
Factorial moment generating function
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
and statistics
, the factorial moment generating function of the probability distribution
of a real-valued
random variable
X is defined as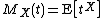
for all complex number
s t for which this expected value
exists. This is the case at least for all t on the unit circle
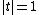 , see characteristic function
, see characteristic function
. If X is a discrete random variable taking values only in the set {0,1, ...} of non-negative integer
s, then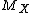 is also called probability-generating function
is also called probability-generating function
of X and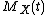 is well-defined at least for all t on the closed
is well-defined at least for all t on the closed
unit disk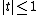 .
.
The factorial moment generating function generates the factorial moments of the probability distribution
.
Provided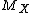 exists in a neighbourhood
exists in a neighbourhood
of t = 1, the nth factorial moment is given by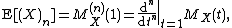
where the Pochhammer symbol
(x)n is the falling factorial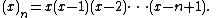
(Confusingly, some mathematicians, especially in the field of special functions, use the same notation to represent the rising factorial.)
with expected value
λ, then its factorial moment generating function is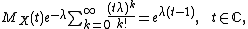
(use the definition of the exponential function) and thus we have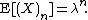
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
and statistics
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the factorial moment generating function of the probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
of a real-valued
Real number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
X is defined as
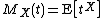
for all complex number
Complex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
s t for which this expected value
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
exists. This is the case at least for all t on the unit circle
Unit circle
In mathematics, a unit circle is a circle with a radius of one. Frequently, especially in trigonometry, "the" unit circle is the circle of radius one centered at the origin in the Cartesian coordinate system in the Euclidean plane...
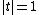 , see characteristic function
, see characteristic functionCharacteristic function (probability theory)
In probability theory and statistics, the characteristic function of any random variable completely defines its probability distribution. Thus it provides the basis of an alternative route to analytical results compared with working directly with probability density functions or cumulative...
. If X is a discrete random variable taking values only in the set {0,1, ...} of non-negative integer
Integer
The integers are formed by the natural numbers together with the negatives of the non-zero natural numbers .They are known as Positive and Negative Integers respectively...
s, then
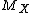 is also called probability-generating function
is also called probability-generating functionProbability-generating function
In probability theory, the probability-generating function of a discrete random variable is a power series representation of the probability mass function of the random variable...
of X and
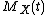 is well-defined at least for all t on the closed
is well-defined at least for all t on the closedClosed set
In geometry, topology, and related branches of mathematics, a closed set is a set whose complement is an open set. In a topological space, a closed set can be defined as a set which contains all its limit points...
unit disk
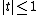 .
.The factorial moment generating function generates the factorial moments of the probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
.
Provided
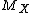 exists in a neighbourhood
exists in a neighbourhoodNeighbourhood (mathematics)
In topology and related areas of mathematics, a neighbourhood is one of the basic concepts in a topological space. Intuitively speaking, a neighbourhood of a point is a set containing the point where you can move that point some amount without leaving the set.This concept is closely related to the...
of t = 1, the nth factorial moment is given by
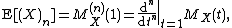
where the Pochhammer symbol
Pochhammer symbol
In mathematics, the Pochhammer symbol introduced by Leo August Pochhammer is the notation ', where is a non-negative integer. Depending on the context the Pochhammer symbol may represent either the rising factorial or the falling factorial as defined below. Care needs to be taken to check which...
(x)n is the falling factorial
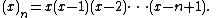
(Confusingly, some mathematicians, especially in the field of special functions, use the same notation to represent the rising factorial.)
Example
Suppose X has a Poisson distributionPoisson distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
with expected value
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
λ, then its factorial moment generating function is
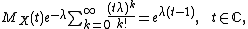
(use the definition of the exponential function) and thus we have
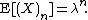
See also
- Moment (mathematics)Moment (mathematics)In mathematics, a moment is, loosely speaking, a quantitative measure of the shape of a set of points. The "second moment", for example, is widely used and measures the "width" of a set of points in one dimension or in higher dimensions measures the shape of a cloud of points as it could be fit by...
- Moment-generating functionMoment-generating functionIn probability theory and statistics, the moment-generating function of any random variable is an alternative definition of its probability distribution. Thus, it provides the basis of an alternative route to analytical results compared with working directly with probability density functions or...
- Cumulant-generating function

