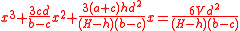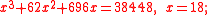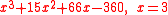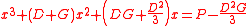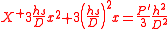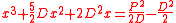Jigu Suanjing
Encyclopedia
Jigu suanjing was the work of early Tang dynasty
calendarist and mathematician Wang Xiaotong
, written some time before the year 626, when he presented his work to the Emperor. Jigu Suanjing was included as one of the requisited texts for Imperial examination
; the amount of time required for the study of Jigu Suanjing was three years, the same as for The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art
plus The Sea Island Mathematical Manual
.
The book began with presentations to the Emperor, followed by a pursuit problem similar to the one in Jiu Zhang Suan shu, followed by 13 three dimensional geometry problems based mostly on engineering construction of astronomic observation tower, dike, barn, excavation of a canal bed etc., and 6 problems in right angled triangle plane geometry
. Except the first problem which was solved by arithematics, the remaining 19 problems deal with the solution of cubic equations, the first known Chinese work to deal with complete cubic equations, as such, it played important roles in the development for solution of high order polynomial equations in the history of Chinese mathematics. Before his time, The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art
developed algorithm of solving simple cubic equation numerically , often referred to as the "finding the root method".
numerically , often referred to as the "finding the root method".
Wang Xiaotong used an algebraic method to solve three dimensional geometry problems, and his work is a major advance in Algebra
in the history of Chinese mathematics.
Each problem in Jigu Suanjing follows the same format, the question part begins with "suppose we have such and such,... question:...how may are there ?"; followed by "answer:", with concrete numbers; then followed by "The algorithm says:...." , in which Wang Xiaotong detailed the reasoning and procedure for the construction of equations, with a terse description of the method of solution. The emphasis of the book is a how to solve engineering problem by construction of mathematical equations from geometric properties of the relevant problem.
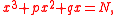
In Jigu Suanjin, Wang established and solved 25 cubic equations, 23 of then from problem 2 to problem 18 have the form
The remaining two problems 19, and 20 each has a double quadratic equation
:
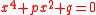
Wang's work influence later Chinese mathematicians, like Jia Xian
and Qin Jiushao of Song dynasty
.
there were hand copied Jigu Suanjing in ciculation. During the Song dynasty
there were 1084 government printed edition. However by Ming dynasty
those Tang dynasty handcopied editions and Song dynasty printed editions were almost all lost, only a single copy of Southern Song printed copy survived. This copy later was obtained by early Qing dynasty
publisher Mao Jin, who made an image handcopy(hand copied character by character, following the form of printed form closely) of it. Mao Jin's image copy of Jigu Suanjing later became the source for a printed edition during the Emperor Qian Long era and was also incorporated in to the Siku Quanshu
. The Qian Long era printed edition disappeared, only Mao Jin's image copy edition of Jigu Suanjing survived at the Fobidden City Museum
, the copy in Siku Quanshu still exist.
During the Qing dynasty, study of Jigu Suangjing was in vogue, half a dozen books devoted to the study of Jigu Suanjing by mathematicians were published, some of which concentrated on filling the gaps left by many missing characters due to age, and some devoted to the detail elaboration of algorithm either from geometry point of view ( Li Huang ) or from Tian yuan shu
(Zhang Dunren).
In 1963, Chinese mathematic historian Qian Baocong published edited The Ten Computational Canons
, which included Jigu Suanjing.
Jigu Suanjing was introduced to the English speaking world by Alexander Wylie in his book Notes on Chinese Literature
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
calendarist and mathematician Wang Xiaotong
Wang Xiaotong
Wang Xiaotong , also known as Wang Hs'iao-t'ung, was a Chinese mathematician and calendarist. He is famous as the author of the Jigu Suanjing one of the Ten Computational Canons....
, written some time before the year 626, when he presented his work to the Emperor. Jigu Suanjing was included as one of the requisited texts for Imperial examination
Imperial examination
The Imperial examination was an examination system in Imperial China designed to select the best administrative officials for the state's bureaucracy. This system had a huge influence on both society and culture in Imperial China and was directly responsible for the creation of a class of...
; the amount of time required for the study of Jigu Suanjing was three years, the same as for The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art
The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art
The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art is a Chinese mathematics book, composed by several generations of scholars from the 10th–2nd century BCE, its latest stage being from the 1st century CE...
plus The Sea Island Mathematical Manual
The Sea Island Mathematical Manual
The Sea Island Mathematical Manual or Haidao suanjing was written by the Chinese mathematician Liu Hui of the Three Kingdoms era as an extension of chapter 9 of The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art....
.
The book began with presentations to the Emperor, followed by a pursuit problem similar to the one in Jiu Zhang Suan shu, followed by 13 three dimensional geometry problems based mostly on engineering construction of astronomic observation tower, dike, barn, excavation of a canal bed etc., and 6 problems in right angled triangle plane geometry
Plane geometry
In mathematics, plane geometry may refer to:*Euclidean plane geometry, the geometry of plane figures,*geometry of a plane,or sometimes:*geometry of a projective plane, most commonly the real projective plane but possibly the complex projective plane, Fano plane or others;*geometry of the hyperbolic...
. Except the first problem which was solved by arithematics, the remaining 19 problems deal with the solution of cubic equations, the first known Chinese work to deal with complete cubic equations, as such, it played important roles in the development for solution of high order polynomial equations in the history of Chinese mathematics. Before his time, The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art
The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art
The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art is a Chinese mathematics book, composed by several generations of scholars from the 10th–2nd century BCE, its latest stage being from the 1st century CE...
developed algorithm of solving simple cubic equation
 numerically , often referred to as the "finding the root method".
numerically , often referred to as the "finding the root method".Wang Xiaotong used an algebraic method to solve three dimensional geometry problems, and his work is a major advance in Algebra
Algebra
Algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning the study of the rules of operations and relations, and the constructions and concepts arising from them, including terms, polynomials, equations and algebraic structures...
in the history of Chinese mathematics.
Each problem in Jigu Suanjing follows the same format, the question part begins with "suppose we have such and such,... question:...how may are there ?"; followed by "answer:", with concrete numbers; then followed by "The algorithm says:...." , in which Wang Xiaotong detailed the reasoning and procedure for the construction of equations, with a terse description of the method of solution. The emphasis of the book is a how to solve engineering problem by construction of mathematical equations from geometric properties of the relevant problem.
In Jigu Suanjin, Wang established and solved 25 cubic equations, 23 of then from problem 2 to problem 18 have the form
The remaining two problems 19, and 20 each has a double quadratic equation
Quadratic equation
In mathematics, a quadratic equation is a univariate polynomial equation of the second degree. A general quadratic equation can be written in the formax^2+bx+c=0,\,...
:
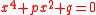
- Problem 3, two cubic equations:
-
-
 ;
;
- Problem 4 two cubic equations:
-
- Problem 5
- Problem 7:
- Problem 8:
- Problem 15:
-
-
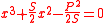 。
。
-
- Problem 17:
- Problem 20:"Suppose the long side of a right angle triangle equals to sixteen and a half, the square of the product of the short side and the hypothenus equals to one hundred sixty four and 14 parts of 25, question, what is the length of the short side ?"
- Answer: "the length of the short side is eight and four fifth."
- Algorithm:"Let the square of the square of product as 'shi' (the constant term), and let the square of the long side of right angle triangle be the 'fa' (the coefficent of the y term). Solve by 'finding the root method', then find the square root again."
- The algorithm is about setting up a double guadratic equation:
-
-
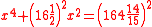 。
。
-
- where x is the short side.
Wang's work influence later Chinese mathematicians, like Jia Xian
Jia Xian
Jia Xian was a Chinese mathematician from Kaifeng of the Song Dynasty, in the first half of the 11th century.-Biography:...
and Qin Jiushao of Song dynasty
Song Dynasty
The Song Dynasty was a ruling dynasty in China between 960 and 1279; it succeeded the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, and was followed by the Yuan Dynasty. It was the first government in world history to issue banknotes or paper money, and the first Chinese government to establish a...
.
Editions
During the Tang dynastyTang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
there were hand copied Jigu Suanjing in ciculation. During the Song dynasty
Song Dynasty
The Song Dynasty was a ruling dynasty in China between 960 and 1279; it succeeded the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, and was followed by the Yuan Dynasty. It was the first government in world history to issue banknotes or paper money, and the first Chinese government to establish a...
there were 1084 government printed edition. However by Ming dynasty
Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
those Tang dynasty handcopied editions and Song dynasty printed editions were almost all lost, only a single copy of Southern Song printed copy survived. This copy later was obtained by early Qing dynasty
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
publisher Mao Jin, who made an image handcopy(hand copied character by character, following the form of printed form closely) of it. Mao Jin's image copy of Jigu Suanjing later became the source for a printed edition during the Emperor Qian Long era and was also incorporated in to the Siku Quanshu
Siku Quanshu
The Siku Quanshu, variously translated as the Imperial Collection of Four, Emperor's Four Treasuries, Complete Library in Four Branches of Literature, or Complete Library of the Four Treasuries, is the largest collection of books in Chinese history and probably the most ambitious editorial...
. The Qian Long era printed edition disappeared, only Mao Jin's image copy edition of Jigu Suanjing survived at the Fobidden City Museum
Forbidden City
The Forbidden City was the Chinese imperial palace from the Ming Dynasty to the end of the Qing Dynasty. It is located in the middle of Beijing, China, and now houses the Palace Museum...
, the copy in Siku Quanshu still exist.
During the Qing dynasty, study of Jigu Suangjing was in vogue, half a dozen books devoted to the study of Jigu Suanjing by mathematicians were published, some of which concentrated on filling the gaps left by many missing characters due to age, and some devoted to the detail elaboration of algorithm either from geometry point of view ( Li Huang ) or from Tian yuan shu
Tian yuan shu
' is a Chinese system of algebra for polynomial equations created in the 13th century. It is first known from the writing of Li Zhi , though it was created earlier....
(Zhang Dunren).
In 1963, Chinese mathematic historian Qian Baocong published edited The Ten Computational Canons
The Ten Computational Canons
The Ten Computational Canons is a collection of Chinese mathematical works, compiled by early Tang dynasty mathematician Li Chunfeng The Ten Computational Canons is a collection of Chinese mathematical works, compiled by early Tang dynasty mathematician Li Chunfeng The Ten Computational Canons is a...
, which included Jigu Suanjing.
Jigu Suanjing was introduced to the English speaking world by Alexander Wylie in his book Notes on Chinese Literature