
Indolamines
Encyclopedia
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
s that share a common molecular structure
Molecular structure
The molecular structure of a substance is described by the combination of nuclei and electrons that comprise its constitute molecules. This includes the molecular geometry , the electronic properties of the...
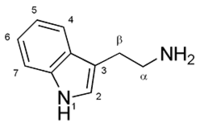
(namely, indolamine). A common example of an indolamine is serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
,a neurotransmitter involved in mood
Mood (psychology)
A mood is a relatively long lasting emotional state. Moods differ from emotions in that they are less specific, less intense, and less likely to be triggered by a particular stimulus or event....
and sleep
Sleep
Sleep is a naturally recurring state characterized by reduced or absent consciousness, relatively suspended sensory activity, and inactivity of nearly all voluntary muscles. It is distinguished from quiet wakefulness by a decreased ability to react to stimuli, and is more easily reversible than...
. Another example of an indolamine is melatonin
Melatonin
Melatonin , also known chemically as N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine, is a naturally occurring compound found in animals, plants, and microbes...
, which regulates the sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm) in human
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
s.
In biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
, indoleamines are substituted indole
Indole
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered nitrogen-containing pyrrole ring. Indole is a popular component of fragrances and the precursor to many pharmaceuticals. Compounds that contain an...
compounds that contain an amino group. Examples of indoleamines include the lysergamides.
Synthesis
Pineal gland
The pineal gland is a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain. It produces the serotonin derivative melatonin, a hormone that affects the modulation of wake/sleep patterns and seasonal functions...
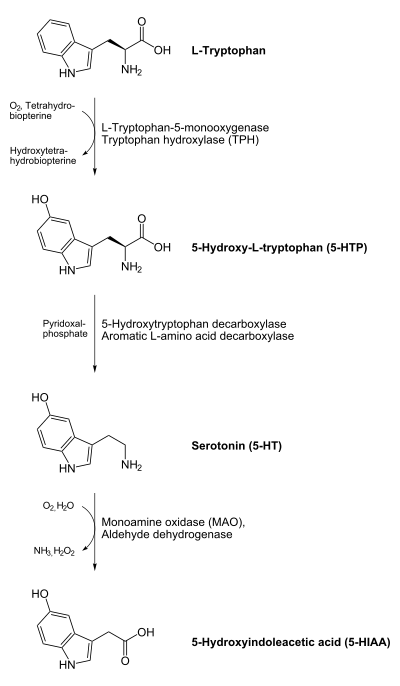
. Indolamines are biologically synthesized
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
from the essential amino acid
Essential amino acid
An essential amino acid or indispensable amino acid is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized de novo by the organism , and therefore must be supplied in the diet.-Essentiality vs. conditional essentiality in humans:...
tryptophan
Tryptophan
Tryptophan is one of the 20 standard amino acids, as well as an essential amino acid in the human diet. It is encoded in the standard genetic code as the codon UGG...
.

