
Magnetic pressure
Encyclopedia
Magnetic pressure is an energy density
associated with the magnetic field
. It is identical to any other physical pressure
except that it is carried by the magnetic field rather than (in the case of gas
) kinetic energy
of the gas molecules. Interplay between magnetic pressure and ordinary gas pressure is important to both the fields of magnetohydrodynamics
and plasma physics. Any magnetic field has an associated pressure that is contained by the boundary conditions on the field, and a gradient in field strength causes a force due to the magnetic pressure gradient
; this force is called the magnetic pressure force.
The magnetic pressure force is most readily observed in an unsupported loop of wire
: if an electric current
passes through the loop, then the wire serves as an electromagnet
, so that the magnetic field strength inside the loop is much greater than the field strength just outside the loop. The gradient in field strength gives rise to a magnetic pressure force that tends to stretch the wire uniformly outward. If enough current travels through the wire, then the loop of wire will form a circle
. At even higher currents, the magnetic pressure can create tensile stress that exceeds the tensile strength
of the wire itself, causing it to fracture or even explosively fragment. Management of magnetic pressure is a significant challenge in the design of ultrastrong electromagnets. Magnetic pressure can be used to propel projectiles; this is the operating principle of a railgun
.
If any currents present are parallel to the field, the magnetic field lines follow shapes in which the magnetic pressure gradient is exactly balanced by the magnetic tension force. Such a field configuration is called force-free
, because there is no Lorentz force
(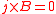 ). The familiar potential magnetic field
). The familiar potential magnetic field
is a special case of a force-free field: potential field configurations occupy space that contains no electric current at all.
The magnetic pressure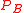 is given in SI
is given in SI
units (P in Pa
, B in T
, μ0 in H/m) by
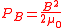
and in cgs units (P in dyn/cm²
, B in G
) by
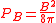 .
.
Energy density
Energy density is a term used for the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Often only the useful or extractable energy is quantified, which is to say that chemically inaccessible energy such as rest mass energy is ignored...
associated with the magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
. It is identical to any other physical pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
except that it is carried by the magnetic field rather than (in the case of gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
) kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
of the gas molecules. Interplay between magnetic pressure and ordinary gas pressure is important to both the fields of magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics is an academic discipline which studies the dynamics of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes...
and plasma physics. Any magnetic field has an associated pressure that is contained by the boundary conditions on the field, and a gradient in field strength causes a force due to the magnetic pressure gradient
Pressure gradient
In atmospheric sciences , the pressure gradient is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the pressure changes the most rapidly around a particular location. The pressure gradient is a dimensional quantity expressed in units of pressure per unit length...
; this force is called the magnetic pressure force.
The magnetic pressure force is most readily observed in an unsupported loop of wire
Wire
A wire is a single, usually cylindrical, flexible strand or rod of metal. Wires are used to bear mechanical loads and to carry electricity and telecommunications signals. Wire is commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. Standard sizes are determined by various...
: if an electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
passes through the loop, then the wire serves as an electromagnet
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by the flow of electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off...
, so that the magnetic field strength inside the loop is much greater than the field strength just outside the loop. The gradient in field strength gives rise to a magnetic pressure force that tends to stretch the wire uniformly outward. If enough current travels through the wire, then the loop of wire will form a circle
Circle
A circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius....
. At even higher currents, the magnetic pressure can create tensile stress that exceeds the tensile strength
Tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength , often shortened to tensile strength or ultimate strength, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before necking, which is when the specimen's cross-section starts to significantly contract...
of the wire itself, causing it to fracture or even explosively fragment. Management of magnetic pressure is a significant challenge in the design of ultrastrong electromagnets. Magnetic pressure can be used to propel projectiles; this is the operating principle of a railgun
Railgun
A railgun is an entirely electrical gun that accelerates a conductive projectile along a pair of metal rails using the same principles as the homopolar motor. Railguns use two sliding or rolling contacts that permit a large electric current to pass through the projectile. This current interacts...
.
If any currents present are parallel to the field, the magnetic field lines follow shapes in which the magnetic pressure gradient is exactly balanced by the magnetic tension force. Such a field configuration is called force-free
Force-free magnetic field
A force-free magnetic field is a type of field which arises as a special case from the magnetostatic equation in plasmas. This special case arises when the plasma pressure is so small, relative to the magnetic pressure, that the plasma pressure may be ignored, and so only the magnetic pressure is...
, because there is no Lorentz force
Lorentz force
In physics, the Lorentz force is the force on a point charge due to electromagnetic fields. It is given by the following equation in terms of the electric and magnetic fields:...
(
 ). The familiar potential magnetic field
). The familiar potential magnetic fieldPotential magnetic field
Potential magnetic field is a special case of a force-free field.Potential field configurations occupy space that contains no electric current at all....
is a special case of a force-free field: potential field configurations occupy space that contains no electric current at all.
The magnetic pressure
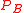 is given in SI
is given in SIInternational System of Units
The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system and is generally a system of units of measurement devised around seven base units and the convenience of the number ten. The older metric system included several groups of units...
units (P in Pa
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
, B in T
Tesla (unit)
The tesla is the SI derived unit of magnetic field B . One tesla is equal to one weber per square meter, and it was defined in 1960 in honour of the inventor, physicist, and electrical engineer Nikola Tesla...
, μ0 in H/m) by
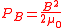
and in cgs units (P in dyn/cm²
Barye
The barye , or sometimes barad, barrie, bary, baryd, baryed, or barie, is the centimetre-gram-second unit of pressure. It is equal to 1 dyne per square centimetre....
, B in G
Gauss (unit)
The gauss, abbreviated as G, is the cgs unit of measurement of a magnetic field B , named after the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss. One gauss is defined as one maxwell per square centimeter; it equals 1 tesla...
) by
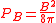 .
.

