
Hfq protein
Encyclopedia
Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms . Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes can cause serious food poisoning in humans, and are occasionally responsible for product recalls...
host factor that was essential for replication of the bacteriophage Qβ
Bacteriophage Qβ
Bacteriophage Qβ is an icosahedral virus with a diameter of 25 nm. Its host is Escherichia coli. Qβ enters its host cell through the side of the F pilus.-Genetics:...
. It is now clear that Hfq is an abundant bacterial RNA binding protein which has many important physiological roles. Usually mediated by interacting with Hfq binding sRNA
Hfq binding sRNA
A Hfq binding sRNA is an sRNA that binds the bacterial RNA binding protein called Hfq. A number of bacterial small RNAs which have been shown to bind to Hfq have been characterised ....
.
In E. coli, Hfq mutants show multiple stress response related phenotypes. The Hfq protein is now known to regulate the translation of two major stress transcription
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
factors ( σS (RpoS) and σE (RpoE) ) in Enterobacteria. It also regulates sRNA in Vibrio cholerae
Vibrio cholerae
Vibrio cholerae is a Gram-negative, comma-shaped bacterium. Some strains of V. cholerae cause the disease cholera. V. cholerae is facultatively anaerobic and has a flagella at one cell pole. V...
, a specific example being MicX sRNA
MicX sRNA
MicX sRNA is a small non-coding RNA found in Vibrio cholerae. It was given the name MicX as it has a similar function to MicA, MicC and MicF in E. coli. MicX sRNA negatively regulates an outer membrane protein and also a component of an ABC transporter...
.
In Salmonella typhimurium Hfq has been shown to be an essential virulence factor as its deletion attenuates the ability of S.typhimurium to invade epithelial cells, secrete virulence factors or survive in cultured macrophages. In Salmonella Hfq deletion mutants are also non motile and exhibit chronic activation of the sigma mediated envelope stress response.
Hfq mediates its plieotrophic effects through several mechanisms. It interacts with regulatory sRNA
Hfq binding sRNA
A Hfq binding sRNA is an sRNA that binds the bacterial RNA binding protein called Hfq. A number of bacterial small RNAs which have been shown to bind to Hfq have been characterised ....
and facilitates their antisense interaction with their targets. Its also acts independently to modulate mRNA decay (directing mRNA transcripts for degradation) and also acts as a repressor of mRNA translation
Translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. Whereas interpreting undoubtedly antedates writing, translation began only after the appearance of written literature; there exist partial translations of the Sumerian Epic of...
. Genomic SELEX has been used to show that Hfq binding RNAs are enriched in the sequence motif
Sequence motif
In genetics, a sequence motif is a nucleotide or amino-acid sequence pattern that is widespread and has, or is conjectured to have, a biological significance...
5'-AAYAAYAA-3'.
Electron microscopy imaging reveals that, in addition to the expected localization of this protein in cytoplasmic regions and in the nucleoid, an important fraction of Hfq is located in close proximity to the membrane.
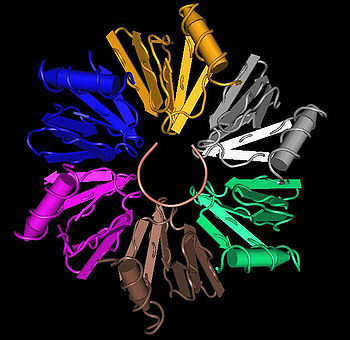
Crystallographic structures
Six crystallographic structures of 4 different Hfq proteins have been published so far; E. coli Hfq , P. aeruginosa Hfq in a low salt condition and a high salt condition , Hfq from S. aureusStaphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus is a facultative anaerobic Gram-positive coccal bacterium. It is frequently found as part of the normal skin flora on the skin and nasal passages. It is estimated that 20% of the human population are long-term carriers of S. aureus. S. aureus is the most common species of...
with bound RNA and without , and the Hfq(-like) protein from M. jannaschii .
All six structures confirm the hexameric ring-shape of a Hfq protein complex.

