
Constant k filter
Encyclopedia
Constant k filters, also k-type filters, are a type of electronic filter
designed using the image
method. They are the original and simplest filters produced by this methodology and consist of a ladder network of identical sections of passive components. Historically, they are the first filters that could approach the ideal filter
frequency response to within any prescribed limit with the addition of a sufficient number of sections. However, they are rarely considered for a modern design, the principles behind them having been superseded by other methodologies
which are more accurate in their prediction of filter response.
. He published his work in 1922, but had clearly invented the filters some time before, as his colleague at AT&T Co
, Otto Zobel, was already making improvements to the design at this time. Campbell's filters were far superior to the simpler single element circuits that had been used previously. Campbell called his filters electric wave filters, but this term later came to mean any filter that passes waves of some frequencies but not others. Many new forms of wave filter were subsequently invented; an early (and important) variation was the m-derived filter
by Zobel who coined the term constant k for the Campbell filter in order to distinguish them.
The great advantage Campbell's filters had over the RL circuit
and other simple filters of the time was that they could be designed for any desired degree of stop band
rejection or steepness of transition between pass band
and stop band. It was only necessary to add more filter sections until the desired response was obtained.
The filters were designed by Campbell for the purpose of separating multiplexed telephone channels on transmission line
s, but their subsequent use has been much more widespread than that. The design techniques used by Campbell have largely been superseded. However, the ladder topology used by Campbell with the constant k is still in use today with implementations of modern filter designs such as the Tchebyscheff filter. Campbell gave constant k designs for low-pass, high-pass and band-pass filters. Band-stop and multiple band filters are also possible.
, and in the case of the filters being discussed, an infinite ladder network of L-sections. Here "L" should not be confused with the inductance
L – in electronic filter topology
, "L" refers to the specific filter shape which resembles inverted letter "L".
 The sections of the hypothetical infinite filter are made of series elements having impedance 2Z and shunt elements with admittance 2Y. The factor of two is introduced for mathematical convenience, since it is usual to work in terms of half-sections where it disappears. The image impedance
The sections of the hypothetical infinite filter are made of series elements having impedance 2Z and shunt elements with admittance 2Y. The factor of two is introduced for mathematical convenience, since it is usual to work in terms of half-sections where it disappears. The image impedance
of the input and output port of a section will generally not be the same. However, for a mid-series section (that is, a section from halfway through a series element to halfway through the next series element) will have the same image impedance on both ports due to symmetry. This image impedance is designated
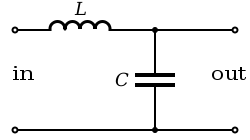
The building block of constant k filters is the half-section "L" network, composed of a series impedance
Z, and a shunt admittance
Y. The "k" in "constant k" is the value given by,
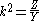
Thus, k will have units of impedance, that is, ohm
s. It is readily apparent that in order for k to be constant, Y must be the dual impedance of Z. A physical interpretation of k can be given by observing that k is the limiting value of Zi as the size of the section (in terms of values of its components, such as inductances, capacitances, etc.) approaches zero, while keeping k at its initial value. Thus, k is the characteristic impedance
, Z0, of the transmission line that would be formed by these infinitesimally small sections. It is also the image impedance of the section at resonance
, in the case of band-pass filters, or at ω = 0 in the case of low-pass filters. For example, the pictured low-pass half-section has
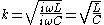 .
.
Elements L and C can be made arbitrarily small while retaining the same value of k. Z and Y however, are both approaching zero, and from the formulae (below) for image impedances,
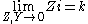 .
.
The image impedances of the section are given by
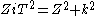
and
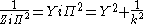
Provided that the filter does not contain any resistive elements, the image impedance in the pass band of the filter is purely real
and in the stop band it is purely imaginary
. For example, for the pictured low-pass half-section,
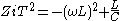
The transition occurs at a cut-off frequency given by
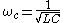
Below this frequency
, the image impedance is real,
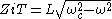
Above the cut-off frequency the image impedance is imaginary,
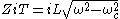

and for a chain of n half-sections
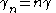
For the low-pass L-shape section, below the cut-off frequency, the transmission parameters are given by
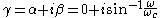
That is, the transmission is lossless in the pass-band with only the phase of the signal changing.
Above the cut-off frequency, the transmission parameters are:

section. The prototype has a cut-off frequency of ωc = 1 rad/s and a nominal impedance k = 1 Ω. This is produced by a filter half-section with inductance L = 1 henry and capacitance C = 1 farad
. This prototype can be impedance scaled and frequency scaled to the desired values. The low-pass prototype can also be transformed into high-pass, band-pass or band-stop types by application of suitable frequency transformations.
It should be borne in mind that the characteristics of the filter predicted by the image method are only accurate if the section is terminated with its image impedance. This is usually not true of the sections at either end, which are usually terminated with a fixed resistance. The further the section is from the end of the filter, the more accurate the prediction will become, since the effects of the terminating impedances are masked by the intervening sections.
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
designed using the image
Image impedance
Image impedance is a concept used in electronic network design and analysis and most especially in filter design. The term image impedance applies to the impedance seen looking in to the ports of a network. Usually a two-port network is implied but the concept is capable of being extended to...
method. They are the original and simplest filters produced by this methodology and consist of a ladder network of identical sections of passive components. Historically, they are the first filters that could approach the ideal filter
Sinc filter
In signal processing, a sinc filter is an idealized filter that removes all frequency components above a given bandwidth, leaves the low frequencies alone, and has linear phase...
frequency response to within any prescribed limit with the addition of a sufficient number of sections. However, they are rarely considered for a modern design, the principles behind them having been superseded by other methodologies
Network synthesis filters
Network synthesis is a method of designing signal processing filters. It has produced several important classes of filter including the Butterworth filter, the Chebyshev filter and the Elliptic filter. It was originally intended to be applied to the design of passive linear analogue filters but...
which are more accurate in their prediction of filter response.
History
Constant k filters were invented by George CampbellGeorge Ashley Campbell
George Ashley Campbell was a pioneer in developing and applying quantitative mathematical methods to the problems of long-distance telegraphy and telephony. His most important contributions were to the theory and implementation of the use of loading coils and the first wave filters designed to...
. He published his work in 1922, but had clearly invented the filters some time before, as his colleague at AT&T Co
American Telephone & Telegraph
AT&T Corp., originally American Telephone and Telegraph Company, is an American telecommunications company that provides voice, video, data, and Internet telecommunications and professional services to businesses, consumers, and government agencies. AT&T is the oldest telecommunications company...
, Otto Zobel, was already making improvements to the design at this time. Campbell's filters were far superior to the simpler single element circuits that had been used previously. Campbell called his filters electric wave filters, but this term later came to mean any filter that passes waves of some frequencies but not others. Many new forms of wave filter were subsequently invented; an early (and important) variation was the m-derived filter
M-derived filter
m-derived filters or m-type filters are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They were invented by Otto Zobel in the early 1920s. This filter type was originally intended for use with telephone multiplexing and was an improvement on the existing constant k type filter...
by Zobel who coined the term constant k for the Campbell filter in order to distinguish them.
The great advantage Campbell's filters had over the RL circuit
RL circuit
A resistor-inductor circuit ', or RL filter or RL network, is one of the simplest analogue infinite impulse response electronic filters. It consists of a resistor and an inductor, either in series or in parallel, driven by a voltage source.-Introduction:The fundamental passive linear circuit...
and other simple filters of the time was that they could be designed for any desired degree of stop band
Stopband
A stopband is a band of frequencies, between specified limits, through which a circuit, such as a filter or telephone circuit, does not allow signals to pass, or the attenuation is above the required stopband attenuation level...
rejection or steepness of transition between pass band
Passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter without being attenuated.A bandpass filtered signal , is known as a bandpass signal, as opposed to a baseband signal....
and stop band. It was only necessary to add more filter sections until the desired response was obtained.
The filters were designed by Campbell for the purpose of separating multiplexed telephone channels on transmission line
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
s, but their subsequent use has been much more widespread than that. The design techniques used by Campbell have largely been superseded. However, the ladder topology used by Campbell with the constant k is still in use today with implementations of modern filter designs such as the Tchebyscheff filter. Campbell gave constant k designs for low-pass, high-pass and band-pass filters. Band-stop and multiple band filters are also possible.
Terminology
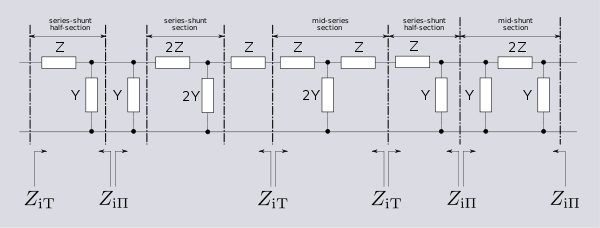
Some of the impedance terms and section terms used in this article are pictured in the diagram below. Image theory defines quantities in terms of an infinite cascade of two-port sectionsTwo-port network
A two-port network is an electrical circuit or device with two pairs of terminals connected together internally by an electrical network...
, and in the case of the filters being discussed, an infinite ladder network of L-sections. Here "L" should not be confused with the inductance
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
L – in electronic filter topology
Electronic filter topology
Electronic filter topology defines electronic filter circuits without taking note of the values of the components used but only the manner in which those components are connected....
, "L" refers to the specific filter shape which resembles inverted letter "L".

Image impedance
Image impedance is a concept used in electronic network design and analysis and most especially in filter design. The term image impedance applies to the impedance seen looking in to the ports of a network. Usually a two-port network is implied but the concept is capable of being extended to...
of the input and output port of a section will generally not be the same. However, for a mid-series section (that is, a section from halfway through a series element to halfway through the next series element) will have the same image impedance on both ports due to symmetry. This image impedance is designated
ZiT due to the "T" topology of a mid-series section. Likewise, the image impedance of a mid-shunt section is designated ZiΠ due to the "Π" topology. Half of such a "T" or "Π" section is called a half-section, which is also an L-section but with half the element values of the full L-section. The image impedance of the half-section is dissimilar on the input and output ports: on the side presenting the series element it is equal to the mid-series ZiT, but on the side presenting the shunt element it is equal to the mid-shunt ZiΠ . There are thus two variant ways of using a half-section.Derivation

The building block of constant k filters is the half-section "L" network, composed of a series impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
Z, and a shunt admittance
Admittance
In electrical engineering, the admittance is a measure of how easily a circuit or device will allow a current to flow. It is defined as the inverse of the impedance . The SI unit of admittance is the siemens...
Y. The "k" in "constant k" is the value given by,
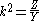
Thus, k will have units of impedance, that is, ohm
Ohm
The ohm is the SI unit of electrical resistance, named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm.- Definition :The ohm is defined as a resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant potential difference of 1 volt, applied to these points, produces in the conductor a current of 1 ampere,...
s. It is readily apparent that in order for k to be constant, Y must be the dual impedance of Z. A physical interpretation of k can be given by observing that k is the limiting value of Zi as the size of the section (in terms of values of its components, such as inductances, capacitances, etc.) approaches zero, while keeping k at its initial value. Thus, k is the characteristic impedance
Characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance of a uniform transmission line, usually written Z_0, is the ratio of the amplitudes of a single pair of voltage and current waves propagating along the line in the absence of reflections. The SI unit of characteristic impedance is the ohm...
, Z0, of the transmission line that would be formed by these infinitesimally small sections. It is also the image impedance of the section at resonance
Electrical resonance
Electrical resonance occurs in an electric circuit at a particular resonance frequency where the imaginary parts of circuit element impedances or admittances cancel each other...
, in the case of band-pass filters, or at ω = 0 in the case of low-pass filters. For example, the pictured low-pass half-section has
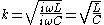 .
.Elements L and C can be made arbitrarily small while retaining the same value of k. Z and Y however, are both approaching zero, and from the formulae (below) for image impedances,
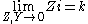 .
.Image impedance
- See also Image impedance#Derivation
The image impedances of the section are given by
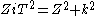
and
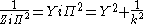
Provided that the filter does not contain any resistive elements, the image impedance in the pass band of the filter is purely real
Real number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
and in the stop band it is purely imaginary
Imaginary number
An imaginary number is any number whose square is a real number less than zero. When any real number is squared, the result is never negative, but the square of an imaginary number is always negative...
. For example, for the pictured low-pass half-section,
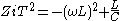
The transition occurs at a cut-off frequency given by
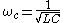
Below this frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, the image impedance is real,
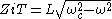
Above the cut-off frequency the image impedance is imaginary,
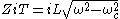
Transmission parameters
The transmission parameters for a general constant k half-section are given by
and for a chain of n half-sections
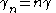
For the low-pass L-shape section, below the cut-off frequency, the transmission parameters are given by
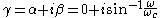
That is, the transmission is lossless in the pass-band with only the phase of the signal changing.
Above the cut-off frequency, the transmission parameters are:

Prototype transformations
The presented plots of image impedance, attenuation and phase change correspond to a low-pass prototype filterPrototype filter
Prototype filters are electronic filter designs that are used as a template to produce a modified filter design for a particular application. They are an example of a nondimensionalised design from which the desired filter can be scaled or transformed. They are most often seen in regards to...
section. The prototype has a cut-off frequency of ωc = 1 rad/s and a nominal impedance k = 1 Ω. This is produced by a filter half-section with inductance L = 1 henry and capacitance C = 1 farad
Farad
The farad is the SI unit of capacitance. The unit is named after the English physicist Michael Faraday.- Definition :A farad is the charge in coulombs which a capacitor will accept for the potential across it to change 1 volt. A coulomb is 1 ampere second...
. This prototype can be impedance scaled and frequency scaled to the desired values. The low-pass prototype can also be transformed into high-pass, band-pass or band-stop types by application of suitable frequency transformations.
Cascading sections
Several L-shape half-sections may be cascaded to form a composite filter. Like impedance must always face like in these combinations. There are therefore two circuits that can be formed with two identical L-shaped half-sections. Where a port of image impedance ZiT faces another ZiT, the section is called a Π section. Where ZiΠ faces ZiΠ the section so formed is a T section. Further additions of half-sections to either of these section forms a ladder network which may start and end with series or shunt elements.It should be borne in mind that the characteristics of the filter predicted by the image method are only accurate if the section is terminated with its image impedance. This is usually not true of the sections at either end, which are usually terminated with a fixed resistance. The further the section is from the end of the filter, the more accurate the prediction will become, since the effects of the terminating impedances are masked by the intervening sections.
See also
- Image impedanceImage impedanceImage impedance is a concept used in electronic network design and analysis and most especially in filter design. The term image impedance applies to the impedance seen looking in to the ports of a network. Usually a two-port network is implied but the concept is capable of being extended to...
- m-derived filterM-derived filterm-derived filters or m-type filters are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They were invented by Otto Zobel in the early 1920s. This filter type was originally intended for use with telephone multiplexing and was an improvement on the existing constant k type filter...
- mm'-type filterMm'-type filtermm'-type filters, also called double-m-derived filters, are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They were patented by Otto Zobel in 1932...
- Composite image filterComposite image filterA composite image filter is an electronic filter consisting of multiple image filter sections of two or more different types.The image method of filter design determines the properties of filter sections by calculating the properties they have in an infinite chain of such sections. In this, the...

