
GPS satellite
Encyclopedia
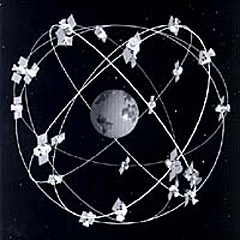
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
used by the NAVSTAR Global Positioning System
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System is a space-based global navigation satellite system that provides location and time information in all weather, anywhere on or near the Earth, where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites...
(GPS). The first satellite in the system, Navstar 1, was launched February 22, 1978. The GPS satellite constellation
Satellite constellation
A group of artificial satellites working in concert is known as a satellite constellation. Such a constellation can be considered to be a number of satellites with coordinated ground coverage, operating together under shared control, synchronised so that they overlap well in coverage and...
is operated by the 50th Space Wing
50th Space Wing
The 50th Space Wing is a wing of the United States Air Force under the major command of Air Force Space Command . It was activated on 30 January 1992, replacing the 2d Space Wing, which was deactivated on the same date.-Overview:...
of the United States Air Force
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the American uniformed services. Initially part of the United States Army, the USAF was formed as a separate branch of the military on September 18, 1947 under the National Security Act of...
.
Block I satellites
Beginning with Navstar 1 in 1978, ten "Block I" GPS satellites were successfully launched. One satellite, "Navstar 7", was lost due to an unsuccessful launch on December 18, 1981. The Block I satellites were launched from Vandenberg Air Force BaseVandenberg Air Force Base
Vandenberg Air Force Base is a United States Air Force Base, located approximately northwest of Lompoc, California. It is under the jurisdiction of the 30th Space Wing, Air Force Space Command ....
using Atlas
Atlas (rocket family)
Atlas is a family of U.S. space launch vehicles. The original Atlas missile was designed in the late 1950s and produced by the Convair Division of General Dynamics, to be used as an intercontinental ballistic missile...
rockets that were converted intercontinental ballistic missile
Intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile is a ballistic missile with a long range typically designed for nuclear weapons delivery...
s. The satellites were built by Rockwell International
Rockwell International
Rockwell International was a major American manufacturing conglomerate in the latter half of the 20th century, involved in aircraft, the space industry, both defense-oriented and commercial electronics, automotive and truck components, printing presses, valves and meters, and industrial automation....
at the same plant in Seal Beach, CA where the S-II
S-II
The S-II was the second stage of the Saturn V rocket. It was built by North American Aviation. Using liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen it had five J-2 engines in a cross pattern...
second stages of the Saturn V
Saturn V
The Saturn V was an American human-rated expendable rocket used by NASA's Apollo and Skylab programs from 1967 until 1973. A multistage liquid-fueled launch vehicle, NASA launched 13 Saturn Vs from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida with no loss of crew or payload...
rockets had been built. The final Block I launch was conducted on October 9, 1985.
The last Block I satellite was taken out of service on November 18, 1995.
Initial Block II series
The first of the nine satellites in the initial Block II series was launched February 14, 1989; the last was launched October 1, 1990. The final satellite of the series to be taken out of service was decommissioned March 15, 2007.Block IIA series
Nineteen satellites in the Block IIA series were launched, the first on November 26, 1990 and the last on November 6, 1997. As of January 17, 2009, six satellites of this series have been removed from service.Two of the satellites in this series, numbers 35 and 36, are equipped with laser retro-reflectors, allowing them to be tracked independently of their radio signals, providing unambiguous separation of clock and ephemeris errors.
Block IIR series
The Block IIR series are "replenishment" satellites developed by Lockheed MartinLockheed Martin
Lockheed Martin is an American global aerospace, defense, security, and advanced technology company with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It is headquartered in Bethesda, Maryland, in the Washington Metropolitan Area....
. Each satellite weighs 4480 pounds (2,032.1 kg) at launch and 2370 pounds (1,075 kg) once on orbit. The first attempted launch of a Block IIR satellite failed on January 17, 1997 when the Delta II
Delta II
Delta II was an American space launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas. Delta II is part of the Delta rocket family and was in service from 1989 until November 1, 2011...
rocket exploded 12 seconds into flight. The first successful launch was on July 23, 1997. Twelve satellites in the series were successfully launched.
Block IIR-M series
The Block IIR-M satellites include a new military signal and a more robust civil signal, known as L2C. There are eight satellites in the Block IIR-M series, which were built by Lockheed MartinLockheed Martin
Lockheed Martin is an American global aerospace, defense, security, and advanced technology company with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It is headquartered in Bethesda, Maryland, in the Washington Metropolitan Area....
. The first Block IIR-M satellite was launched on September 26, 2005. The final launch of a IIR-M was on August 17, 2009.http://news.prnewswire.com/DisplayReleaseContent.aspx?ACCT=104&STORY=/www/story/08-17-2009/0005078475&EDATE=
Block IIF series
The Block IIF series are "follow-on" satellites developed by Boeing. On September 9, 2007 Boeing announced that it had completed assembly of the first satellite in the Block IIF series. Boeing is under contract to build a total of twelve Block IIF satellites. The first was launched in May 2010 on a Delta IV rocket. The second satellite was launched on July 16th 2011. The spacecraft have a mass of 1,630 kilograms (3,600 lb) and a design life of 12 years.See also
- List of GPS satellite launches
- GPS modernizationGPS modernizationThe United States' Global Positioning System , having reached Fully Operational Capability on July 17, 1995, has completed its original design goals. However, additional advances in technology and new demands on the existing system led to the effort to modernize the GPS system. Announcements from...
, 'GPSIII' to launch from 2014.

