
The Sea Island Mathematical Manual
Encyclopedia

Chinese mathematics
Mathematics in China emerged independently by the 11th century BC. The Chinese independently developed very large and negative numbers, decimals, a place value decimal system, a binary system, algebra, geometry, and trigonometry....
Liu Hui
Liu Hui
Liu Hui was a mathematician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history. In 263, he edited and published a book with solutions to mathematical problems presented in the famous Chinese book of mathematic known as The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art .He was a...
of the Three Kingdoms
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms period was a period in Chinese history, part of an era of disunity called the "Six Dynasties" following immediately the loss of de facto power of the Han Dynasty rulers. In a strict academic sense it refers to the period between the foundation of the state of Wei in 220 and the...
era (220–280) as an extension of chapter 9 of The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art
The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art
The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art is a Chinese mathematics book, composed by several generations of scholars from the 10th–2nd century BCE, its latest stage being from the 1st century CE...
.
During the Tang Dynasty
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
, this appendix was taken out from The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art as a separate book, titled Haidao suanjing
(Sea Island Mathematical Manual), named after problem No 1 "Looking at a sea island".
Content
This book contained many practical problems of surveying using geometry. This work provided detailed instructions on how to measure distances and heights with tall surveyor's poles and horizontal bars fixed at right angles to them. The unit of measurement was 1 li = 180 zhang= 1800chi, 1 zhang = 10 chi, 1 chi = 10 cun, 1 step(bu) = 6 chi. Calculation was carried out with place value decimal Rod calculusRod calculus
Rod calculus or rod calculation is the method of mathematical computation with counting rods in China from the Warring States to Ming dynasty before the counting rods were replaced by the more convenient and faster abacus.-Hardware:...
.
Liu Hui used his rectangle in right angle triangle theorem as the mathematical basis for survey. With his "In-out-compliment" principle, he
proved that the area of two inscribed rectangles in the two complementary right angle triangles have equal area, thus
CE * AF = FB * BC
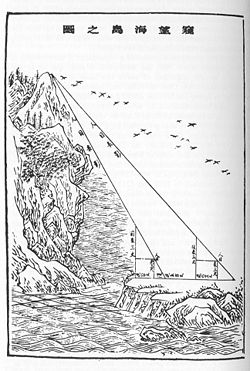
Survey of sea island
Q:Now surveying a sea island, set up two three zhang poles at one thousand steps apart, let the two poles and the island in a straight line. Step back from the front post 123 steps, with eye on ground level, the tip of the pole is on a straight line with the peak of island. Step back 127 steps from the rear pole, eye on ground level also aligns with the tip of pole and tip of island. What is the height of the island, and what is the distance to the pole ?A: The height of the island is four li and 55 steps, and it is 120 li and 50 steps from the pole.
Algorithm: Let the numerator equals to the height of pole multiplied by the separation of poles, let denominator be the difference of ofsets, add the quotient to the height of pole to obtain the height of island.
As the distance of front pole to the island could not be measured directly, Liu Hui set up two poles of same height at a known distance apart
and made two measurements. The pole was perpendicular to the ground, eye view from ground level when the tip of pole was on a straight line sight with the peak of island, the distance of eye to the pole was called front ofset =DG, similarly, the back ofset =FH, difference of ofsetsFH-DG.
- Pole height =CD= 30 chi
- Front pole offset=DG=123 steps
- Back pole offset FH=127 steps
- Difference of offset=FH-DG
- Distance between the poles =DF
- Height of island =AB
- Disttance of front pole to island=BD
Using his principle of inscribe rectangle in right angle triangle for ABG and ABH, he obtained:
- Height of island AB=
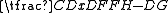 +CD
+CD
- Distance of front pole to island BD=
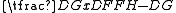 .
.
Height of a hill top pine tree
A pine of unknown height on a hill. Set up two poles of two zhang each, one at front and one at the rear 50 steps in between. Let the rear pole aligns with the front pole. Step back 7 steps and 4 chi, view the tip of pine tree from the ground till it aligns in a straight line with the tip of the pole. Then view the tree trunk, the line of sight intersects the poles at 2 chi and 8 cun from its tip . Step back 8 steps and 5 chi from the rear pole, the view from ground also aligns with tree top and pole top. What is the height of the pine tree, and what is its distance from the pole ?Answer: the height of the pine is 11 zhang 2 chi 8 cun, the distance of mountain from the pole is 1 li and 28 and four seventh steps.
Algorithm: let the numerator be the product of separation of the poles and intersection from tip of pole, let the denominator be the difference of offsets. Add the height of pole to the quotient to obtain the height of pine tree.
The size of a square city wall viewed afar
Q:View a square city at the south of unknow size. Set up a east gnome anda west pole, six zhang apart, linked with a rope at eye level. Let the
east pole aligned with the NE and SE corners. Step back 5 steps from the
north gnome, watch the NW corner of the city, the line of sight
intersects the rope at 2 zhang 2 chi and 6.5 cun from the east end. Step
back northward 13 steps and 2 chi, watch the NW corner of the city, the
line of sight just aligns with the west pole. What is the length of the
square city, and what is its distance to the pole ?
A: The length of the square city is three li 43 and three quarter steps,
the distance of the city to the pole is four li and 45 steps.
The size of a city seen from a mountain
The 19th century British Protestant ChristianChristian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
missionary
Missionary
A missionary is a member of a religious group sent into an area to do evangelism or ministries of service, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care and economic development. The word "mission" originates from 1598 when the Jesuits sent members abroad, derived from the Latin...
Alexander Wylie in his article "Jottings on the Sciences of Chinese Mathematics" published in North China Herald 1852, was the first person to introduce Sea Island Mathematical Manual to the West. French mathematician translated the book into French in 1932. In 1986 Ang Tian Se and Frank Swetz translated Haidao into English.
After comparing the development of surveying in China and the West, Frank Swetz concluded that "in the endeavours of mathematical surveying, China's accomplishments exceeded those realized in the West by about one thousand years."

