
Helix bundle
Encyclopedia
A helix bundle is a small protein
fold
composed of several alpha helices
that are usually nearly parallel or antiparallel to each other.
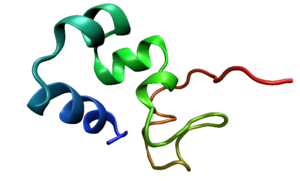 Three-helix bundles are among the smallest and fastest known cooperatively folding structural domains. The three-helix bundle in the villin
Three-helix bundles are among the smallest and fastest known cooperatively folding structural domains. The three-helix bundle in the villin
headpiece domain is only 36 amino acid
s long and is a common subject of study in molecular dynamics
simulations because its microsecond
-scale folding time is within the timescales accessible to simulation The 40-residue HIV
accessory protein has a very similar fold and has also been the subject of extensive study. There is no general sequence motif
associated with three-helix bundles, so they cannot necessarily be predicted
from sequence alone. Three-helix bundles often occur in actin-binding protein
s and in DNA-binding protein
s.
between charged amino acids. The helix axes typically are oriented about 20 degrees from their neighboring helices, a much shallower incline than in the larger helical structure of the globin fold
.
The specific topology of the helices is dependent on the protein - helices that are adjacent in sequence are often antiparallel
, although it is also possible to arrange antiparallel links between two pairs of parallel helices. Because dimeric
coiled-coils are themselves relatively stable, four-helix bundles can be dimer
s of coiled-coil pairs, as in the Rop protein
. Four-helix bundle can have thermal stability more than 100℃. Other examples of four-helix bundles include cytochrome
, ferritin
, human growth hormone, cytokine
, and Lac repressor
C-terminal. The four-helix bundle fold has proven an attractive target for de novo protein design
, with numerous de novo four-helix bundle proteins having been successfully designed by rational and by combinatorial methods. Although sequence is not conserved among four-helix bundles, sequence patterns tend to mirror those of coiled-coil structures in which every fourth and seventh residue is hydrophobic.
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
fold
Tertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
composed of several alpha helices
Alpha helix
A common motif in the secondary structure of proteins, the alpha helix is a right-handed coiled or spiral conformation, in which every backbone N-H group donates a hydrogen bond to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid four residues earlier...
that are usually nearly parallel or antiparallel to each other.
Three-helix bundles

Villin
Villin is a 92.5 kDa tissue-specific actin-binding protein associated with the actin core bundle of the brush border. Villin contains multiple gelsolin-like domains capped by a small "headpiece" at the C-terminus consisting of a fast and independently-folding three-helix bundle that is stabilized...
headpiece domain is only 36 amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s long and is a common subject of study in molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics is a computer simulation of physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a period of time, giving a view of the motion of the atoms...
simulations because its microsecond
Microsecond
A microsecond is an SI unit of time equal to one millionth of a second. Its symbol is µs.A microsecond is equal to 1000 nanoseconds or 1/1000 millisecond...
-scale folding time is within the timescales accessible to simulation The 40-residue HIV
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
accessory protein has a very similar fold and has also been the subject of extensive study. There is no general sequence motif
Sequence motif
In genetics, a sequence motif is a nucleotide or amino-acid sequence pattern that is widespread and has, or is conjectured to have, a biological significance...
associated with three-helix bundles, so they cannot necessarily be predicted
Protein structure prediction
Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse...
from sequence alone. Three-helix bundles often occur in actin-binding protein
Actin-binding protein
Actin-binding proteins are proteins that bind to actin. This may mean ability to bind actin monomers, or polymers, or both....
s and in DNA-binding protein
DNA-binding protein
DNA-binding proteins are proteins that are composed of DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for either single or double stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, because it exposes more functional groups that...
s.
Four-helix bundles
Four-helix bundles typically consist of four helices packed in a coiled-coil arrangement with a sterically close-packed hydrophobic core in the center. Pairs of adjacent helices are often additionally stabilized by salt bridgesSalt bridge (protein)
Salt bridges fall into the broader category of noncovalent interactions. A salt bridge is actually a combination of two noncovalent interactions: hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions . This is most commonly observed to contribute stability to the entropically unfavorable folded...
between charged amino acids. The helix axes typically are oriented about 20 degrees from their neighboring helices, a much shallower incline than in the larger helical structure of the globin fold
Globin fold
The globin fold is a common three-dimensional fold in proteins. This fold typically consists of eight alpha helices, although some proteins have additional helix extensions at their termini. The globin fold is found in its namesake proteins hemoglobin and myoglobin as well as in phycocyanin proteins...
.
The specific topology of the helices is dependent on the protein - helices that are adjacent in sequence are often antiparallel
Antiparallel (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, two molecules are antiparallel if they run side-by-side in opposite directions or when both strands are complimentary to each other....
, although it is also possible to arrange antiparallel links between two pairs of parallel helices. Because dimeric
Protein dimer
In biochemistry, a dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two, usually non-covalently bound, macromolecules like proteins or nucleic acids...
coiled-coils are themselves relatively stable, four-helix bundles can be dimer
Protein dimer
In biochemistry, a dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two, usually non-covalently bound, macromolecules like proteins or nucleic acids...
s of coiled-coil pairs, as in the Rop protein
Rop protein
is a small homodimeric four-helix bundle protein formed by the antiparallel interaction of two helix-turn-helix monomers. The protein is expressed in Escherichia coli as a mechanism for regulating the gene copy numbers of plasmids. The Rop protein's structure has been solved to high resolution...
. Four-helix bundle can have thermal stability more than 100℃. Other examples of four-helix bundles include cytochrome
Cytochrome
Cytochromes are, in general, membrane-bound hemoproteins that contain heme groups and carry out electron transport.They are found either as monomeric proteins or as subunits of bigger enzymatic complexes that catalyze redox reactions....
, ferritin
Ferritin
Ferritin is a ubiquitous intracellular protein that stores iron and releases it in a controlled fashion. The amount of ferritin stored reflects the amount of iron stored. The protein is produced by almost all living organisms, including bacteria, algae and higher plants, and animals...
, human growth hormone, cytokine
Cytokine
Cytokines are small cell-signaling protein molecules that are secreted by the glial cells of the nervous system and by numerous cells of the immune system and are a category of signaling molecules used extensively in intercellular communication...
, and Lac repressor
Lac repressor
The lac repressor is a DNA-binding protein which inhibits the expression of genes coding for proteins involved in the metabolism of lactose in bacteria. These genes are repressed when lactose is not available to the cell, ensuring that the bacterium only invests energy in the production of...
C-terminal. The four-helix bundle fold has proven an attractive target for de novo protein design
Protein design
Protein design is the design of new protein molecules, either from scratch or by making calculated variations on a known structure. The use of rational design techniques for proteins is a major aspect of protein engineering....
, with numerous de novo four-helix bundle proteins having been successfully designed by rational and by combinatorial methods. Although sequence is not conserved among four-helix bundles, sequence patterns tend to mirror those of coiled-coil structures in which every fourth and seventh residue is hydrophobic.

