
Demihexeract
Encyclopedia
| Demihexeract (6-demicube) |
||
|---|---|---|
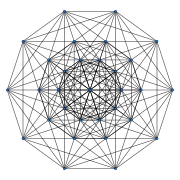 Petrie polygon Petrie polygon In geometry, a Petrie polygon for a regular polytope of n dimensions is a skew polygon such that every consecutive sides belong to one of the facets... projection |
||
| Type | Uniform 6-polytope | |
| Family | demihypercube | |
| Schläfli symbol | {3,33,1} h{4,3,3,3,3} s{2,2,2,2,2} |
|
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram Coxeter-Dynkin diagram In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors... |
||
| Coxeter symbol | 131 | |
| 5-faces | 44 | 12 {31,2,1} Demipenteract In five dimensional geometry, a demipenteract or 5-demicube is a semiregular 5-polytope, constructed from a 5-hypercube with alternated vertices deleted.It was discovered by Thorold Gosset... 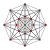 32 {34} |
| 4-faces | 252 | 60 {31,1,1} 16-cell In four dimensional geometry, a 16-cell or hexadecachoron is a regular convex 4-polytope. It is one of the six regular convex 4-polytopes first described by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli in the mid-19th century.... 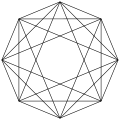 192 {33} |
| Cells | 640 | 160 {31,0,1} Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... 480 {3,3} Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
| Faces | 640 | {3} Triangle A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted .... |
| Edges | 240 | |
| Vertices | 32 | |
| Vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
Rectified 5-simplex |
|
| Symmetry group Coxeter notation In geometry, Coxeter notation is a system of classifying symmetry groups, describing the angles between with fundamental reflections of a Coxeter group. It uses a bracketed notation, with modifiers to indicate certain subgroups. The notation is named after H. S. M... |
D6, [35,1,1] = [1+,4,34] [25]+ |
|
| Petrie polygon Petrie polygon In geometry, a Petrie polygon for a regular polytope of n dimensions is a skew polygon such that every consecutive sides belong to one of the facets... |
decagon Decagon In geometry, a decagon is any polygon with ten sides and ten angles, and usually refers to a regular decagon, having all sides of equal length and each internal angle equal to 144°... |
|
| Properties | convex Convex polytope A convex polytope is a special case of a polytope, having the additional property that it is also a convex set of points in the n-dimensional space Rn... |
|
In geometry
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, a 6-demicube or demihexteract is a uniform 6-polytope, constructed from a 6-cube (hexeract
Hexeract
In geometry, a 6-cube is a six-dimensional hypercube with 64 vertices, 192 edges, 240 square faces, 160 cubic cells, 60 tesseract 4-faces, and 12 5-cube 5-faces....
) with alternate vertices deleted. It is part of a dimensionally infinite family of uniform polytope
Uniform polytope
A uniform polytope is a vertex-transitive polytope made from uniform polytope facets of a lower dimension. Uniform polytopes of 2 dimensions are the regular polygons....
s called demihypercubes.
Coxeter named this polytope as 131 from its Coxeter-Dynkin diagram
Coxeter-Dynkin diagram
In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors...
, with a ring on one of the 1-length Coxeter-Dynkin diagram
Coxeter-Dynkin diagram
In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors...
branches. It can named similarly by a 3-dimensional exponential Schläfli symbol, {3,33,1}.
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a demihexeract centered at the origin are alternate halves of the hexeractHexeract
In geometry, a 6-cube is a six-dimensional hypercube with 64 vertices, 192 edges, 240 square faces, 160 cubic cells, 60 tesseract 4-faces, and 12 5-cube 5-faces....
:
- (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1)
with an odd number of plus signs.

