Interplanetary Magnetic Field
Encyclopedia
The interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) is the term for the solar magnetic field carried by the solar wind
among the planet
s of the Solar System
.
 Since the solar wind is a plasma
Since the solar wind is a plasma
, it has the characteristics of a plasma
, rather than a simple gas
. For example, it is highly electrically conductive so that magnetic field line
s from the Sun are carried along with the wind. The dynamic pressure
of the wind dominates over the magnetic pressure
through most of the solar system (or heliosphere
), so that the magnetic field is pulled into an Archimedean spiral
pattern (the Parker spiral
) by the combination of the outward motion and the Sun's rotation. Depending on the hemisphere
and phase of the solar cycle
, the magnetic field spirals inward or outward; the magnetic field follows the same shape of spiral in the northern and southern parts of the heliosphere, but with opposite field direction. These two magnetic domains are separated by a two current sheet
(an electric current
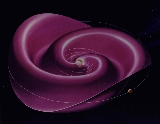
that is confined to a curved plane). This heliospheric current sheet
has a shape similar to a twirled ballerina
skirt, and changes in shape through the solar cycle as the Sun's magnetic field reverses about every 11 years.
The plasma
in the interplanetary medium
is also responsible for the strength of the Sun's magnetic field at the orbit of the Earth being over 100 times greater than originally anticipated. If space were a vacuum, then the Sun's 10-4 tesla magnetic dipole field would reduce with the cube of the distance to about 10-11 tesla. But satellite observations show that it is about 100 times greater at around 10-9 tesla. Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) theory predicts that the motion of a conducting fluid (e.g. the interplanetary medium) in a magnetic field, induces electric currents which in turn generates magnetic fields, and in this respect it behaves like a MHD dynamo.
Solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles ejected from the upper atmosphere of the Sun. It mostly consists of electrons and protons with energies usually between 1.5 and 10 keV. The stream of particles varies in temperature and speed over time...
among the planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
s of the Solar System
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
.

Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
, it has the characteristics of a plasma
Magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics is an academic discipline which studies the dynamics of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes...
, rather than a simple gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
. For example, it is highly electrically conductive so that magnetic field line
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
s from the Sun are carried along with the wind. The dynamic pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
of the wind dominates over the magnetic pressure
Magnetic pressure
Magnetic pressure is an energy density associated with the magnetic field. It is identical to any other physical pressure except that it is carried by the magnetic field rather than kinetic energy of the gas molecules. Interplay between magnetic pressure and ordinary gas pressure is important to...
through most of the solar system (or heliosphere
Heliosphere
The heliosphere is a bubble in space "blown" into the interstellar medium by the solar wind. Although electrically neutral atoms from interstellar volume can penetrate this bubble, virtually all of the material in the heliosphere emanates from the Sun itself...
), so that the magnetic field is pulled into an Archimedean spiral
Archimedean spiral
The Archimedean spiral is a spiral named after the 3rd century BC Greek mathematician Archimedes. It is the locus of points corresponding to the locations over time of a point moving away from a fixed point with a constant speed along a line which rotates with constant angular velocity...
pattern (the Parker spiral
Parker spiral
The Parker spiral is the shape of the Sun's magnetic field as it extends through the solar system. Unlike the familiar shape of the field from a bar magnet, the Sun's extended field is twisted into an arithmetic spiral by the magnetohydrodynamic influence of the solar wind...
) by the combination of the outward motion and the Sun's rotation. Depending on the hemisphere
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
and phase of the solar cycle
Solar cycle
The solar cycle, or the solar magnetic activity cycle, is a periodic change in the amount of irradiation from the Sun that is experienced on Earth. It has a period of about 11 years, and is one component of solar variation, the other being aperiodic fluctuations. Solar variation causes changes in...
, the magnetic field spirals inward or outward; the magnetic field follows the same shape of spiral in the northern and southern parts of the heliosphere, but with opposite field direction. These two magnetic domains are separated by a two current sheet
Current sheet
A current sheet is an electric current that is confined to a surface, rather than being spread through a volume of space. Current sheets feature in magnetohydrodynamics , the study of the behavior of electrically conductive fluids: if there is an electric current through part of the volume of such...
(an electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
that is confined to a curved plane). This heliospheric current sheet
Heliospheric current sheet
The heliospheric current sheet is the surface within the Solar System where the polarity of the Sun's magnetic field changes from north to south. This field extends throughout the Sun's equatorial plane in the heliosphere. The shape of the current sheet results from the influence of the Sun's...
has a shape similar to a twirled ballerina
Ballerina
A ballerina is a title used to describe a principal female professional ballet dancer in a large company; the male equivalent to this title is danseur or ballerino...
skirt, and changes in shape through the solar cycle as the Sun's magnetic field reverses about every 11 years.
The plasma
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
in the interplanetary medium
Interplanetary medium
The interplanetary medium is the material which fills the solar system and through which all the larger solar system bodies such as planets, asteroids and comets move.-Composition and physical characteristics:...
is also responsible for the strength of the Sun's magnetic field at the orbit of the Earth being over 100 times greater than originally anticipated. If space were a vacuum, then the Sun's 10-4 tesla magnetic dipole field would reduce with the cube of the distance to about 10-11 tesla. But satellite observations show that it is about 100 times greater at around 10-9 tesla. Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) theory predicts that the motion of a conducting fluid (e.g. the interplanetary medium) in a magnetic field, induces electric currents which in turn generates magnetic fields, and in this respect it behaves like a MHD dynamo.

