most systems attempt to correlate the degree of injury with symptoms, pathology and prognosis...
due to myelomalacia. Once damaged, the nervous system will not respond to any treatment, but there is a possibility for the condition to worsen. Because motor functions are affected, development of tightening and whithering muscles will occur. The option of surgery is implicated to stop further damage from compression of occurring, though damage already attained may not be cured as of yet. Other medical options to consider may include the use of steroids to reduce the swelling of the spinal cord, reduce the amount of pain, or decrease the tightness of the muscles (spasticity
Spasticity
Spasticity is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance in muscle tone involving hypertonia, which is also referred to as an unusual "tightness" of muscles...
).
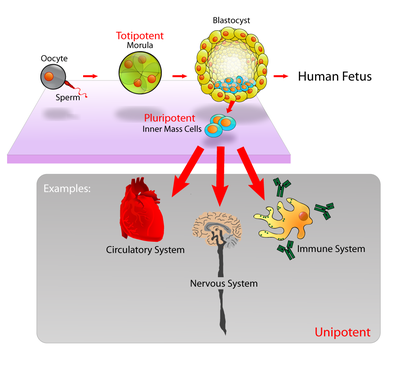
Stem Cell Research
The demand for treatments on diseases has sparked a controversy among those involved with stem cell researchStem cell controversy
The stem cell controversy is the ethical debate primarily concerning the creation, treatment, and destruction of human embryos incident to research involving embryonic stem cells. Not all stem cell research involves the creation, use, or destruction of human embryos...
. Since stem cells have the ability to differentiate into any type of cell, they offer something in the development of medical treatments for a wide range of conditions. Treatments that have been proposed include treatment for physical trauma
Physical trauma
Trauma refers to "a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident." It can also be described as "a physical wound or injury, such as a fracture or blow." Major trauma can result in secondary complications such as circulatory shock, respiratory failure and death...
, degenerative conditions
Degenerative disease
A degenerative disease, also called neurodegenerative disease, is a disease in which the function or structure of the affected tissues or organs will progressively deteriorate over time, whether due to normal bodily wear or lifestyle choices such as exercise or eating habits...
, and genetic diseases
Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes, especially a condition that is present from before birth. Most genetic disorders are quite rare and affect one person in every several thousands or millions....
(in combination with gene therapy). The hope for a treatment for myelomalacia lies in the hands of stem cell research. Further treatments using stem cells could potentially be developed thanks to their ability to repair extensive tissue damage. Much success and potential has been demonstrated from research using adult stem cell
Adult stem cell
Adult stem cells are undifferentiated cells, found throughout the body after embryonic development, that multiply by cell division to replenish dying cells and regenerate damaged tissues...
s. There are no approved treatments or human trials using embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst, an early-stage embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells...
s. Nevertheless, some researchers are of the opinion that the differentiation potential of embryonic stem cells is broader than most adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells can become all cell types of the body because they are Totipotent. Adult stem cells are generally limited to differentiating into different cell types of their tissue of origin.
However, some evidence suggests that adult stem cell plasticity
Plasticity
Plasticity may refer to:Science* Plasticity , in physics and engineering, plasticity is the propensity of a material to undergo permanent deformation under load...
may exist, increasing the number of cell types a given adult stem cell can become. In addition, embryonic stem cells are considered more useful for nervous system therapies, because researchers have struggled to identify and isolate from adult tissues. Embryonic stem cells, however, might be rejected by the immune system - a problem which wouldn't occur if the patient received his or her own stem cells. Medical scientists believe that these stem cell therapies have the ability to change the treatment of human diseases tremendously. Stem cell therapies are currently being conducted in patients with bone marrow transplants, used to treat leukemia. The future use of this treatment looks to be able to treat diseases such as cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, spinal cord injury, Lou Gehrig's disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis , also referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a form of motor neuron disease caused by the degeneration of upper and lower neurons, located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and the cortical neurons that provide their efferent input...
, multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms...
, and a number of other muscular conditions.
Stem Cell Controversy
Stem cell research has the potential to cure many diseases, though much skepticism surrounds the issue. Those opposed to stem cell research concordantly agree on the primary basis that the research is unethical. Currently, technology allows for the destruction of the human embryoEmbryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
and/or therapeutic cloning
Somatic cell nuclear transfer
In genetics and developmental biology, somatic-cell nuclear transfer is a laboratory technique for creating a clonal embryo, using an ovum with a donor nucleus . It can be used in embryonic stem cell research, or, potentially, in regenerative medicine where it is sometimes referred to as...
of the cells, therefore enabling eyebrows to be raised, although recent research has shown the ability to manipulate adult stem cells into embryonic like cells which can serve with the same purpose. Both scientists and those opposing stem cell research may soon agree on the use of adult stem cells, rather than embryonic stem cells.
See also
|
|

